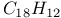јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Leverenz H.W. Ч An introduction to luminescence of solids
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: An introduction to luminescence of solidsјвтор: Leverenz H.W. јннотаци€: This book is designed to provide an introductory and useful description of luminescent solids, particularly artificial (man-made) phosphors, in language comprehensible to science graduates. Much of the material is drawn from personal experience in synthesizing, studying, and applying luminescent solids since 1931, that is, during the recent era of intensive phosphor research which made possible such modern developments as electronic television, "fluorescent" lighting, radar, electron microscopy, and devices for seeing many otherwise invisible forme of energy. Although the book is intended for nonspecialists in luminescence, it is expected that it will be useful as a text in training future specialists and in aiding scientists who wish (a) to refresh and increase their knowledge of solid matter and its interactions with radiations and charged material particles, and (b) to use phosphors for detecting radiation and material particles.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1st edition√од издани€: 1950 оличество страниц: 569ƒобавлена в каталог: 20.08.2009ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Molecule, ionic 22Ч28 484Ч487 Molecule, nonionic 24Ч28 484r-487 Molecule, nonpolar 24Ч28 Molecule, polar 22Ч28 Molecule, sizes of 31 486 487 Mollwo, E. 161 Momentum diagram, need for 104 Momentum space 113 Monochrome television 438 monocl.- 411 monocl.- 44 monocl.- 359 401 430 438 441 452 monocl.- 232 233 290 293 monocl.- 232 monocl.- 221 monocl.- 192 239 452 monocl.- 411 monocl.- 81 100 381 monocl.- 44 monocl.- 230 232 233 240 293 338 371 monocl.- 411 monocl.- 335 monocl.- 99 100 191 194 255 370 401 417Ч420 430 465 monocl.- 44 monocl.- 346 monocl.-Anthracene, 61 250 252 monocl.-Naphthalene, 61 98 250 252 381 425Ч427 467 468 485 monocl.-Phenanthrene, 61 250 monocl.-Stilbene, 61 250 381 426 465 Moore, C.N. 321 Morley, C. 1 Mosaic crystals 53 Mosaic structure 47 48 Mott, N.F. 144 Mukhopadhyay, B. 160 Multiplicity 21 183 247 Multivalent atoms 12 18 57Ч59 77 Nagy, E. 145 Nagy, R. 230 418 419 Nail, N.R. 334 348 350 Negative modulation 460 Nelson, H. 437 Neutron 2 6Ч11 Neutron, detection of 468 New Jersey Zinc Co. 409 Newcomer, H.S. 426 Nicoll, F.H. 200 219 446 Nonradiative transitions 55 125Ч127 131Ч135 265Ч269 285 287 301 306 309 310 312 336 337 345 349 352 361 Nottingham, W.B. 310 Nucleons 10 O'Bryan, H.M. 118 119 O-dominated phosphors 119 185Ч187 217Ч239 346Ч349 O-versus S-dominated crystals 242Ч245 292 411 447 449 461 463 Objective versus subjective detectors 406 407 463Ч465 Omission defects 46Ч48 50Ч58 73 96 331 375 Optical lifetime 19 Optical modes 115 309 310 Optical photon 149 Optical transition 19 124 149 Optical trap depth 180 181 298 Optical vibrations 115 309 310 Optimum proportion of activator 77 78 328Ч332 477Ч480 Ordered structure 45 Organic luminophors 61 248 250Ч254 389 409Ч411 425Ч427 467 468 Originative activator 240 Oscillator damping 116 149 Oscillator strength 155 158 Oxidation, catalyzed by cupric ion 103 Oxidation, of ZnS-type phosphors 74 102 103 Pair formation and annihilation 5 6 Paired electrons 24 112 Paired spins 17 20 24 27 35 Paramagnetism 20 140 391 Parentheses, numbers in 65 364 Parker, W.L. 288 302 303 306 309 390 Particle size 63 476 Particles, elementary 2Ч11 Particles, interaction of 7 9 20 Particles, material 2 4 5Ч11 Particles, momenta of 4Ч9 Particles, properties of 7 8 9 Particles, size of 7 486 487 Particles, wave behavior of 3 4 7Ч9 14 25Ч27 Pauli, W. 16 Pauling, L. 13 27 119 191 Peak output 195 Peak value 75 Peak wavelength 137 142 Pearlman, D. 233 334 348 350 Peckham, R.H. 423 