јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Leverenz H.W. Ч An introduction to luminescence of solids
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: An introduction to luminescence of solidsјвтор: Leverenz H.W. јннотаци€: This book is designed to provide an introductory and useful description of luminescent solids, particularly artificial (man-made) phosphors, in language comprehensible to science graduates. Much of the material is drawn from personal experience in synthesizing, studying, and applying luminescent solids since 1931, that is, during the recent era of intensive phosphor research which made possible such modern developments as electronic television, "fluorescent" lighting, radar, electron microscopy, and devices for seeing many otherwise invisible forme of energy. Although the book is intended for nonspecialists in luminescence, it is expected that it will be useful as a text in training future specialists and in aiding scientists who wish (a) to refresh and increase their knowledge of solid matter and its interactions with radiations and charged material particles, and (b) to use phosphors for detecting radiation and material particles.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1st edition√од издани€: 1950 оличество страниц: 569ƒобавлена в каталог: 20.08.2009ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Rothschild, S. 215 Ruby 68 see Rupp, E. 391 s center 94 132 133 142 144 331 333 346 350 351 364 S-dominated phosphors 188Ч190 193Ч217 343Ч346 Satellite lines and bands 109 110 Saturation of luminescence 353Ч355 357Ч362 440 441 443 Scattering of radiation 154 159Ч161 314 315 321 380 381 386 426 432Ч435 443 447 448 Scheelite 48 67 Schilling, M. 272 273 Schleede, A. 96 101 Schoen, M. 124 141 Schoenflies, notation 42Ч46 Schroedinger, E. 14 Schulman, J.H. 228 340Ч342 Scintillation counters 250 424Ч426 466Ч468 Scotophors 146 147 148 310Ч312 470 Scotopic eye 299 313 403 405 406 Screen texture 382 439 Screen thickness 412 413 421Ч426 432Ч435 445Ч447 463 Screen thickness, compacted 421 Screen thickness, optimum 434 435 Screen thickness, transmission of light by 445 Screens, aluminized 350 354 357 423 433 438 444 448 451 461 471 Screens, fluoroscopic 422Ч424 Screens, intensifier 422 423 Screens, stratified 439 440 454Ч459 Screw axes 46 Second crossover voltage 435 Second unity intercept 435 436 Secondary electron 120 317 319Ч322 435Ч438 Secondary emission 63 427 428 435Ч438 449 Secondary excitants 316Ч322 340Ч342 Secondary particles 159 Secondary-electron emission 63 427 428 435Ч438 449 Secondary-emission ratio 435 Sedimentation 387 Seitz, F. 1 144 Selection rules 21 99 106Ч110 112Ч117 131 149 247 260 Selective absorption 146Ч148 337 377 380 411 412 439 440 Selective emission 197 200 210 212 360Ч362 375 Self-activation 88 90 99 100 102 Self-diffusion coefficient 54 Self-excitation 165 166 Selwood, P.W. 96 Semiconduction 471 Semiconductor crystal 36 Semiconductor crystal, N-type 115 116 Semiconductor crystal, P-type 116 Semilog versus log-log plots 253 254 272 Sensitivities of detectors 298 299 313 315 403 405 Sensitized luminescence 338 340Ч342 Sensitizer center 341 Settling phosphors 382 Settling, selective 