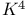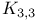|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Diestel R. Ч Graph Theory |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Independent edges 3 29Ч38
Independent events 231
Independent paths 7 55 56Ч57 283
Independent vertices 3 39 110 232
Indicator random variable 234 295
Induced subgraph 3 111 116Ч117 290
Induced subgraph in Ramsey theory 196Ч206
Induced subgraph in random graph 232 249
Induced subgraph of all imperfect graphs 116Ч117 120
Induced subgraph of all large connected graphs 207
Induced subgraph of almost all graphs 238 248
Induced subgraph, cycle 7Ч8 21 47 75 86 111 117 290
Induced subgraph, tree 178
Infinite graphs ix 2 28 41 166 209 248 280
Infinity lemma 192 210 294
init(e) 23
Initial vertex 25
Inner face 70
Inner vertex 6
Integral, flow 126 128
Integral, function 126
Integral, random variable 242
Interior of a path, P 6Ч7
Interior of an arc 68
Internally disjoint see УIndependentФ
Intersection 3
Intersection, graph 279
Interval graph 120 279
INTO 255
Intuition 70 231
Invariant 3
Irreducible graph 279
Isolated vertex 5 248
Isomorphic 3
Isomorphism 3
Isomorphism of plane graphs 76Ч80
Isthmus see УBridgeФ
Jaeger, F. 146
Janson, S. 249
Jensen, T.R. 120 146 281
Johnson, D. 282
Join 2
Jordan, C. 68 70
Jung, H.A. 62 186
k-choosable 105
k-chromatic 95
k-colourable 95
k-constructible 101Ч102 118
k-list-colourable see Уk-choosableФ
k-mesh 265
k-set 1
Kahn, J. 122
Karonski, M. 249
Kempe, A.B. 121 227
Kernel of directed graph 108Ч109
Kernel of incidence matrix 24
KirchhoffТs law 123 124
Klein four-group 135
Kleitman, D.J. 121
Knot theory 146
Knotless graph 277
Kohayakawa, Y. 167
Kollar, J. 167
Komlos, J. 167 170 186 210 226
Konig, D. 30 42 52 103 119 192 210
Konig, duality theorem 30 39 111
Konig, infinity lemma 192 210 294
Konigsberg bridges 19
Kostochka, A.V. 179
Kruskal, J.A. 253 280 296
Kuratowski, C 80Ч84 274
Kuratowski-type characterization 90 274Ч275 281Ч282
L(G) 4
Larman, D.G. 62
Latin square 119
Leaf 12 27
Lean tree-decomposition 261
Length of a cycle 7
Length of a path 6 8
Length of a walk 9
Line (edge) 2
Line (edge), graph 4 96 185
Linear algebra 20Ч25 47Ч49 85Ч86 116
Linear programming 145
Linked by a path 6
Linked by an arc 68
Linked, (k,l)-linked 170
Linked, k-linked 61Ч63 66
Linked, k-linked vs. k-connected 62 65
Linked, set 170
Linked, tree-decomposition 261
Linked, vertices 6 68
List colouring 105Ч110 121Ч122
List colouring, bipartite graphs 108Ч110 119
List colouring, BrooksТs theorem 121
List colouring, conjecture 108 119 122
List-chromatic index 105 108Ч110 121Ч122
List-chromatic number see УChoice numberФ
log, ln 1
Logarithms 1
Loop 25
Lovasz, L. 42 112 115 121 122 167
Luczak, T. 249 250
MacLane, S. 85 92
Mader, W. 11 56Ч57 61 65 66 178 184 186 187
Magnanti, T.L. 145
Mani, P. 62
Map colouring 95Ч97 117 120 136
Markov chain 250
MarkovТs inequality 233 237 242 244
Marriage theorem 31 33 42 285
Matchable 36
Matching 29Ч42
Matching and edge colouring 119
Matching in bipartite graphs 29Ч34 111
Matching in general graphs 34Ч38
Matching of vertex set 29
Mate, A. 210
Matroid theory 66 93
Max-flow min-cut theorem 125 127 144 145
Maximal 4
Maximal acyclic graph 12
Maximal planar graph 80 84 90 92 183 185
Maximal plane graph 73 80
Maximum degree 5
Maximum degree and chromatic index 103Ч105
Maximum degree and chromatic number 99
Maximum degree and list-chromatic index 110 122
Maximum degree and radius 9 26
Maximum degree and Ramsey numbers 194Ч196
Maximum degree, bounded 161 194
Menger, K. 42 50Ч55 64 144 288
Milgram, A.N. 39
Minimal 4
Minimal connected graph 12
Minimal cut 22 88 136
Minimal k-connected graph 65
Minimal non-planar graph 90
Minimal separating set 63
Minimal set of forbidden minors 274 280 281Ч282
Minimum degree 5
Minimum degree and average degree 5
Minimum degree and choice number 106
Minimum degree and chromatic number 99 100
Minimum degree and circumference 8
Minimum degree and connectivity 11 65Ч66
Minimum degree and girth 178 179Ч180 237
Minimum degree and linkability 171