Penetration "limit" 157Ч159 Persistence 147Ч151 Persistence of vision 151 Phonons 113Ч117 123 125 126 136 137 140 142 144 Phonons, number versus temperature 142 Phosphor families 75 Phosphor notation 64Ч76 238 364 365 Phosphor particles 81Ч83 Phosphor symbolism 64Ч76 238 364 365 Phosphor-rod light source 355 356 359 360 Phosphorescence 124 148Ч151 152 246 247 251Ч312 Phosphorescence emission, maximum 368 Phosphorescence growth 261 281 Phosphorescence light sum 273 Phosphorescence mechanisms 251Ч261 269Ч271 281Ч289 Phosphorescence, duration of 278 294Ч299 366 367 Phosphorescence, efficiency of 314 315 322 323 334 335 338 339 348 350 368 384 412 413 Phosphorescence, versus crystal size 294 386 Phosphorescent materials 147Ч150 Phosphorogen 64 Phosphoroscopes 63 phosphors 48 61 64Ч80 146Ч148 363 Phosphors, constitutions of 83Ч103 Phosphors, crystallinity of 81Ч88 Phosphors, i-center 121 128 142 Phosphors, long-persistent 414 415 417 420 Phosphors, operating temperatures of 2 139 185Ч191 342Ч347 365 366 Phosphors, quenchable 309 414 415 Phosphors, s-center 121 128 142 Phosphors, stimulable 309 414 415 Phosphors, surface-active 90 Photo- versus thermostimulation 180Ч182 Photoconduction 63 120Ч130 164 258 286 288 298 302Ч304 390 391 393Ч396 471 Photoconductor 120 photoelectrons 120 317 319Ч321 421 435 Photographing phosphor emissions 465 photoluminescence 148 165Ч170 464 465 Photoluminescence efficiency 316 317 322Ч326 331Ч334 339Ч349 351 367 378 383 400 407Ч421 Photoluminescence efficiency, effect of substrate on 412 413 Photoluminescence efficiency, reference standard for 195 Photolysis 376 377 414 461 463 photometers 63 Photon 2 4Ч9 115 Photon, absorption of 4Ч7 18 19 21 154 Photon, emission of 4Ч9 18 19 21Ч23 131 149 Photon, polarization of 7 155 394Ч396 486 487 Photophosphorescence 253 254 262 264 265 272 273 295Ч297 407Ч415 Photopic eye 209 313 403 405Ч407 Photoquenching 151 181Ч183 299Ч310 Photostimulation 151 180Ч182 299Ч312 323 Photostimulation, effect of temperature on 305 Phototube sensitivities 403 406 Pigment 146Ч148 311 312 Place exchange 101 Planck's constant 4 150 Planck's radiation law 137 Plastics, luminescent 413 414 Platinocyanide radical 98 Platzwechsel 101 Plymale, W.S. 406 Podschus, E. 273 335 386 Pohl, R.W. 129 Point group 42Ч44 Poisons 125 132 177 233 309 333Ч338 364 Polarization 7 Polarization of atoms 51 91Ч93 410 Polarization of conduction cells 130 Polarization of radiation 7 155 394Ч397 486 487 Polaron 176 Positive hole 6 55 117 134 Positive hole, detection of 120 Positive hole, migration of 124Ч127 134 135 Positive hole, transfer of 134 135 Positive hole, traps for 57 121 Positive modulation 460 Positron 5 6 Potassium chloride molecule 22 26 30 485Ч487 Potential barrier 23 37 51 133 Potential well 29 57 Power-law "tail" 262Ч266 Power-law decay 169 252 254Ч257 263Ч281 285Ч312 366Ч373 Preparation of phosphors 59Ч80 214Ч217 235Ч239 Pressure, during crystallization 71 74 79 80 96 Pressure, during operation 152 Prices of phosphors 401 Print-out effect 321 Probability distribution function 4 5 14 258Ч260 283 487 Production of phosphors 401 Protective coatings for phosphors 414 419 Proton 2 6Ч11 Proximity of excitation and emission bands 377 378 Pseudoisocyanin 248 Purification procedures 71 73Ч76 473Ч476 Quanta 1 2 4 Quantum efficiency 21 316 318 354 400 405 415 420Ч422 Quantum number, angular-momentum 15Ч18 20 21 Quantum number, magnetic-moment 15 16 Quantum number, principal 14 Quantum number, spin-moment 16 Quencher 132 Quenching 148 150 299Ч310 469Ч471 Quenching by infrared 164 Quenching of photoconduction 396 R salt 410 Radar kinescopes 453Ч460 Radiance 23 150 195 209 315 Radiant flux from screens 432Ч434 Radiation 1Ч9 486 487 Radiation, coherent versus incoherent 153 Radiation, electric-dipole 109 Radiation, generation of 1 6 18 19 21Ч23 30 31 104Ч106 136Ч142 149 152 153 165Ч194 