|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hendrik Wade Bode Ч Network Analysis and Feedback Amplifier Design |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
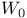 see УComputation of see УComputation of 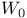 Ф Ф
 and and  loops in a feedback circuit 158 loops in a feedback circuit 158
 circuit 35 44Ч45 56 385 circuit 35 44Ч45 56 385
 equalization 283 391 equalization 283 391
 loss 457 462 477 486 511 loss 457 462 477 486 511
 and and  circuits 31Ч40 circuits 31Ч40
 circuit see УForward circuit also circuit see УForward circuit also
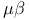 32Ч33 47 32Ч33 47
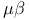 characteristic 32Ч33 512Ч513 see characteristic 32Ч33 512Ч513 see
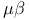 effect or error 33 effect or error 33
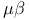 loop 32Ч42 loop 32Ч42
A and B prescribed in different frequency ranges 328Ч331
Absolute level of attenuation 287
Absolute level of gain, around a feedback loop 475 493
Absolute level of gain, in an interstage network of four terminals 431Ч440
Absolute level of gain, in an interstage network of two terminals 408 415Ч420
Absolute level of resistance 287
Absolutely stable amplifier see УStabilityФ
Absolutely stable amplifier, change from unstable to 288Ч290
Active circuit, impedance 66Ч71
Active circuit, mesh equations for an 6Ч7
Active circuit, nodal equations for an 13Ч15
Active circuit, TheveninТs theorem in an 76Ч78
Active element 246Ч248
Active element, effect of introduction upon location of zeros 117
Active impedances, combinations of 191Ч195
Active impedances, construction of 170 185 189Ч191 246Ч248
Active impedances, relation of feedback to 66Ч71
Active structures, physical 134
Active transfer impedance, representation 244Ч248
Active transmission characteristic see УExternal gain characteristicФ
Admittances, driving-point 15 24
Admittances, mutual 11
Admittances, self- 11
Admittances, transfer 15 24
Admittances, zeros and poles of 24Ч25
Adpedance 15
Affel, H.A. 499
All-pass phase correcting structures 236Ч242 247
All-pass phase correcting structures, addition of, to a transfer impedance 239
All-pass phase correcting structures, definition of 239
All-pass phase correcting structures, design parameters of 241Ч242
All-pass phase correcting structures, properties of 239Ч242
All-pass phase correcting structures, simple and anti-resonant types of 237
Alternative cut-off characteristics 471Ч476
Alternative forms of equalizing structures 270Ч272
Amplification 1 6Ч7
Amplification, representation by equivalent plate generator 1
Amplifier 7 31Ч32 35Ч37 45 48
Amplifier as a repeater 499
Amplifier with a double feed back path 499Ч502
Amplifier with band-pass transmission characteristics 502Ч509
Amplifier, absolutely stable 162Ч164 288 453
Amplifier, available feedback in band-pass 479 485
Amplifier, conditionally stable 162Ч164 289 452
Amplifier, design, applications of phase area, law in 288Ч291
Amplifier, design, single loop see УSingle loop amplifiersФ
Amplifier, feedback see УFeedback amplifierФ also УType
Amplifier, forward circuit 53
Amplifier, frequency transformations in design of 208 210Ч211
Amplifier, gain 32Ч33
Amplifier, impedance 37Ч38 73
Amplifier, lower cut-off characteristics for 509Ч517
Amplifier, non-feedback 52
Amplifier, phase and gain margins 479 497
Amplifier, regenerative 53
Amplifier, regulating broad band 509Ч529
Amplifier, stage see УInterstage networkФ
Analysis methods, mesh and nodal 13Ч17
Analytic conditions on network characteristics 278Ч280
Analytic functions 27Ч28
Analytic functions, CauchyТs theory of 137Ч151
Antenna coupling circuit for radio transmitter 360
Anti-resonant networks see УResonant or anti-resonant networksФ
Approximation of actual characteristics by straight lines 337Ч339
Arc-discharge 186
Arithmetic frequency scale, relation between phase and attenuation characteristics on 318Ч319
Armstrong frequency modulation receiver 490
Asymptote of feedback loop characteristic see УAsymptotic characteristicФ
Asymptotic characteristic 458Ч461 471 493 495Ч496
Asymptotic contributions of tubes and circuits to 476Ч477
Asymptotic crossover frequency, 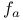 465 465
Asymptotic frequency, effective 484Ч485
Asymptotic limitation on maximum available feedback 461Ч468
Asymptotic loss of the loop 495Ч496
Asymptotic path in feedback circuit 463Ч464 496
Asymptotic slope 459Ч460 474 475 478 485 496 513 518
