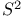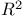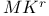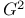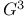|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Diestel R. Ч Graph Theory |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Cut, minimal 22 88
Cut-cycle duality 136Ч138
Cut-edge see УBridgeФ
Cutvertex 10 43Ч44
CYCLE 7Ч9
Cycle in multigraphs 25
Cycle with orientation 136Ч138
Cycle, directed 119
Cycle, double cover conjecture 141 144
Cycle, expected number 234
Cycle, Hamilton 144 213Ч228
Cycle, induced 7Ч8 21 47 86 111 117 290
Cycle, length 7
Cycle, long 8 26 64 118
Cycle, non-separating 47 86
Cycle, odd 15 99 117 290
Cycle, short 101 179Ч180 235 237
Cycle, space 21 23Ч24 27Ч28 47Ч49 85Ч86 89 92Ч93
Cycle, threshold function 247
Cycle-cut duality 136Ч138
Cyclomatic number 21
d(G) 5
D(V) 5
d(x,y) 8
Degeneracy see УColouring numberФ
Degree 5
Degree, sequence 216
Deletion 4
Dense graphs 148 150
Density of pair of vertex sets 153
Density, edge density 148
Density, upper density 166
Depth-first search tree 13 27
Deuber, W. 197
diam(G) 8
Diameter 5Ч9 248
Diameter and girth 8
Diameter and radius 9
Diestel, R. 186 281
Difference of graphs 4
Digon see УDouble edgeФ
Digraph see УDirected graphФ
Dilworth, R.P. 40 285 294
Dirac, G.A. 111 186 187 214 226
Directed cycle 119
Directed edge 25
Directed graph 25 108 119
Directed path 39
Direction 124
Disjoint graphs 3
Distance 8
Double counting 75 92 114Ч115 234 244
Double edge 25
Double wheel 208
Drawing 67 76Ч80
Drawing convex 92
Drawing straight-line 90
Dual and connectivity 91
Dual, abstract 55Ч89 91
Dual, plane 81 91
Duality of plane multigraphs 87Ч89
Duality, cycles and cuts 23Ч24 88Ч89 136
Duality, flows and colourings 136Ч139 291
E(G) 2
E(v), E'(w), ... 2
E(X) 231
E(X,Y), E'(U,W), ... 2
EDGE 2
Edge colouring 96 103Ч105 191
Edge colouring and flow number 135
Edge colouring and matchings 119
Edge contraction 16
Edge contraction and 3-connectedness 45
Edge contraction in multigraph 25
Edge contraction vs. minors 17
Edge cover 119
Edge density 5 148
Edge density and average degree 5
Edge density and regularity lemma 154 166
Edge density, forcing minors/topological minors 169Ч180
Edge density, forcing subgraphs 147Ч167
Edge of a multigraph 25
Edge space 20 85
Edge, crossing a partition 21
Edge, directed 25
Edge, double 25
Edge, plane 10
Edge, X-Y edge 2
Edge-chromatic number see УChromatic indexФ
Edge-connectivity 11 55 58
Edge-disjoint spanning trees 58Ч61
Edge-maximal 4
Edge-maximal vs. extremal 149 182
Edge-maximal without  183 183
Edge-maximal without  182 182
Edge-maximal without  , ,  84 84
Edge-maximal without  185 185
Edmonds, J. 42 282
Embedding in  69Ч70 77 69Ч70 77
Embedding in surface 74 92 274Ч276 280 281Ч282
Embedding in the plane 16 80Ч93
Embedding of bipartite graphs 202Ч204
Empty graph 2
End of edge 2 25
End of path 6
Endpoints of arc 68
Endvertex 2 25
Endvertex, terminal vertex 25
Equivalence in quasi-order 211
Equivalence of planar embeddings 76Ч80 19 90
Equivalence of points in 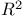 68 68
Erdos Ч Sos conjecture 152 166 167
Erdos, P. 101 121 151 152 163 166 167 187 191 208 209 210 215 228 232 235Ч231 243 249 295
Euler, characteristic 276
Euler, formula 74Ч75 89 90 289
Euler, L. 18Ч19 14
Euler, tour 19Ч20 291
Eulerian graph 19
Even, degree 19 33
Even, graph 133 135 145
Event 231
Evolution of random graphs 241 249
ex(n,H) 149
Exceptional set 153
Excluded minors see УForbidden minorsФ
Existence proof, probabilistic 121 229 233 235Ч237
Expanding a vertex 113
Expectation 233Ч234 242
Exterior face see УOuter faceФ
Externally k-connected 264 280
Extremal vs. edge-maximal 149 182
Extremal without  183 183
Extremal without  182 182
Extremal without  184 184
Extremal without  185 185
Extremal, bipartite graph 165
Extremal, graph 149Ч150
Extremal, graph theory 147 151 160 166
F(G) 70
f(X,Y), g(U,W), ... 124
Face 70
Factor 29
Factor, 1-factor 29Ч38
Factor, 1-factor theorem 35 42 66
Factor, 2-factor 33
Factor, k-factor 29
Factor-critical 36 285
Fajtlowicz, S. 187
Fan 55
Fan-version of MengerТs theorem 55
| Finite graph 2
First order sentence 239
First point on frontier 68
