јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Leverenz H.W. Ч An introduction to luminescence of solids
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: An introduction to luminescence of solidsјвтор: Leverenz H.W. јннотаци€: This book is designed to provide an introductory and useful description of luminescent solids, particularly artificial (man-made) phosphors, in language comprehensible to science graduates. Much of the material is drawn from personal experience in synthesizing, studying, and applying luminescent solids since 1931, that is, during the recent era of intensive phosphor research which made possible such modern developments as electronic television, "fluorescent" lighting, radar, electron microscopy, and devices for seeing many otherwise invisible forme of energy. Although the book is intended for nonspecialists in luminescence, it is expected that it will be useful as a text in training future specialists and in aiding scientists who wish (a) to refresh and increase their knowledge of solid matter and its interactions with radiations and charged material particles, and (b) to use phosphors for detecting radiation and material particles.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1st edition√од издани€: 1950 оличество страниц: 569ƒобавлена в каталог: 20.08.2009ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
cub.- 107 cub.- 107 cub.- 91 110 167 228 232 240 244 255 291 293 371 cub.- 243 cub.- 222 238 cub.- 167 232 244 291 cub.- 107 cub.-(Ca:Sr)S:Bi 299 408 411 414 cub.-(Zn:Cd)S:Ag 239 cub.-(Zn:Cd)S:[Zn:Cd] 243 cub.-AgBr 118 140 cub.-BaFCl 423 cub.-BaO 118 cub.-BaO:Sm 107 cub.-BaS:Sm 107 cub.-C (diamond) 47 110 487 cub.-Ca(S:Se):Sm:Eu 308 cub.-CaO 118 cub.-CaO:Pb 232 338 cub.-CaO:Pr:Sm 300 cub.-CaO:Sm 107 108 cub.-CaS:Bi 240 319 323 373 391 411 cub.-CaS:Sm 107 340 cub.-CaS:Sm:Bi 339 340 cub.-CaS:Sm:Eu 308 cub.-CaS:Sm:Pb 339 cub.-CdO 161 cub.-CdS 84 161 cub.-CsCl 46 47 cub.-CsCl:Sb 96 98 280 cub.-KBr 118 140 cub.-KCl 46 47 51 70 88 95 140 146 147 310Ч312 454 477Ч479 484Ч487 cub.-KCl:Ag 165 243 272 298 312 378 cub.-KCl:Cu 298 378 cub.-KCl:Mn 378 cub.-KCl:Sb 64 89 96 240 243 385 cub.-KCl:Tl 64 81 94 168 231 272 285 289 cub.-KF 118 cub.-LiBr 118 cub.-LiF 118 cub.-MgO 118 cub.-MgO:Sm 107 108 cub.-MgS:Sb 64 65 72 180 241 243 364 377Ч379 428 429 465 466 cub.-MgS:Sm 107 cub.-MnS 118 cub.-NaBr 118 cub.-NaCl 86 128 140 cub.-NaCl:Ag 298 cub.-NaCl:Cu 298 cub.-NaCl:Mn 102 cub.-NaF 118 cub.-NaI:Tl 81 424 465 cub.-RbBr 118 cub.-RbI:Tl 232 338 cub.-Sr(S:0):Bi 233 cub.-Sr(S:Se):Sm:Eu 48 66 67 87 170 175 180Ч182 286 298 302 303 306Ч308 312 323 379 469 cub.-SrO 118 cub.-SrO:Sm 107 cub.-SrS:Ag:Pr 339 cub.-SrS:Bi 373 cub.-SrS:Eu 240 cub.-SrS:Sm 107 cub.-SrS:Sm:Ce 87 170 276 306Ч308 cub.-SrS:Sm:Eu 181 193 276 278 279 302 304 306 308 322 373 cub.-Zn (S:Se:Te):Cu 294 cub.-Zn(S:Se) 87 93 95 cub.-Zn(S:Se):Ag 142 201 202 213 239 344 379 461 cub.-Zn(S:Se):Cu 142 202 207 213 344 cub.-Zn(S:Se):Mn 204 205 213 cub.-Zn(S:Se):[Zn] 142 200 202 213 379 cub.