јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Fetter A.L., Walecka J.D. Ч Quantum theory of many-particle systems
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Quantum theory of many-particle systemsјвторы: Fetter A.L., Walecka J.D. јннотаци€: "Singlemindedly devoted to its job of educating potential many-particle theorists ... deserves to become the standard text in the field." Ч "Physics Today. "The most comprehensive textbook yet published in its field and every postgraduate student or teacher in this field should own or have access to a copy." Ч "Endeavor. A self-contained treatment of nonrelativistic many-particle systems, this text discusses both formalism and applications. Chapters on second quantization and statistical mechanics introduce ground-state (zero-temperature) formalism, which is explored by way of Green's functions and field theory (fermions), Fermi systems, linear response and collective modes, and Bose systems. Finite-temperature formalism is examined through field theory at finite temperature, physical systems at finite temperature, and real-time Green's functions and linear response. Additional topics cover canonical transformations and applications to physical systems in terms of nuclear matter, phonons and electrons, superconductivity, and superfluid helium as well as applicati
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2003 оличество страниц: 601ƒобавлена в каталог: 14.09.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Linear response, zero sound 183Ч187 Linearization of equations of motion 440Ч441 538Ч543 London equations 420Ч423 425 434 459Ч460 474p 415p London gauge 425 427 454 461 London penetration depth 422 London superconductor 427 Long-range order 489n Macroscopic occupation 198 218 Magnetic field 309p 418 420 Magnetic field, thermodynamics 418Ч420 Magnetic impurities 179 magnetic susceptibility 174 254p 309p 310p magnetization 169p 309p Majorana space-exchange operator 346 354 Many-body forces 377 MaxwellТs equations 417Ч418 Meissner effect 414 421 423 457 459Ч460 Meissner effect, criterion for 429 Meissner effect, for Bose gas 501p Melting curves for He 480 499Ч500p Metallic films 194 476p Metals 21 49 121 180 188 333 389 microcanonical ensemble 486n 500p MigdalТs theorem 406Ч410 Mixed state of superconductors 415n 439 Molecules 503 567 Momentum 24 74 204 332 Multipole expansion of two-body interaction 516 Neutron scattering 171 194 196p 485 Neutron stars 49 NewtonТs Second Law 183 186 420 Noncondensate 491 494Ч495 Nonlocal potentials 322 Nonuniform Bose system 488Ч492 495Ч499 Normal-fluid density 481 486Ч487 500p Normal-ordered product 87 327 Nuclear magnetic resonance 179 nuclear matter 116 128 348Ч352 480 Nuclear matter, binding energy of 387p Nuclear matter, binding energy/particle 352 353Ч355 371 377 Nuclear matter, BruecknerТs theory 150 357Ч377 382Ч383 Nuclear matter, compressibility 387p Nuclear matter, correlations in 362Ч363 365Ч366 Nuclear matter, density 348Ч352 Nuclear matter, effective mass 356 369Ч370 Nuclear matter, energy gap 330 360 383Ч385 388p Nuclear matter, Fermi wavenumber 352 Nuclear matter, healing distance 366 Nuclear matter, independent-pair approximation 357Ч377 Nuclear matter, independent-particle model 352Ч357 366 376 Nuclear matter, many-body forces 377 Nuclear matter, pairing 351 383 385 Nuclear matter, reference-spectrum method 377 Nuclear matter, saturation 355 357 375 Nuclear matter, single-particle potential 355Ч357 381 Nuclear matter, stability 355 Nuclear matter, symmetry energy 386p Nuclear matter, tensor force, effect of 367 375 386p Nuclear matter, three-body clusters 376Ч377 Nuclear matter, with УrealisticФ nucleon-nucleon potential 366Ч377 Nuclear reactions 171 Nucleon-nucleon interaction 341Ч348 354 367 504 567 Nucleon-nucleon interaction, nucleon-nucleon scattering 342Ч347 Nucleon-nucleon interaction, phenomenological potentials 348 361 367 557 573 Nucleon-nucleon interaction, summary of properties 347Ч348 Nucleus 49 50p 121 188 503 Nucleus, Bogoliubov transformation 316n 326Ч336 527Ч537 Nucleus, charge distribution 348Ч349 Nucleus, deformed 515 Nucleus, energy at fixed N 532 Nucleus, energy gap 385 526 533 Nucleus, excited states, application to 555Ч558 Nucleus, excited states, construction of 566 Nucleus, excited states, GreenТs function methods 558Ч566 Nucleus, excited states, Hartree Ч Fock excitation energy 539 Nucleus, excited states, particle-hole interaction 539 Nucleus, excited states, quasiboson approximation 542 543 Nucleus, excited states, random-phase approximation (RPA) 540Ч543 564Ч565 Nucleus, excited states, reduction of basis 543Ч546 Nucleus, excited states, relation between RPA and TDA 565Ч566 Nucleus, excited states, Tamm Ч Dancroff approximation (TDA) 538Ч540 565Ч566 Nucleus, excited states, the [15] supermultiplet 548 Nucleus, excited states, the [1] supermultiplet 555 Nucleus, excited states, transition matrix elements 540 543 Nucleus, excited states, with 547Ч555 Nucleus, fluctuations of 527Ч528 537 Nucleus, for even and odd nuclei 533Ч534 Nucleus, for pairing