|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hendrik Wade Bode Ч Network Analysis and Feedback Amplifier Design |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Equivalent  for four-terminal interstage 432 for four-terminal interstage 432
Equivalent low-pass amplifier 210Ч211 288 298 469
Equivalent plate generator voltage 1 7
Equivalent T-network 229 459
Even and odd symmetry 106 120
Everitt, W.L. 1
Excess gain and phase margin computation and allocation 523Ч526
Excess phase frequency, 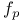 484 484
Excess phase in feedback loop 480
Excess phase margins 485
Excess phase, causes of 481Ч484
Excess phase, compensation for 484 486
Excess phase, maximum available feedback with 484Ч485
Exponential representation of physical sinusoids 19Ч22
External gain 35 86 290
External gain with feedback 80Ч81 86Ч87
External gain, characteristic 45 389Ч392 401
External gain, definition 387
External gain, requirement 463
External gain, voltage 389
Extraction of poles of driving-point impedance 175Ч176
Feedback 31Ч43 see
Feedback amplifier 31
Feedback amplifier, backward circuit see У -circuitФ -circuitФ
Feedback amplifier, characteristic, active admittance 386
Feedback amplifier, characteristic, external gain 387
Feedback amplifier, characteristic, loop transmission 44 47 386 389
Feedback amplifier, characteristic, volume performance 387 389
Feedback amplifier, design 305
Feedback amplifier, design, single loop see УSingle loop amplifiersФ
Feedback amplifier, forward or  -circuit see УForward circuitФ -circuit see УForward circuitФ
Feedback amplifier, gain 245Ч246
Feedback amplifier, gain, input and output circuits 56
Feedback amplifier, gain, mathematical definition 44
Feedback amplifier, gain, reduction factor 44 46Ч47
Feedback amplifier, gain, representation of negative structure by 246
Feedback amplifier, gain, transconductance of tubes in 156Ч162
Feedback circuits, elementary theory of 31Ч35
Feedback circuits, general theorems for 66Ч102
Feedback circuits, ideal 60Ч61
Feedback circuits, regeneration and degeneration in general 285Ч286
Feedback circuits, types of see УType of feedback circuitФ
Feedback factor 32
Feedback for bilateral elements 71Ч73
Feedback for two elements 75Ч76
Feedback impedance 67Ч68 387 389 519
Feedback in band 457Ч458 474
Feedback limiting circuit 456
Feedback paths 45 60Ч61
Feedback, effect of, on input and output impedances of amplifiers 73Ч75
Feedback, envelope or voice-frequency 479Ч480 493Ч498 504
Feedback, external gain with 80Ч81 86Ч87
Feedback, individual 49
Feedback, loop asymptote 458Ч459
Feedback, loop asymptote, capacity potentiometer 459
Feedback, loop asymptote, characteristic see УLoop cut-off characteristicФ
Feedback, loop asymptote, excess phase 480
Feedback, loop asymptote, principal and subsidiary 158 489
Feedback, maximum available see УMaximum available feedbackФ
Feedback, radio frequency 584
Feedback, reduction of distortion by 79Ч80
Feedback, reference, as a balanced bridge 83Ч84
Feedback, relation to stability 44
Feedback, residual 89
Figure of frequency 477Ч480 496
Figure of merit 457 477 485 518
Filter see УWave filterФ
Final gain characteristic 33Ч34
Finite line segments in attenuation-phase computations 338
Flat loop gain in useful band 455Ч456 486
Flat loop gain, advantage at edge of band of 455
Formulae for networks of lumped electrical elements extended to other systems 298Ч301
Formulae for physical network characteristics at real frequencies 291Ч302
Formulae involving A and B at finite points 296Ч298
Formulae involving coefficients of higher order terms in power series 291Ч293
Formulae involving integral of A and B over finite ranges 296Ч298
Formulae involving products of functions 293Ч294
Formulae involving products of functions with reversed symmetry 295Ч296
Formulae, tabulation of 301Ч302
Forward circuit 44Ч45 55 see
Forward circuit design 523
Forward circuit gain 45 490 492 499 501
Forward circuit impedance 519
Foster, R.M. 10 177 198 271
Four-terminal interstage network 427Ч431
Four-terminal interstage network of maximum constant gain 440Ч444
Four-terminal interstage network of symmetrical configuration 438
Four-terminal interstage network with ideal transformers 429
Four-terminal interstage network with restricted phase shift 433Ч435
Four-terminal interstage network, equivalent circuits 431Ч433 440 444
Four-terminal interstage network, filter types of 407 428Ч431
Four-terminal interstage network, gain, general limitations on 435Ч440
Four-terminal interstage network, positive and negative resistance integral relations in 434
Four-terminal interstage network, relation to two-terminal interstage 440 442
Four-terminal interstage network, separation of plate and grid capacities 428
Four-terminal network 31 228 236 see
Four-terminal network, parameters 201
Four-terminal network, representation by simple structures in tandem 201
Fractionated gain 81 87 386Ч387
Free oscillations 107
Frequency modulation receiver 489Ч493
Frequency transformations 196 208Ч210 218
Frequency transformations for dissipation 214Ч216
Frequency transformations for dissipation, parasitic 216Ч222
Frequency transformations for filters 210Ч211 214
Frequency transformations for networks of two kinds of elements 214Ч215
Frequency transformations in amplifier, design 210Ч211