-ZnS 46Ч51 59 86 88 91 95 115 118Ч123 161 477Ч480 487 cub.-ZnS:Ag 94 120Ч123 127 145 162 167 197 201 202 206 211 217 243 244 289 290 295 330 333 343 344 350 356 358 360 366 373 383 401 408 428 430 440Ч442 445 479 480 cub.-ZnS:Ag:Cu 255 cub.-ZnS:Ag:Ni 333 334 350 411 cub.-ZnS:Au 203 211 343 cub.-ZnS:Cu 65 71 74 94 120Ч123 127 139 145 162 167 177 178 198 203 208 211 215 217 240 289 294 296 334 343 344 348 373 391 cub.-ZnS:Cu:Mn 255 256 cub.-ZnS:Mn 66 71 89 94 120Ч122 127Ч129 167 168 171 193 204 207 217 240 289 331 333 371 391 478 cub.-ZnS:Sm 107 cub.-ZnS:[Zn] 99 119Ч123 127 162 163 167 178 196 200 202 203 206 208 211 217 220 244 251 280 289 294 343 361 373 391 403 437 cub.-ZnS:[Zn]:Cu 208 cub.-ZnS:[Zn]:Mn 123 127 361 cub.-ZnS:[Zn]:Ni 334 344 cub.-ZnS:[Zn]:P 241 438 cub.-ZnSe 46 51 84 86 95 cub.-ZnSe:Ag 162 201 244 364 373 cub.-ZnSe:Cu 162 202 207 373 cub.-ZnSe:Mn 162 204 205 207 cub.-ZnSe:[Zn] 99 162 200 207 220 244 373 Curie 462 Dana, E.S. 485 Daniels, F. 1 Dark burn 388 449 Dark-trace screens 460 see de Broglie, M. 4 Deaggregation of crystals 381Ч385 Decay 150 261 301 454Ч459 Decay, "constant", apparent 265Ч269 272 277 293Ч295 298 Decay, "tails" 305 329 330 375 Decay, bimolecular 270 366 Decay, concave-downward 454Ч456 458 Decay, constant 257 293Ч295 366 Decay, curve 261 Decay, effect, of excitation time on 261 277 278 281 Decay, effect, of intensity of excitation on 262Ч265 277 279Ч281 Decay, effect, of kind of excitant on 262 264 277Ч279 289 Decay, effect, of operating temperature on 264Ч281 298 Decay, effect, of phosphor constitution on 289Ч298 Decay, exponential 121 151 255Ч269 366Ч373 Decay, monomolecular 257 366 Decay, nonexponential 121 Decay, phosphors versus scotophors 454 470 Decay, power-law 169 252 203Ч281 366 456 457 Deceleration radiation 156 158 483 Defect structure 45 Deficiency structure 45 233 235 328Ч Definition in images 448 Deflection of cathode rays 428 Degeneracy 16 35 117 Degeneracy, removal of 107Ч109 Density of energy levels in bands 36 114 117 120 Destriau, G. 392 393 Detail contrast 447 Detection, of gamma rays 424Ч 426 Detection, of infrared 469 470 Detection, of luminescence radiation 63 136 401Ч407 463Ч465 Detection, of neutrons 468 Detection, of surface flaws and cracks 410 Detection, of thermal radiation 469 Detectors 4 63 80 136 399Ч407 463Ч465 Deutschbein, O. 108 109 Diamagnetism 20 391 diamond 47 452 485Ч487 Dielectric constants of crystals 51 70 155 156 390 Dielectric properties of phosphors 390Ч392 Dielectric-cell bolometer 470 Diffraction 3 4 7 Diffraction by solids 113 117 Diffusion, of impurities 100Ч102 Diffusion, of reactants 71 Dipole 11 25 32 33 Dipole moment 24 25 32 149 Dipole radiation 149 150 Dirac, P.A.M. 5 16 Directed valence 28 Directional bonding 28 97 Disordered structure 45 Distortions in crystals 52Ч54 Domain, imperfection 52 57 58 Domain, magnetic 20 21 Dominant activator 274 Dyes 146 148 Echoes, simulated 470 471 Edge emission bands 99 100 162 175 197 200Ч202 218Ч220 251 340 361 362 435 483 Effective