Asymptotic zero gain intercept 460
Attenuation 28 233 236
Attenuation characteristic for given phase 320Ч322
Attenuation integral theorem 280Ч283
Attenuation reduction 226Ч236
Attenuation units 287
Attenuation, complementary 249
Attenuation-phase charts 337
Automatic compensation for phase 310
Available characteristic, definition 105
Average dissipation, Q, in coils and condensers 219Ч223
Balancing network 500
Band width, conservation of 211Ч214 361 363 382 454 485
Band-pass equivalent 375 see
Band-pass equivalent, dissipation distribution 507
Band-pass equivalent, transmission characteristics 502Ч509
Barnes, J.L. 13
Bartlett, A.C. 268
Bierens de Haan, D. 314
Bilateral  -circuit 60 -circuit 60
Bilateral elements 10 47 54 71Ч73 78 134
Bilinear transformations 223
Black, H.S. 31
Blackman, R.B. 66 378
Blackwell, O.B. 378
Blocking condenser 404 492 510Ч511 513
Blocking-grid leak combinations 513
Bocher, M. 110
Bode, H.W. 208 326 374 376 392 451 517
Boghosian, W.H. 430 489
Boundary values of a function, relation of values in the interior to 147
Branch equations, for a passive circuit 1Ч4
Bridge circuits 243 271
Bridge-type feedback 464
Bridge-type network 56
Bridge-type network, reference feedback as a balanced 61 83Ч85 88Ч90
Bridged-T equalizer, design formulae 272Ч275
Broad-band amplifier, regulating see УRegulating broad-band amplifierФ
Brune network 233 235 247 250 253 259
Brune network, analytic inverse of 198
Brune network, to represent lattice branch impedance 254
Brune, O. 171
BruneТs method of developing a general passive impedance 171 182Ч185 190
Burrows, C.R. 482 489
Bush, V. 300
Calculus of residues 144Ч147
Campbell, G.A. 19 231 266 271
Capacity potentiometer 401 459 495 505
Capacity, interstage 177
Capacity, lumped 1
Capacity, parasitic see УParasitic capacityФ
Capacity, path at infinite frequency 177 459
Capacity, reciprocal, or stiffness 2
Capacity, resistance combinations in cathode leads 510Ч513
Carson, J.R. 19 222 300
Cathode 1 6 14
Cathode, biasing 510Ч513
Cathode, directly heated 35
Cathode, feedback circuit 39Ч41 45
Cathode, type feedback, general 86 361
Cathode, type feedback, in coaxial repeaters 388
Cathode, volume performance and external gain relations in 400
Cauchy integral 145
| CauchyТs Theorem 142 276 278 280
Chaffee, J.G. 489
Charge, electrical 2
Charge, law of conservation of 3
Charts 1Ч6, characteristics of four-element interstages 445Ч450
Charts IЧXIV, computation methods for semi-infinite constant slope characteristics of 341Ч344
Charts IЧXIV, illustrative applications of 344Ч345
Charts IЧXIV, imaginary component of complex function 346Ч359
Charts IЧXIV, summary of 339Ч341
Charts IЧXIV, use of 372 377 380 395 423
Choice between mesh and nodal analysis 15Ч17
Choice of coefficients in impedance expressions 206Ч208
Choke coils 404 510
Circuit determinant 48Ч49
Circuit loss, 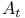 477Ч480 496 see 477Ч480 496 see
Circuits,  - 31Ч34 37Ч38 40 45Ч46 - 31Ч34 37Ч38 40 45Ч46
Circuits,  - 7 31Ч33 35 37 39Ч40 45Ч46 - 7 31Ч33 35 37 39Ч40 45Ч46
Circuits, active 1 51 66 134 170 244
Circuits, amplifying see УAmplifierФ
Circuits, bridge-type 243
Circuits, feedback see УFeedback amplifierФ also УType
Circuits, input and output see УInput and output circuitsФ
Circuits, ladder or series-shunt type 243
Circuits, passive 1Ч4 51
Circular impedance loci 223 382
Coaxial line 305 309Ч312
Coaxial system, design of repeater 360 see
Coaxial system, external gain and volume performance 388Ч392
Coefficient, coupling 5
Combination of active impedances 191Ч195
Combination of low-pass and high-pass characteristics 509
Comparison amplifier 35
Compensation theorem 80
Complementary equalizer characteristics 249Ч250 264
Complementary impedance characteristics 199Ч200
Complex branch impedance 223
Complex frequency 18 137 223
Complex frequency, driving-force 18
Complex frequency, physical validity of 28Ч30
Complex frequency, plane 22Ч24 29
Complex frequency, response measurement 29
Complex integration vs real 138Ч139
Composite equalizer structures 250Ч260
Computation of 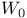 78Ч79 88Ч91 78Ч79 88Ч91
Computation of 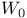 for amplifier with local feedback 95Ч97 for amplifier with local feedback 95Ч97
Computation of local feedback and sensitivity 98Ч99
Computation of phase for prescribed attenuation 337Ч345
Computation of transmission from plate to grid 91Ч95
Condenser see УCapacityФ
Conditional and unconditional stability 162Ч164
