|
Ýëåêòðîííàÿ áèáëèîòåêà Ïîïå÷èòåëüñêîãî ñîâåòà ìåõàíèêî-ìàòåìàòè÷åñêîãî ôàêóëüòåòà Ìîñêîâñêîãî ãîñóäàðñòâåííîãî óíèâåðñèòåòà |
| Ãëàâíàÿ Ex Libris Êíèãè Æóðíàëû Ñòàòüè Ñåðèè Êàòàëîã Wanted Çàãðóçêà ÕóäËèò Ñïðàâêà Ïîèñê ïî èíäåêñàì Ïîèñê |
© Ýëåêòðîííàÿ áèáëèîòåêà ïîïå÷èòåëüñêîãî ñîâåòà ìåõìàòà ÌÃÓ, 2004-2026 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|




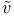 parameter
parameter 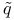
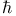 (Planck’s constant)
(Planck’s constant)