luminescence efficiency 316 Efficiency, of luminescence 71Ч80 312Ч Efficiency, of x-ray fluorescence 467 Efficiency, relative 315 Efficiency, standards 75 195 Einstein, A. 5 Electric conduction of phosphors 145 146 390Ч392 Electric conduction of solids 120 127Ч130 Electric conduction, bombardment-induced 129 Electric conduction, stimulated 301Ч304 Electric conduction, versus glow curve 179 Electroluminescence 148 152 Electromagnetic spectrum 403 Electron "shells" 17Ч20 27 33 58 Electron "shells", incomplete (unfilled) 20 58 104Ч112 140 Electron affinity 22 35 Electron cloud 12 19 27 28 41 104 149 484Ч487 Electron cloud, fluctuations of 19 25Ч27 32 89 144 Electron spin 7 8 16Ч21 35 58 Electron trap 57 58 73 309 312 331 335Ч337 346 348 366 367 375 380 390 393 Electron velocities in solids 113 114 127 Electron volt 6 60 Electron volt, per simple molecule 60 Electron, excited 36 37 132Ч135 Electron, in periodic field 112Ч117 Electron, interaction with other electrons 7 9 19 20 Electron, localization of 4 5 Electron, negative-energy 5 6 Electron, positive-energy 2 4Ч9 Electron, wavelength of 4 5 7 8 14 27 36 Electron-microscope phosphors 461 Electronic configurations 111 Electronic excitation, optical versus thermal 144 145 Electronic transitions 18Ч21 29 58 104Ч135 Electrons, mean free path of, in solids 129 Electrons, mean free path of, trapped 52 55 57 58 Electrons, mean free path of, valence 140 Elementary particles 6Ч9 486 487 Ellickson, R.T. 305Ч307 313 Emission activator 274 Emission band, double 231Ч235 Emission band, multiple 123 Emission band, origin 184 Emission band, shape 208Ч210 Emission band, temperature variation 218 219 Emission band, width 138 150 185 186 245Ч245 252 254 255 258 Emission band, width, origin of 251 259 260 281Ч284 Emission lines 185 186 188 Emission lines, natural breadth of 149 150 Emission spectra 2 29Ч31 98Ч100 104 105 112Ч124 162 183Ч252 254Ч256 327Ч330 352 409 Emission spectra, during and after excitation 254Ч256 288 Emission spectra, during stimulation 299 300 304 Emission spectra, temperature variation 184Ч194 410 411 Emission types 104 105 Emission, anisotropic 109 Emission, selective 197 200 210 212 360Ч362 375 Enamels, luminescent 414 Energy 2Ч5 173 Energy "bit" 155 156 317 318 321 322 349 353 Energy band 29Ч31 35Ч39 54Ч58 112Ч124 Energy band, conduction 35 36 54Ч58 114Ч135 Energy band, filled 6 35 36 54Ч58 114Ч124 Energy band, overlapping 145 Energy band, width 37 54Ч58 118 119 133 Energy deficit 21 51 169 277 Energy degradation 1 130Ч132 140Ч 336 337 345 346 348 362 367 Energy level 6 18 19 29 30 35Ч39 54Ч58 70 103Ч135 Energy level, allowed 5 6 122 Energy level, crossover 131 132 Energy level, discrete 36 54Ч58 106Ч112 117 118 133 Energy level, due to imperfections 55Ч58 122Ч126 Energy level, excited-state 19 35Ч38 54Ч58 114Ч126 131Ч135 281Ч289 Energy level, forbidden 5 6 122 Energy level, ground-state 18Ч20 29 30 35Ч37 54Ч58 131Ч135 281Ч289 Energy level, indeterminacy of 149 Energy level, overlapping 103 128 129 133 134 