Conductance reduction see УResistance reductionФ
Conformal variation of network characteristic 224
Conjugacy 38 106 115 172
Conservation of band width 211Ч214 361 363 382 454 485
Constant impedance devices 224
Constant loop gain area condition 456
Constant resistance equalizers 283Ч285
Constant resistance filters 255
Constant resistance, image impedance 229
Constant resistance, representation of a general transfer impedance 227Ч235
Constant-k high-pass or low-pass filter 207
Constituents of general impedances 246Ч248
Construction of a general transfer impedance 230Ч235
Contour integrals in limiting cases 139Ч141
Contour integration in the complex plane 138Ч139
Contour integration of the logarithmic derivative 147Ч151
Contour integration path 143 278Ч280 296
Contour integration path, relation between integral and 141Ч144
Contour integration, formulae for network functions 277Ч280 291Ч302 305Ч307
Contour integration, general 137Ч169
Contour integration, interstage network design 377
Contour integration, relations in input and output network design 377 380Ч381
Contour integration, two theorems from function theory 167Ч169
Conversion circuit, FM to AM 490
CR product 511Ч513
Critical frequency 218
Critical frequency, displacement by parasitic dissipation 244
Critical point 154 158 452 475Ч476
Current 22
Current branch 3
Current condition, nodal 2 4
Current equilibrium 1 11
Current generator 12 14 189
Current in-phase and quadrature components 19
Current instantaneous 8
Current mesh 3 6
Current nodal 7
Cut-off characteristics, alternative 471Ч476
Cut-off characteristics, loop see УLoopФ
Cut-off characteristics, Q and element value limitations on 507
Cut-off characteristics, variable see УRegulating broad-band amplifierФ
Cut-off rate 471
Darlington, S. 171 203 217 229 370
Decade, definition 315
Decibels 33
Decino, A. 489
Decomposition of general transfer characteristic 251
Degeneration in a general feedback circuit 285Ч286
Delay distortion 310
Design formulae for bridged-T equalizers 272Ч275
Design methods for feedback structures 104Ч105 see
Determinants 24
Dickson, L.E. 110
Dietzold, R.L. 489
Differential mesh equations 109Ч110
Direct transmission 53 56Ч57 60Ч61 82
Discontinuity in one component of  or its derivative 339 or its derivative 339
Dissipation in filter design 217
Dissipation in filter design, TaylorТs series expansion 219
Dissipation, energy function 127 171
Dissipation, parasitic 216
Dissipation, parasitic, formulae for effects of 220Ч222
Dissipation, parasitic, in distortionless media 222Ч223
Distortion generator 79Ч80
Distortion generator, reduction of effects of, by feedback 45 79Ч80
Distortionless media 222
Double feedback path 499Ч502
Driving-point functions 226Ч228 231Ч232 236 263
Driving-point functions, constituents of general 246Ч248
Driving-point immittance 196 226 244Ч248
Driving-point immittance functions, representation of general 188Ч195
Driving-point impedance 8Ч9 223 244Ч248
Driving-point impedance as a function of a single element 9Ч10
Driving-point impedance, physical representation of 170Ч195
Duality between impedance and admittance analysis 13 196 227
Dynatron 186
Effective asymptotic frequency 484 485
Effective band width of feedback amplifier 453 458 470Ч471
Effects of parasitic dissipation 216Ч222
Electrical engineering staff of M.I.T. 31
Element values, range of 503
Elementary equalizer structures 251Ч253
Elementary theory of feedback circuits 31Ч35
Energy functions in a passive network 125Ч128
Energy functions in a passive network, dissipative 127
Energy functions in a passive network, positive definite 128 134
Energy functions in a passive network, relation to impedance and power to 127Ч132
Energy functions in a passive network, relation to stability 132Ч134
Energy functions in a passive network, stored 127
Envelope feedback for radio frequency transmitter 479Ч480 493Ч498
Equalizer 83 238Ч239 245 518
Equalizer design 249Ч275
Equalizer design, alternative forms of 270Ч272
Equalizer design, bridged-T 271Ч275
Equalizer design, parameters 265Ч266
Equalizer in  -circuit 492Ч493 518 -circuit 492Ч493 518
Equalizer with parasitic capacity 283Ч285
Equalizer, the line 391 518
Equilibrium, current 11
Equilibrium, voltage 10
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



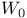
 and
and  loops in a feedback circuit
loops in a feedback circuit  and
and 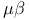
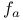
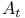
 or its derivative
or its derivative