448 461 Shockley, W. 1 Shrader, R.E. 185 186 188Ч190 194 275 278 279 443 Signal flags 410 Smith, A.L. 476 Sniperscope 460 Snooperscope 460 solarization 146 312 359 377 451 Solid 34 35 485Ч487 Solid solution 85 93 Solid, real versus ideal 103 104 Solid-state reactions 48Ч50 60 64Ч81 Space charge in solids 54 127Ч130 Space groups 42 43 44Ч47 Space lattice 44 Specific heat 143 Specific heat of phosphors 397 398 Spectra, band emission 2 29Ч31 98Ч100 104 105 112Ч124 162 183Ч245 254Ч256 327Ч330 352 409 Spectra, line-emission 2 18Ч21 98 104Ч112 242 246Ч249 Spectra, soft x-ray-emission 118 Spectral efficiency 406 Spectral-distribution characteristic 23 Spectroscopic and densitometric apparatus 63 Sphalerite 65 88 Spinels 45 Stability, of crystals 51 Stability, of phosphors 73 252 280 343 353 376 377 380Ч389 410 411 414 417Ч421 448Ч452 453 460 461 Stability, of phosphors and scotophors 312 Stark effect 107 Stationary state 14 Statistics, Bose Ч Einstein 7 9 115 Statistics, Fermi Ч Dirac 7 9 115 Std. VI phosphor 308 Std. VII phosphor 308 Stefan Ч Boltzmann law 137 Stimulation 148 150 284Ч289 298Ч312 Stimulation spectra 302Ч304 306Ч308 310 Stoichiometric proportions 59 70 72 Stokes' law, of luminescence 125 316 Stokes' law, of sedimentation 387 Stokes, G.G. 125 387 Storage of excitation energy 172Ч183 246Ч312 468 469 Storing information 414 415 470 471 Strange, J.W. 254 Stroboscopic effect 420 424 Studer, F.J. 187 256 Substance 59 Substitutional impurities 52 53 Substitutional sites 52 89Ч95 Superexcitation 125 348 Surface imperfections 164 Surface layers on crystals 53 319 438 439 443 Surface sites 89 90 Surface states 115 125 Surface tension 34 Swedlund, L.E. 445 449 Sylvite 88 Symbols, activation energy 23 Symbols, chemical 13 14 46 59 60 Symbols, crystallographie 42Ч47 Symbols, nuclear 10Ч13 Symbols, phosphor 64Ч66 67 68 75 76 89 93 364 365 Symbols, spectroscopic 12 14Ч21 Symmetry elements 41Ч44 Symmetry group 42Ч44 system 16 135 Television phosphors 438Ч453 Television scanning 354 355 358 Temperature break point 126 138Ч147 265 269 334 343Ч354 460 466 Temperature break point, versus excitation density 347 348 Temperature break point, versus peak wavelength of emission 142 144 145 Temperature, Curie 140 Temperature, Debye characteristic 140 142Ч144 Temperature, during crystallization 48Ч51 62 64Ч74 Temperature, effect, on emission spectra 184Ч191 239 Temperature, on luminescence 2 104Ч106 123Ч127 132 136Ч148 342Ч349 Temperature, on thermal radiation 1 2 137Ч139 Tenebrescence 147 148 310Ч312 Tenebrescence, decay of 311 Tenebrescent CRT screen 420Ч430 Terminology of luminescence 147Ч151 Terr ill's equation 158 Tertiary excitants 318 319 321 tetr.- 233 288 291 295 372 429 464 tetr.- 239 tetr.- 168 239 318 370 423 426 tetr.- 417 tetr.- 348 tetr.- 48 67 81 82 88 100 136 156 167 168 243 245 255 335 338 345 346 370 378 381 402 419 420 423 425 426 428 430 437 465 468 tetr.- 337 tetr.- 118 tetr.- 245 tetr.- 107 tetr.- 107 tetr.- 59 88 tetr.- 240 273 289 tetr.- 340 tetr.- 65 81 91 156 169 171 175 177 240 243 245 255 261 262 269 289 290 293 340 349 360 355 359 364 371 379 381 390 391 430 tetr.- 340 tetr.- 256 340 tetr.- 340 tetr.- 240 tetr.- 238 tetr.- 221 tetr.