Energy level, trapping 122Ч124 131Ч135 Energy level, vibrational 29Ч31 37Ч38 55 131 132 144 Energy loss as heat 31 38 130Ч132 281Ч289 Energy losses in solids 154Ч159 Energy of excitants 136 137 Energy of luminescence photons 136 483 Energy state 14 36 103Ч135 Energy storage 1 2 148Ч151 176Ч183 299Ч311 Energy transfer 97 172Ч176 256 320Ч322 337 Energy transmission in solids 53 112Ч117 130 131 Energy, activation 23 33 49Ч51 54 132 134 144 146 Energy, attraction 11 15 32 33 Energy, binding 11 15 22 24 51Ч55 109 486 487 Energy, Coulomb 8 9 11 13 15 17 52 Energy, exchange 9 11 24 27 33 39 52 140 Energy, excitation 5 6 18 19 29Ч31 34Ч37 51 54Ч58 Energy, free 6 50 63 116 125 Energy, ionization 15Ч19 Energy, kinetic 3 7 9 15 19 22 23 29 31 50 112 117 123 Energy, potential 3 4 7 9 15 22Ч26 28Ч30 41 49 50 117 131 Energy, radiant 2 4 Energy, repulsion 11 15 33 Energy, rotational 143 Energy, saturation 11 Energy, self 6 8 15 137 Energy, surface-tension 11 Energy, total 9 15 33 50 96 104 114 116 Energy, van der Waals 11 24 33 81 Energy, vibrational 142Ч144 Energy, zero-point 29 Energy-level diagrams 6 18 28Ч31 35Ч39 54Ч58 103 104 107 108 114Ч135 208 217 256 258Ч260 281Ч289 Energy-level diagrams, mercury atom 248 entropy 50 61 96 Eosin, 248 252 Epstein, D.W. 358 Exchange 9 11 310 see Exchange effect 17 20 26 Exchange forces 410 exchange interaction 336 337 341 Excitant 76 122 146Ч148 152 Excitant, penetration of 126 128 Excitation 6 18 19 21 51 107Ч126 131Ч135 141 142 Excitation additivity 171 Excitation by alpha particles see "Ionoluminescence" Excitation by electrons see "Cathodoluminescence" Excitation by gamma rays see "Roentgenoluminescence" Excitation by ultraviolet see "Photoluminescence" Excitation by x rays see "Roentgenoluminescence" Excitation density 170 277 349 397 Excitation energy, minimum 156 165 Excitation intensity 170 Excitation intensity, effect on multiband spectra 197 200 210 212 Excitation of phosphorescence 168Ч170 Excitation of phosphors 64Ч68 84 89 90 97 99 152 153 Excitation spectra 162Ч170 340 342 Excitation spectra, temperature variation 163 166 Excitation, effect on optical properties 397 Excitation, intermittent 261 290 291 Excitation, modulated versus unmodulated 354Ч360 367 368 Excitation, unmodulated (steady) 253 254 262Ч268 272 273 280 292 295Ч297 Excited state 36 131Ч135 Excited state, natural lifetime of 148Ч151 Exciton 35 55Ч57 119 130 131 Exclusion principle 16 36 54 115 Exponential decay 121 151 168 169 252Ч269 277 281Ч285 287Ч295 299 300 305 Exponential decay, pictorial representation of mechanism 282 283 Exponential decay, temperature-dependent 269Ч272 Exponential decay, temperature-independent 256Ч269 296 298 379 F centers 58 309Ч311 Facilities for phosphor research 61Ч63 73Ч75
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



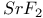 :Sm
:Sm 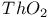 :Sm
:Sm  :Mn
:Mn 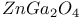 :Cr
:Cr 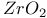 :Sm
:Sm 