force in the 534Ч537 Nucleus, giant dipole resonance 552 Nucleus, Hartree Ч Fock ground state 506 538Ч539 560 Nucleus, magic numbers 511 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, boson approximation 526Ч527 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, coefficients of fractional parentage 523n 516p Nucleus, many-particle shell model, normal-coupling excited states 522Ч523 575p Nucleus, many-particle shell model, normal-coupling ground states 520 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, one-body operator in normal coupling 520Ч522 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, pairing-force problem 523Ч526 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, seniority 524 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, theoretical justification 526 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, two valence particles 515Ч519 Nucleus, many-particle shell model, two-body potential in 522Ч523 Nucleus, odd-odd nuclei 350 517 576p Nucleus, pairing 351 383 385 519 523Ч537 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells 567Ч575 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells, application to 573Ч574 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells, Bethe Ч Goldstone equation 568Ч570 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells, harmonic-oscillator approximation 570Ч575 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells, independent-pair approximation 567Ч575 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells, Pauli principle correction 574 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells, relative wave function 572Ч573 Nucleus, realistic forces for two nucleons outside closed shells, two-particle binding energy 568 Nucleus, restricted basis 528 Nucleus, single particle shell model 508Ч515 Nucleus, single particle shell model, spin-orbit splitting 511Ч512 513 Nucleus, single-particle matrix elements 512Ч515 Nucleus, single-particle matrix elements, magnetic moments 514 Nucleus, single-particle matrix elements, multipoles of the charge density 514Ч515 551 Nucleus, single-quasiparticle matrix elements 533 534 Nucleus, sum rules 577p Nucleus, two-body potential, 518Ч519 Nucleus, two-body potential, general matrix elements 516Ч518 Nucleus, two-body potential, multipole expansion 516 Number density 20 66 229 247 251 Number density, comparison of superconducting and normal state 334 451 Number density, Hartree Ч Fock approximation 124 257 Number density, of electron gas 284 Number density, of ideal Bose gas 39 Number density, of ideal Fermi gas 45 Number density, of quasiparticles in He II 486 Number operator 12 17 20 73 201Ч202 315 Occupation numbers 7 37 38 Occupation-number Hilbert space 12 37 313 Odd-odd nuclei 350 517 576p Operator, one-body 20 66 229 512Ч515 Optical potential 135 357 Order parameter 431 Oscillator spacings in nuclei 509n 569 Pairing 326 337p 351 431 519 Pairing force 523Ч526 Parity 344 504 577p Particle-hole interactions 192 539 562Ч563 Pauli exclusion principle 15 26 47 127 134 184 193 322 344 357 480 520 572 574 Pauli exclusion principle, for nucleons 353 Pauli matrices 75Ч76 104 119p 196p 343 353 Pauli paramagnetism 49p 254p 309p 443 462 477p Penetration length, Ginzburg Ч Landau theory 434 472 415p Penetration length, superconductor see Superconductor penetration Periodic boundary conditions 21 352 392 Persistent currents 415Ч416 Perturbation theory, diagrammatic analysis 92Ч116 Perturbation theory, for bosons 199 207Ч210 Perturbation theory, for density correlation function 301 Perturbation theory, for finite temperatures 234Ч250 Perturbation theory, for scattering amplitude 132Ч133 Perturbation theory, for time-development operator 56Ч58 Phase integral 468Ч469 Phase shift for hard sphere 129 Phase transition 44 259Ч261 431 481 Phonon exchange and superconductivity 320 439 448 Phonons, GreenТs function 400 407 Phonons, GreenТs function, for superconductor 477Ч478p Phonons, GreenТs function, Lehmann representation 410p Phonons, in He II 480 484Ч488 Phonons, interaction with electrons 320 396Ч399 417 Phonons, noninteracting 390Ч395 Phonons, noninteracting, chemical potential 393 Phonons, noninteracting, Debye theory 393Ч395 Phonons, noninteracting, displacement vector 391Ч393 Phonons, noninteracting, normal-mode expansion 392 Phonons, noninteracting, quantization 393 Photon processes 566 Pictures, Heisenberg 58Ч59 Pictures, interaction 54Ч58 Pictures, Schr 53Ч54 Pippard coherence length 426 465 469 Pippard equation 425Ч430 465 Pippard kernel 428Ч429 Pippard superconductor 427 461Ч463 Plane-wave states 21 127 258 352 392 Plasma dispersion function 305 Plasma frequency 180 182 223p 307 Plasma oscillations 21 180Ч183 194 307Ч308 Plasma oscillations, compared to zero sound 186 Plasma oscillations, damping 181 195p 308 310p Plasma oscillations, dispersion relation 181Ч182 307Ч308 310p PoissonТs equation 177 183 279 Polarization propagator 110 152 190 Polarization propagator, analytic continuation 302Ч303 Polarization propagator, at finite temperature 252 271 