Radiation, infrared 2 483 Radiation, luminescence 1 18 19 21 22 30 31 136 482 483 Radiation, magnetic-dipole 109 Radiation, resonance 21 Radiation, retention of 432Ч434 446 447 Radiation, thermal 1 2 23 30 136 483 Radiation, ultraviolet 2 483 Radiation, visible 2 136Ч140 483 Radiationless transitions 125Ч128 132 see Radiative transitions 19 117 123Ч125 131Ч135 144Ч146 149 150 256Ч261 265Ч269 271 285 287 298 300 301 312 336 341 346 349 352 361 482 Radical 13 46 70 143 144 243 Radiescence 136 482 483 Radii of atoms and ions 13 92Ч94 Radioactive watch dials 400 462 463 Radium emanations 462 463 Radius ratio 41 91 Randall, J.T. 270 390 Rare earths 58 98 107Ч112 Raster 465 Rate, of cooling phosphors 72 73 215Ч217 237 238 280 Rate, of decay 261 Rayleigh scattering 161 rbhdl.- 421 478 479 rbhdl.- 294 299 379 414 rbhdl.- 223 224 328 365 438 rbhdl.- 286 372 464 rbhdl.- 224 rbhdl.- 48 82 87 167 168 191 221 223 227 228 230 237 242 255 256 290 294 326Ч330 345 346 359 371 400Ч402 417Ч420 428 430 438 440Ч442 445 449 450 453 460 469 478 479 rbhdl.- 286 288 291 294 299 372 414 464 rbhdl.- 192 359 401 rbhdl.- 220 221 rbhdl.- 68 81 91 109 110 185 186 188 222 228 240 255 354 364 371 381 397 rbhdl.- 110 228 rbhdl.- 107 rbhdl.- 99 118 222 226 243 402 rbhdl.- 85 rbhdl.- 223 rbhdl.- 28 85 rbhdl.- 223 245 rbhdl.- 221 222 226 rbhdl.- 340 342 rbhdl.- 340Ч342 rbhdl.- 340Ч342 rbhdl.- 340Ч342 rbhdl.- 340Ч342 rbhdl.- 110 rbhdl.- 107 rbhdl.- 222 rbhdl.- 85 87 rbhdl.- 142 167 168 221 244 291 327 345 408 411 421 463 478 479 rbhdl.- 220 222 rbhdl.- 220 221 rbhdl.- 230 rbhdl.- 299 rbhdl.- 39 48 49 85 87 88 115 rbhdl.- 48 68 72 74 76Ч81 89 90 93 101 123 128 133 139 141 142 144Ч146 152 162 163 165Ч168 170 175 185Ч187 193Ч195 216 221 223Ч233 235 236 238 240 243Ч245 255 262 263 265Ч267 269 288Ч292 294 324Ч335 337 338 345 349 350 354Ч358 360 364 367 371 378 380 381 383 385 402 417Ч421 425 426 428 430 437 438 441 447 449 450 453 461 464 465 468 478Ч480 rbhdl.- 333 rbhdl.- 254 rbhdl.- 98 202 239 240 338 364 438 441 452 rbhdl.- 39 48 51 60 68 98 99 162 165 167 220Ч224 226 237 240 243 329 Reciprocal lattice 113 recombination of electron and hole 125 Reference standards for efficiency 75 195 Reflection colors 147 206 236 237 Reflection losses 154 159 452 Reflection, of excitant 153 154 452 Reflection, selective 146 148 Refraction 93 154 155 369 Refractive index 154 369Ч374 397 Relative efficiency 315 Relaxation time 127 Reproducibility of phosphors 71Ч80 Resolution 411 423 432Ч434 448 461 462 464 Resonance 24 26Ч28 230 251 310 336 337 361 410 Resonance radiation 21 316 Resonance transfers 130 Retrapping 270 271 277 287 288 304 305 307 323 rhomb.- 68 74 167 168 239 354 364 370 378 423 424 426 450 465 466 469 rhomb.- 240 rhomb.- 222 rhomb.- 93 233 235 240 243 245 255 275 290 293 329 335 346 371 317 rhomb.- 222 rhomb.- 222 rhomb.- 232 240 245 255 371 rhomb.- 107 rhomb.- 167 228Ч230 232 233 290 293 338 rhomb.- 221 rhomb.- 240 rhomb.- 144 232 243 245 rhomb.-Chrysene, 381 Rice, F.O. 1 Riehl, N. 101 Rise time 366 429 Roentgenoluminescence 148 167 168 170 317 421Ч427 Roentgenoluminescence, efficiency 316Ч318 322 367 378 421Ч426 Ronge, F. 129 Rosenbaum, A. 256 Rotary inversion 45 46 Rotational states 29Ч31
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 :Eu
:Eu 
 :Mn
:Mn  :U
:U 
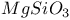 :Mn
:Mn  :U
:U  :[W]
:[W] 
 :[W]
:[W] 

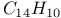

 :Mn
:Mn  :Sn:Mn
:Sn:Mn  :(Ti:Zr:Hf:Th):Mn
:(Ti:Zr:Hf:Th):Mn  :[Si]
:[Si] 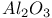 :Cr
:Cr 
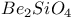
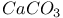 :Ce:Mn
:Ce:Mn  :Cr
:Cr 
 :[Si]
:[Si]  :Mn
:Mn  :Sn:Mn
:Sn:Mn 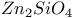
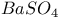 :Pb
:Pb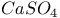 :Bi
:Bi  :Cu
:Cu  :Mn
:Mn  :Bi
:Bi  :Mn
:Mn  :Bi
:Bi  :Mn
:Mn