Minimum degree forcing, Hamilton cycle 214 226
Minimum degree forcing, long cycles 8
| Minimum degree forcing, long paths 8 166
Minimum degree forcing, short cycles 179Ч180 237
Minimum degree forcing, trees 13
Minor 16Ч19 17
Minor 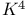 182 263 182 263
Minor 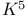 183 186 183 186
Minor 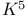 and and 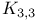 80Ч84 80Ч84
Minor 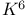 183 183
Minor 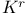 180 181 180 181
Minor 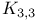 92 185 92 185
Minor and planarity 80Ч84 90
Minor and WQO 251Ч277 (see also УTopological minorФ)
Minor of all large 3- or 4-connected graphs 208
Minor of multigraph 26
Minor vs. topological minor 18Ч19 80
Minor, forbidden 181Ч185 263Ч277 279 280 281Ч282
Minor, forced 174 179Ч186
Minor, infinite 280
Minor, Petersen graph 140
Minor, relation 18 274
Minor, theorem 251 274Ч277 275
Minor, theorem for trees 253Ч254
Minor, theorem, proof 275Ч276
Mobius, crown 208
Mobius, ladder 183
Mohar, B. 92 121 281Ч282
Moment, first see УMarkovТs inequalityФ
Moment, second 242Ч247
Monochromatic (in Ramsey theory), (vertex) set 191Ч193
Monochromatic (in Ramsey theory), induced subgraph 196Ч206
Monochromatic (in Ramsey theory), subgraph 191 193Ч196
Multigraph 25Ч26
Multigraph, list chromatic index of 122
Multigraph, plane 87
Multiple edge 25
Murty, U.S.R. 228
MX 15
N(v), N(U) 4
Nash Ч Williams, C.St.J.A. 58 60 66 280
Neighbour 3 4
Nesetril, J. 210 211
Network 125Ч128
Network theory 145
Node (vertex) 2
Normal tree 13Ч14 27 139 144 296
Nowhere, dense 61
Nowhere, zero 128 146
NULL see УEmptyФ
Obstruction to small tree-width 258Ч260 264Ч265 280 281
octahedron 11 15
Odd component 34
Odd cycle 15 99 117 290
Odd degree 5
ON 2
One-factor theorem 35 66
Oouterplanar 91
Oporowski, B. 208
Order of a bramble 258
Order of a graph 2
Order of a mesh or premesh 265
Order of deletion/contraction 17
Order, partial 13 18 27 40 41 120 277
Order, quasi- 251Ч252 277Ч278
Order, tree- 13 27
Order, well-quasi- 251Ч253 275 277 278 280
Orientable surface 280
Orientable surface, plane as 137
Orientation 25 108 145 289
Orientation, cycle with 136Ч137
Oriented graph 25
Orlin, J.B. 145
Outer face 70 76Ч77
Oxley, J.G. 93 208
P 229
Palmer, E.M. 249
Parallel edges 25
Parallel paths 293
Parity 5 34 37 227
Part of tree-decomposition 255
Partially ordered set 40 41 42
Partition 1 60 191
Pasting 111 182 183 185 261
Path 6Ч9
Path, a-b-path 7 55
Path, alternating 29 32
Path, between given pairs of vertices 61Ч63 66 170
Path, cover 39Ч40 285
Path, directed 39
Path, disjoint paths 39 50Ч55
Path, edge-disjoint 55 57 58
Path, H-path 7 44Ч45 56Ч57 64 65 66
Path, independent paths 7 55 56Ч57 283
Path, induced 207
Path, length 6
Path, linkage 61Ч63 66 170 172
Path, long 8
Path-decomposition 279
Path-hamiltonian sequence 218
Path-width 279 281
Pelikan, J. 185
Perfect 111Ч117 119Ч120 122
Perfect graph conjecture 117
Perfect graph theorem 112 115 117 122
Perfect matching see У1-factorФ
Petersen graph 140Ч141
Petersen, J. 33 36
Physics 146
Piecewise linear 67
Planar 80Ч89 274
Planar, embedding 76 80Ч93
Planarity criteria, Kuratowski 84
Planarity criteria, MacLane 85
Planarity criteria, Tutte 86
Planarity criteria, Whitney 89
Plane, dual 87
Plane, duality 87Ч89 91 136Ч139 288
Plane, graph 70Ч76
Plane, multigraph 37Ч89 136Ч139
Plane, triangulation 73 75 261
Plummer, M.D. 42
Point (vertex) 2
Pointwise greater 216
Polygon 68
Polygonal arc 68 69
Posa, L. 197 226
Power of a graph 218
PRECISION 296
Premesh 265
Probabilistic method 229 235Ч238 249
Projective plane 275 281
Promel, H.J. 117 122
Property 238
Property of almost all graphs 238Ч241 247Ч248
Property, hereditary 263
Property, increasing 241
Pseudo-random graph 210
pw(G) 259
Pym, J.S. 66
q(G) 34
Quasi-ordering 251Ч252 277Ч278
R(H) 191
R(k,c,r) 191
R(r) 189
r-partite 14
rad(G) 9
RADIUS 9
Radius and diameter 9 26
Radius and maximum degree 9 26
Rado, R. 210
RadoТs selection lemma 210
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте