јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Leverenz H.W. Ч An introduction to luminescence of solids
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: An introduction to luminescence of solidsјвтор: Leverenz H.W. јннотаци€: This book is designed to provide an introductory and useful description of luminescent solids, particularly artificial (man-made) phosphors, in language comprehensible to science graduates. Much of the material is drawn from personal experience in synthesizing, studying, and applying luminescent solids since 1931, that is, during the recent era of intensive phosphor research which made possible such modern developments as electronic television, "fluorescent" lighting, radar, electron microscopy, and devices for seeing many otherwise invisible forme of energy. Although the book is intended for nonspecialists in luminescence, it is expected that it will be useful as a text in training future specialists and in aiding scientists who wish (a) to refresh and increase their knowledge of solid matter and its interactions with radiations and charged material particles, and (b) to use phosphors for detecting radiation and material particles.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1st edition√од издани€: 1950 оличество страниц: 569ƒобавлена в каталог: 20.08.2009ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Ferguson, J.N. 128 Fermi function 116 Fermi level 115 116 Ferrites 140 ferromagnetism 20 21 140 First crossover voltage 485 First unity intercept 435 436 Flacker 453 Flash 458 flicker 405 420 447 463 456 Fluidity 33 Fluorescein, 248 251 252 Fluorescence 124 148Ч151 246Ч250 287 Fluorescent materials 147Ч150 Fluorophors 147 148 248 Fluoroscopy 422 423 Fluors 147 148 Flux 49 50 65Ч67 71 74 78-79 84Ч87 308 Flux, effect on efficiency 333 Flux, function of 74 78 79 343 344 Flux, proportion of 78 79 Flux, residual 97 Flying-spot CRT 465 Fonda, G.R. 85 141 231 239 265 304 305 340 403 Foot-lambert 481 Footcandle, effective 481 Foote Mineral Co. 475 Forbidden transition 106 110 115 122 Force, intermolecular attraction 33 Formal valence 12 17 18 Franck Ч Condon principle 29 Free energy 6 173 Frerichs, R. 129 164 182 Furnaces 61 62 73Ч75 Galvanoluminescence 151 Gamma-ray fluorescence 104 105 363 365 366 483 Gamma-ray sources 63 Gamow, G. 11 Garlick, G.F.J. 141 163 177Ч179 288 304 335 348 390 Gas, ideal 31 33 476 Gaus, L. 187 191 Gibson, A.F. 141 163 390 Gittings, H.T. 250 Glasses 35 Glide planes 46 Glow curves 176Ч182 305 307 Gram-atomic weight 60 Gram-molecular weight 60 Grinding phosphors 76 78 90 152 310 333 381Ч389 Ground state 16 36 131Ч135 Ground-state spin 16 17 Growth (of luminescence emission) 160 261 301 314 459 Growth delay 275 276 Gudden, B. 129 Halation 447 448 Hale, D.R. 334 Halophosphate phosphors 339 417 Hardy, A.E. 130 164 301 390 393Ч396 440 Haynes, J.R. 321 Head, R.B. 450 Headrick, L.B. 441 442 449 Health precautions 63 414 415 Heat capacity, classical 143 Heat capacity, Debye relation 142 Heat dissipation in phosphors 105 106 Heat residue 169 170 277 318 319 323 351 353 355 357 416 451 452 460 Heating, by CR beam 82 83 219 311 451 452 460 Heating, by radiation 469 Heisenberg, W. 4 93 Henderson, S.T. 254 Hermann Ч Mauguin notation 42Ч46 hex.- 256 339 417 hex.- 109 hex.- 109 hex.- 175 hex.- 118 220 221 226 hex.-(Zn:Be)O:[Zn:Be] 223 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S 86 93 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S:Ag 48 83 129 147 162 165 167 168 197 199 207 212 239 255 318 333 344 350Ч352 356 359 403 408 411 422 423 430 439 440 445 447 453 460 461 464 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S:Ag:Cu 210 288 456 457 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S:Ag:Ni 423 469 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S:Cu 128 141 162 165 171 178 179 195 198 199 207 212 216 252Ч255 264 276 280 301 304 344 348 350Ч352 364 391 393Ч396 403 408 410 411 414 429 430 450 456Ч458 470 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S:Mn 203Ч208 213 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S:[Zn:Cd] 141 162 164 165 196Ч198 201 207 212 243 hex.