Polarization propagator, dispersion relation for 191 300 Polarization propagator, in finite systems 558 563 Polarization propagator, in finite systems, construction in RPA 566 Polarization propagator, in lowest order 158Ч163 272 275 282 304Ч305 561 Polarization propagator, in ring approximation 193 307 Polarization propagator, relation to density correlation function 153 302 Positron annihilation in metals 171 potential energy 4 67Ч68 200 205Ч206 230 Potentials, core-polarization 574 577p Potentials, nonlocal 322 Potentials, separable 322 Potentials, short range vs. long range 127 167Ч168p 186 Potentials, spin-independent 104Ч110 Potentials, symmetry properties 328 529 PoyntingТs theorem 418n Pressure 30 34Ч35 222 278 Propagation off the energy shell 130 382 Propagator see GreenТs functions at zero temperature; Polarization propagator Proper polarization 110 154 252Ч253 302Ч303 402-405 Proper polarization, at finite temperature 252 Proper polarization, for imperfect Fermi gas 169p 196p Proper polarization, in lowest order 158Ч163 272 275 282 304Ч305 561 Proper self-energy 105Ч106 355 402 Proper self-energy, at finite temperature 250Ч251 264 309p Proper self-energy, for bosons 211 215 219 Proper self-energy, for electron gas 169p 268Ч271 273 402 Proper self-energy, for phonons 402 Proper self-energy, hard-sphere Fermi gas 142Ч146 Proper self-energy, in Hartree Ч Fock approximation 121Ч122 125 256 308p Proper vertex part 403 Pseudopotential 196p 314 Pseudospin operators 524 Quantized circulation 484 496 Quantized flux 415Ч416 425 435Ч436 438-439 Quantized vortex 488 498Ч499 Quantum fluid 479 489 Quantum statistics 6 Quasiboson approximation 542Ч543 Quasielastic peak 193Ч194 196p 495 Quasiparticles 147 316 317 327 487 532Ч537 Quasiparticles, in He II 484Ч488 Quasiparticles, in interacting Fermi gas 332 46n0 Quasiparticles, weight function 309p Random-phase approximation, electron gas 156 Random-phase approximation, innuclei 540Ч543 564Ч565 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature 292Ч297 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, dispersion relations 294Ч295 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, for noninteracting system 298 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, Lehmann representation 293Ч294 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, relation to temperature GreenТs functions 297Ч298 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, retarded and advanced 294Ч297 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, retarded and advanced, relation to time-ordered 295Ч296 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, time-ordered 292Ч293 Real-time GreenТs functions at finite temperature, zero-temperature limit 293 296 308p Reduced mass 129 259 Retarded correlation function 174 299 Riemann zeta function 579Ч580 Ring diagrams 154Ч157 271Ч273 281 564 Rotating He II 482Ч484 500p Rotons 484Ч488 Rydberg 27 Scattering amplitude 128Ч130 143Ч146 314 Scattering amplitude, Born series 132 135 Scattering cross section 189 191 314Ч315 Scattering length 132 143 218 314 342Ч343 481n Scattering length, Born approximation 135 219 Scattering theory in momentum space 130 131 Scattering wave function 129 138Ч139 380 Scattering, opticaltheorem 131 Scattering, phase shifts 128Ч129 Schr 4 54 509 572 Schr 130Ч131 Schr 15 18 Schr 129 320Ч322 Schr 53Ч54 172 Screening in an electron gas 32p 167 175 180 195p 303Ч307 310p 397 Second quantization 4Ч21 353 Second sound 481 482 Self-consistent approximations 120 358Ч360 442Ч446 492 Self-energy 104 107Ч108 250 Self-energy, proper see Proper self-energy Semiempirical mass formula 349Ч352 Seniority 524 536 Separable potential 322 Serber force 346 355 Shell model of nucleus 508Ч515 Shell model of nucleus, boson approximation in 526Ч527 576p Shell model of nucleus, many-particle see Nucleus many-particle Shell model of nucleus, single-particle see Nucleus single-particle Single-particle excitations 147Ч148 171 309p 310p 399 508Ч515 Single-particle GreenТs function see GreenТs functions at zero temperature; Temperature GreenТs function Single-particle operator 20 66 229 512 515 Single-particle potential in nuclear matter 355Ч357 381 Skeleton diagram 403Ч405 Slater determinants 16 Sodium 30 391 Solidification of He 479 Sound velocity 187 391 407 484 Sound velocity, in interacting Bose gas 217 222 317 494 Sound waves, classical theory 186Ч187 (see also Phonons; Zero sound) Specific heat see Heat capacity Spin density 67 196p 229 309p Spin sums 98 104 189 Spin waves 196p Spin-orbit interaction 511Ч512 513 Square-well potential 360Ч361 386p 508Ч510 Stability against collapse 31p 355 Statistical mechanics, review of 34Ч49 Statistical operator 36 228 Step function 27 63 72 Structure factor 189n
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



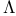 particle in
particle in 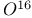
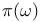 in RPA
in RPA  (x) force
(x) force 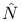
 shell
shell 
 dinger
dinger