- 221 238 312 tetr.-(Ca:Pb) 348 Texture 159 461 Therapy with phosphors 426 427 Thermal agitation 22 23 29 38 41 45 50Ч54 98 140 144 346 351 352 Thermal dissociation of ZnS and CdS 99 Thermal emissive power 137 Thermal radiation 1 2 23 105 136Ч139 153 482 483 Thermoquenching 151 182 183 287 Thermostimulation 151 176Ч183 276 298Ч312 323 Thomsen, S.M. 200 Thomson Ч Whiddington law 158 Thorington, L. 346 Tiede, E. 72 101 Tilgung 148 Time cycles during crystallization 47Ч50 62 64Ч74 Tomaschek, R. 107 108 Tomboulian, D.H. 167 Toxicity of chemicals 63 414 415 426 Transition probability 19 115 120 122 144 149 252 258Ч261 285 Transition, allowed 18 19 21 115 149 Transition, forbidden 21 115 149 Transmission, of excitant 153 154 Trap 57 73 127 131Ч135 284Ч288 299Ч312 Trap concentration 274 367 Trap depth, optical 180 181 298 Trap depth, thermal 180 181 298 Trap, electron 122Ч124 127Ч129 Trap, positive-hole 117 Trapped-electron absorption region 163 164 Trapping 176Ч183 269Ч281 284Ч299 Trapping activator 274 Triboelectric effect 171 172 Triboluminescence 148 171 172 tricl.- 430 465 tricl.- 173 174 Trinoscope 452 Trypaflavine 61 see Tuning indicators 428 Tunnel effect 37 Turkevich, J. 78 Ultraviolet (UV) 2 Ultraviolet lamps 62 63 407 408 415Ч418 Ultraviolet sources and filters 62 Unit cell 40 41 Urbach, F. 276 304 306 334 348 350 469 Valence 17 18 24 25 52 53 57 72Ч75 91 96Ч101 111 van Heerden, P.J. 129 Vegard's law 93 Velocity of electrons 8 36 158 Vibration of atoms 54 Vibrational modes 113 115 Vibrational states 29Ч31 Vielfachstoesse 126 140Ч142 300 viscosity 33 Vitreous luminescent materials 322 414 Volatilization, of ingredients 72 Volatilization, selective 36 82 83 88 89 Voltage, break-even 444 von Hippel, A. 144 Voyatzakis, E. 390 Ward, R. 235 275 303 308 309 Warminsky, R. 129 Washing phosphors 65 76 78 79 Water molecule 28 30 484Ч487 Wave function 4 14 24 26 36 55Ч57 113 133 134 Wave mechanics 4 14 26 33 wave number 107Ч109 Wave-function overlap 56 119 130 131 Wave-number vector, material particle 112Ч117 Wave-number vector, reduced 113 Wavelength, diffraction 4 5 7 8 Wavelength, radiation-conversion 6 8 Weagle, L.T. 413 Weil, M.A. 413 Wells, A.F. 178 Weyl, W.A. 228 White, A.B. 456 457 White, H.E. 484 Wien's displacement law 137 Wigner, E.P. 260 261 Wilkins, M.H.F. 179 270 390 Willemite 48 68 88 Williams, F.E. 177 writing speed 429 Wurtzite 66 88 X-ray emission 248 X-ray fluorescence 104 105 140 318 320 363 366 X-ray radiation, continuous 483 X-ray sources 62 Zeeman effect 397 Zener, C. 141 Zentren verschiedener Dauer 97 288 Zinc blende 65 Zn salt of 8-hydroxyquinoline 409 410 ZnO: 234 ZnO: 187 194 233 234 255 346 371 468 ZnO: 339 ZnO: 222 223 ZnO:BeO: 229 230 236 337 ZnO:BeO: 230 ZnO:CdO: 233 235 294 ZnO:MgO:(rare earth) 409Ч411
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 :Mn
:Mn 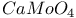 :Pb
:Pb 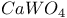 :Pb
:Pb 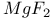
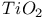 :Sm
:Sm 
 :Mn
:Mn  :[Mo]
:[Mo]  :Ce
:Ce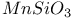
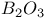 :
: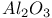 :Mn
:Mn  :Mn
:Mn