-(Zn:Cd)S:[Zn]:Cu 350 352 hex.-BeO 118 hex.-BeO:Sm 107 hex.-Cd-chlorophosphate:Mn 417 hex.-CdO:[Cd] 219 hex.-CdS 51 74 81 84 86 128 129 hex.-CdS:Ag 245 373 hex.-CdS:Cu 373 394 hex.-CdS:Mn 203 207 213 245 hex.-CdS:[Cd] 99 156 162 164 174 194 196 200 214 219 252 361 373 379 381 394 hex.-CdSe 129 hex.-CdTe 129 hex.-HgS 147 hex.-MnS 118 hex.-Zn(S:Se):Mn 205 hex.-ZnO 45 51 59 60 67 74 118 128 484Ч487 hex.-ZnO:[Zn] 67 72 74 88 90 99 156 161 167 171 187 193 194 200 218Ч220 223 225 243 244 251 255 275 294 338 340 345 349 350 355 361 362 370 378 379 381 385 386 390 393 411 420 424 427 428 430 435 437 465 466 469 482 hex.-ZnS 48Ч51 86 88 91 118 477Ч479 hex.-ZnS:Ag 74 76 94 127 138 139 142 145 147 161 167 168 175 184 189 194 199 200 202 214 217 245 254 255 289 318 320 324 332 344 358 360 362 364 366 373 382 383 403 408 411 412 423Ч426 429 430 439 442 444 445 450 452 456Ч458 465Ч468 482 hex.-ZnS:Ag:Cu 340 361 412 413 429 430 450 458 hex.-ZnS:Ag:[0] 127 hex.-ZnS:Cu 66 72 74Ч76 89 94 127Ч129 139 142 145 152 161 167Ч169 175 177Ч179 184 190 194 199 202 203 207 209 215Ч217 240 255 272Ч274 289 290 294Ч297 299 304 310 323 336 343 344 351 356 359 364 373 379 389 407 408 411 414 430 438 462Ч464 469 hex.-ZnS:Cu:Co 273 335 hex.-ZnS:Cu:Fe 414 471 hex.-ZnS:Cu:Ni 178 335 hex.-ZnS:Cu:Pb 72 304 305 308 312 hex.-ZnS:Cu:[O] 272 391 hex.-ZnS:Mn 66 71 89 94 133 139 167 203Ч205 207 213 217 240 245 255 268 269 289 292 331 333 349 350 359 370 391 478 hex.-ZnS:Pb 232 338 hex.-ZnS:Pb:Cu 72 304 305 308 312 hex.-ZnS:Sm 107 hex.-ZnS:[Zn] 99 141 161 167 188 194 196 198 200 202 203 207 209 216 217 220 244 251 280 289 361 362 373 466 476 hex.-ZnS:[Zn]:Cu 207 209 212 288 361 hex.-ZnS:[Zn]:Mn 361 Hofstadter, R. 250 Host crystal 51 64Ч80 99 369Ч374 Host crystal, oxygen-dominated 110 217Ч238 241Ч244 346Ч348 Host crystal, sulphur-dominated 194Ч216 241Ч244 343Ч345 Host-crystal absorption region 163Ч165 175 Host-crystal action 241Ч245 Human eye 80 136 403 405Ч407 Hume-Rothery, W. 1 Hybridization of states 28 485 Hydrofluoric-acrid process 69 Hydrogen atom 10 12 15 16 24 149 484Ч487 hydrogen molecule 24 26 484Ч487 Hydrothermal synthesis 81 Hysteresis of efficiency versus temperature 139 269 280 343 i center 95Ч101 142 144 145 331 333 346 351 352 364 Icaroscope 470 ICI diagram 417 431 Identity translation 41 112Ч115 Identity translation, minimum 41 140 Image intensification 422 Ref. Image repetition frequency (IRF) 453 Image-tube phosphors 460 461 Imperfection absorption region 163Ч165 Imperfections in Solids 38 47Ч58 62 70Ч75 115Ч118 122 Imperfections in solids, action of 125 247 Impurities, added 88Ч103 Impurities, beneficial see "Activators" Impurities, detrimental 333Ч337 see Impurities, induced 88 89 99 100 Impurities, locations of 89Ч102 Impurities, multivalent 134 Impurities, selective adsorption of 102 Impurities, selective inclusion of 102 Impurity atoms in solids 88Ч103 Impurity atoms, distribution of 121 477Ч480 Impurity center, structure of 96Ч100 Impurity energy levels 36 54Ч58 121Ч127 131Ч135 Incandescence 2 137Ч139 483 Incandescent lamp 2 138 400 Indeterminacy 3 4 117 Indeterminacy principle 4 5 15 27 37 149 Index of refraction 154 155 160 161 432 Infrared (IR) 2 483 Infrared (IR), effect on phosphorescence 150 Infrared sources and filters 62 Insulator solid 35 36 54Ч58 114 Intensifier activator 192 193 239 240 Intensity of light 160 Intensity-time relationships 150 Interaction, between impurities 56 57 78 121 310 332 335Ч337 Interaction, of activators 332 Interatomic bonds 22Ч28 89Ч91 250 Internal ionization 123 128 Internal pressure 33 79 Interstitial impurities 51Ч54 Interstitial sites 52 90 94Ч102 Ion 13 18 21 22 26 484Ч487 Ion burn 450 451 462 463 Ion sources 63 Ion spot 450 451 ionic bond 22 484Ч487 Ionic dissociation 70 Ionic valence 