Five colour theorem 96 121 141
Five colour theorem, list version 106 121
Five-flow conjecture 140 141
Fleischner, H. 218 295
Flow 123Ч146 125Ч126
Flow in plane graphs 136Ч139
Flow number 131Ч134 140 144
Flow, 2-flow 133
Flow, 3-flow 133Ч134 141
Flow, 4-flow 134Ч135 140Ч141
Flow, 6-flow theorem 141Ч143
Flow, conjectures 140Ч141
Flow, group-valued 128Ч133 144
Flow, H-flow 128Ч133
Flow, integral 126 128
Flow, k-flow 131Ч134 140Ч143 145
Flow, network flow 125Ч128 291
Flow, polynomial 130 146
Flow, total value of 126
Flow-colouring duality 136Ч139 291
Forbidden minors and chromatic number 181Ч185
Forbidden minors and tree-width 263Ч274
Forbidden minors, expressed by 263 274Ч277
Forbidden minors, minimal set of 274 280 281
Forbidden minors, planar 264
Forcibly hamiltonian see УHamiltonian sequenceФ
Forcing 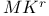 179Ч184 186 179Ч184 186
Forcing  184 187 184 187
Forcing  61 170Ч178 186 61 170Ч178 186
Forcing, high connectivity 11
Forcing, induced trees 178
Forcing, large chromatic number 101Ч103
Forcing, linkability 62Ч63 66 171Ч174
Forcing, long cycles 8 26 118 213Ч228
Forcing, long paths 8 166
Forcing, minor with large minimum degree 174 179
Forcing, short cycles 179Ч180 237
Forcing, subgraph 13 147Ч167
Forcing, tree 13 178
Forcing, triangle 119 209
Ford, L.R. Jr. 127 145
Forest 12
Forest, minor 281
Forest, partitions 60Ч61
Four colour problem 120 186
Four colour theorem 96 141 145 181 183 185 215 227
Four colour theorem, history 120Ч121
Four-flow conjecture 140Ч141
Frank, A. 65 145
Frobenius, F.G 42
From ... to 6
Frontier 68
Fulkerson, D.R. 122 127 145
g(G) 7
Gallai Ч Edmonds matching theorem 36Ч38 42
Gallai, T. 39 42 66 167
Galvin, F. 109
Gasparian, G.S. 122
Genus and colouring 121
Genus of a graph 90 280
Genus of a surface 276
Geometric dual see УPlane dualФ
Gibbons, A. 145
Gilmore, P.C. 120
girth 7
Girth and average degree 237
Girth and chromatic number 101 121 235Ч237
Girth and connectivity 237
Girth and diameter 8
Girth and minimum degree 8 179Ч180 237
Girth and minors 179Ч180
Girth and planarity 89
Girth and topological minors 178
Godsil, C. 28
Golumbic, M.C. 122
Good characterization 274 282
Good pair 252
Good sequence 252
Gorbunov, K.Yu. 281
Goring, F. 66
Graham, R.L. 210
Graph 2Ч4 25 26
Graph, invariant 3
Graph, minor theorem 251 274Ч277 275
Graph, partition 60
Graph, plane 70Ч76 87Ч89 96Ч97 106Ч108 136Ч139
Graph, process 250
Graph, property 238
Graph, simple 26
Graph-theoretical isomorphism 77Ч78
Graphic sequence see УDegree sequenceФ
Greedy algorithm 98 108 117
grid 90 184 258
Grid, minor 260 264Ч274
Grid, theorem 264
Grid, tree-width of 260 278 281
Griinwald, T. 66
Grotzsch, H. 97 141 145
Group-valued flow 128Ч133
Guthrie, F. 120
Gyarfas, A. 178 185
Hadwiger, conjecture 169Ч170 181Ч183 185 186Ч187
Hadwiger, H. 181 186 187
Hajnal, A. 197 210
Hajos, construction 101Ч102
Hajos, G. 102 187
Haken, W. 121
Halin, R. 65Ч66 227 280Ч281
Hall, P. 31 42
Hamilton closure 226
Hamilton cycle 213Ч228
Hamilton cycle and 4-flows 144 215
Hamilton cycle and degree sequence 216Ч218 226
Hamilton cycle and minimum degree 214
Hamilton cycle and the four colour theorem 215
Hamilton cycle in 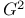 218Ч226 218Ч226
Hamilton cycle in 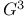 227 227
Hamilton cycle in almost all graphs 241
Hamilton cycle in planar graphs 215
Hamilton cycle, power of 226
Hamilton cycle, sufficient conditions 213Ч218
Hamilton path 213 218
Hamilton, W.R. 227
Hamiltonian sequence 216
Hamiltonian, graph 213
Harant, J. 66
head see УTerminal vertexФ
Heawood, P.J. 121 145
Heesch, H. 121
Hereditary graph property 263 274Ч277
Hereditary graph property, algorithmic decidability 276Ч277
Higman, D.G. 252 280
Hoffman, A.J. 120
Hypergraph 25
In (a graph) 7
incidence 2
Incidence, encoding of planar embedding see УCombinatorial isomorphismФ
Incidence, map 25Ч26
Incidence, matrix 24
incident 2 72
Increasing property 241 248
Independence number 110Ч117
Independence number and connectivity 214Ч215
Independence number and Hamilton cycles 215
Independence number and long cycles 118
Independence number and path cover 39
Independence number of random graph 232 248
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте





 ,
,