12 17 18 Ionization 15 Ionization continuum 19 35 Ionization potential 15 35 Ionization, internal 123 128 Ionoluminescence 148 Ionoluminescence efficiency 317 320 321 323 359 367 378 467 Isostructures 91 Isotopes 10 12 Ivey, H.F. 311 Johnson, R.P. 1 Kabakjian, D.H. 463 Kallmann, H. 424 425 467 Kasha, M. 252 Kato, M. 296 KCl 22 83 Killers 132 177 309 310 333Ч337 Kinescope 431 Kirchhoff's law 137 Klasens, H.A. 124 145 334 335 Knoll, M. 437 Kroeger, F.A. 72 110 163 165 197 200 228 265 268 334 347 348 361 403 Lambert's cosine law 434 Larach, S. 443 Lasof, S. 200 263 266Ч268 280 349 351 352 Latent heat of vaporization 34 Lattice point 41Ч47 Lattice site 50 Laundry marks 410 Lenard, P. 97 228 Levshin, V.L. 288 Lifetime of excited state 14 19 116 246Ч248 252 255 257 264 269 288 291Ч294 348 351 361 379 Ligands 27 91 112 Light 1 2 4 Light sum 273 298 301 302 304 305 307 314 315 Limiting potential 437 Line emission 18 19 106Ч112 338 409Ч411 Line spectra 18 19 106Ч112 409Ч411 line width 149 150 246 248 251 252 257 258 Linwood, S.H. 228 Liquid, formation of 32Ч35 Lithium, arc spectrum of 19 Lithium, energy-level diagram 18 Locations of activator atoms 78 89Ч102 London dispersion effect 32 Lonsdale, K. 1 Loose packing of atoms 41 Loss of efficiency 381Ч389 Lowry, E.F. 419 Lumen 9 481 Luminance 481 Luminance of "fluorescent" lamps 420 Luminance of CR-excited phosphors 354Ч358 428 439 440 453 454 462 468 Luminance of fluoroscope screens 422 423 Luminance of ion-excited phosphors 463 Luminance of IR-stimulated phosphor 180 Luminance of photoluminescent screens 408 Luminance, peak versus average 354 355 Luminescence analysis 233 241 243Ч246 Luminescence center 99 250 288 300 Luminescence decay 252Ч312 Luminescence efficiency 84 90 97 106 125 140Ч147 172 252 267 278 279 312 313Ч362 Luminescence efficiency, effect, of atmosphere on 414 418 419 Luminescence efficiency, effect, of grinding on 152 381Ч386 Luminescence efficiency, effect, of pressure on 152 Luminescence efficiency, effect, of temperature on 2 30 31 136Ч148 185Ч191 269 280 334 342Ч348 Luminescence efficiency, hysteresis 139 269 280 343 Luminescence efficiency, temperature variation of 173Ч175 334 342Ч349 Luminescence emission, effect, maximum 354 355 359 367 Luminescence emission, effect, of electric field on 391Ч394 Luminescence emission, effect, of magnetic field on 391 392 Luminescence growth 252Ч254 256 261 275 276 280 281 366 429 Luminescence mechanisms 131Ч135 251 281Ч288 Luminescence of cp solids 174 175 Luminescence radiation 1 136 147 482 483 Luminescence terminology 147Ч152 Luminescence, conventional 140 149 150 482 483 Luminescence, definition of 1 2 30 31 136 140 Luminescence, versus conduction 127Ч130 393 394 Luminescence-pure (lp) 61 Luminogen 64 Luminophor 147 148 Luminous efficiency 400 Magnetic moments 8 111 112 Magnetic properties of phosphors 391 392 Mallinckrodt Chemical Co. 476 Manganese, valence of 57 89 91Ч94 96 97 110Ч112 Marden, J.W. 334 335 Martin, S.T. 441 442 Mass 5 Mass defect 11 Mass number 10 12 Mass, moving 8 Mass, rest 5 8 material 59Ч61 63 Matrix 64 Matter 2Ч39 484Ч487 Meister, G. 334 335 418 419 Melting points of crystals 34 54 255 370Ч373 389 Mercury, arc spectrum of 249 Mercury, energy-level diagram of 248 Mesopic eye 299 Messineo, P.J. 358 Metallized screens see "Aluminized screens" Metascopes 470 Metastable crystals 73 139 269 280 343 Metastable states 124 131 247 252 269 287 Mg salt of 8Чhydroxyquinoline 409 410 Millilambert 9 481 Millson, H.E. 299 Minerals, luminescent 48 61 Minimum voltage 466 Modulated versus unmodulated excitation 451 452 454Ч459 Modulation of phosphor emission 469 Modulation, positive versus negative 459 460 Mole 60 Molecular models 484Ч487 Molecule 13 22Ч31 36 45 486 487 Molecule, dissociation of 30 31 Molecule, formation of 22Ч29
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



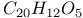
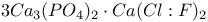 :Sb:Mn
:Sb:Mn