Frequency, asymptotic crossover 465
Frequency, complex 23 28Ч30
Frequency, definition 22
Frequency, effective asymptotic 484
Frequency, figure of merit 477
Frequency, horizontal step 465Ч467
Frequency, ideal cut-off 455
Frequency, negative 24
Frequency, plane 24
Frequency, real 23
Frequency, transit time 484
Fry, T.C. 19
Gain 52Ч53 see
Gain area redistribution 407
Gain before feedback 81Ч82
Gain characteristics 498 ff
Gain characteristics of simple interstages 426Ч427
Gain in interstage 403Ч440
Gain in interstage,  -circuit 283Ч284 -circuit 283Ч284
Gain in interstage, local feedback circuit 284
Gain with 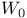 reference 88Ч97 reference 88Ч97
Gain, external, with feedback 32Ч33 80Ч82 87
Gain, fractionated 81
Gain, margin 453 466Ч467 479 492 495Ч496 505 523Ч529
Gain, reduction rate 454
Gardner, M.F. 13
Generator with zero or infinite internal impedance 12
Generator, current 12 14
Generator, equivalent cathode 6
Generator, equivalent plate 1 6Ч7 15
Generator, voltage 2 5
Generator, voltage, equivalent plate 6Ч7
Gewertz, C.M. 229 437
Goursat Ч Hedrick 137 300
Graphical computation of relations between real and imaginary components of network functions 337Ч345
grid 1 6 13
Grid-cathode impedance 6Ч7 284 457 see
Grid-leak combinations 510Ч511 514Ч516
Grid-plate coupling capacities 7 42 46 95 505
Guillemin, E.A. 1 13 83 197 231 326 373
Heaviside, O. 19
High frequency path see УAsymptotic characteristicФ
Horizontal step for excess phase 484 485 507
| Horizontal step for ideal phase 465
Horizontal step in loop cut-off characteristic 471 505 513
Horizontal step with gain and phase margins 468
Hunting 43
Hybrid coil circuits 464
Hybrid coil feedback, high side 464
Hybrid coil feedback, low side 464 499
Ideal flat gain amplifier 244Ч245
Ideal non-dissipative transmission line 222
Ideal transformer 25 230Ч233
Ideal transformer for phase reversal 456
Ideal transformer in input and output circuits 363
Ideal transformer in interstage circuits 429 432
Ideal transmission characteristics 222
Image parameters 229
Imaginary component charts see УCharts IЧXIVФ
Immittance 15 see also
Impedance 8Ч9
Impedance coefficient, general 24...
Impedance expressions, choice of coefficients in 206Ч208
Impedance generator 7
Impedance level 388
Impedance measurements to determine feedback 75
Impedance of C for the given band width 363 372
Impedance with addition of active elements 66
Impedance with feedback 66Ч69
Impedance, active 66Ч71
Impedance, bilateral 9
Impedance, complex 22Ч24
Impedance, complex, self- and transfer 22
Impedance, coupling 4
Impedance, driving-point see УDriving-point impedanceФ
Impedance, energy relations at real frequencies 128-131
Impedance, general, partial fraction expansion of a 200Ч203
Impedance, grid 7
Impedance, input, of an ordinary feedback amplifier 66
Impedance, mutual or coupling 4
Impedance, mutual, between two meshes 11
Impedance, passive 51 56
Impedance, reconstruction of a, from aknowledge of either component 203
Impedance, self-, of a mesh 4
Impedance, transfer see УTransfer impedanceФ
Impedance, transimpedance or mutual, of a tube 6Ч7
Impedance, values at infinite frequency 298
Impedance, zeros and poles of 24Ч25
Index of stability 158
Indicial admittance 299Ч300
Inductance 5 13
Inductance, coupling 3
Inductance, distributed 1
Inductance, lumped 1
Inductance, mutual 3
Inductance, reciprocal 13
Input and output amplifier impedances with feedback 73Ч75
Input and output circuit design 372Ч378 383Ч388 392Ч402
Input and output circuit theorems 368Ч371
Input and output circuit, applications of general theorems to 360Ч402
Input and output circuit, impedance match with filter, ladder structure, or resistance-reactance combination 373Ч376
Input and output circuits 360Ч402 462Ч463 469 486
Input and output circuits and resistance 363Ч368
Input and output circuits for series feedback amplifier 392Ч399
Input and output circuits with varying gain characteristic 518
Input and output circuits, contribution of, to final gain 387
Input and output circuits, equivalent ideal transformer for 363
Input and output circuits, external gain characteristic of 387
Input and output circuits, filters as ideal designs for 369
Input and output circuits, illustrative reflection coefficient design of 378Ч383
Input and output circuits, reconstruction of the imaginary component as an aid to the design of 372Ч378
Input and output circuits, reflection coefficient theorem for 364
Input and output circuits, terminated in capacity 361Ч363
Input and output circuits, volume performance in 387 389
Input and output circuitsnumber of elements in the design of 370
Input or output transformer 360Ч362 463
Instability see УStabilityФ
Integration around a circle 141
Integration around a square 143
Integration in the complex plane 138 ff
Integration of 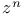 141 141
Integration of 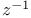 140 140
Integration over very small or large paths 139Ч140
Interstage capacities 213 419 436 462 495 518
Interstage circuit see УInterstage networkФ
Interstage circuit gain 458 498
Interstage circuit impedance 32 47 511
Interstage network 48 230 469 486 see also
Interstage network design, application of general theorems to 403Ч444
Interstage network design, technique 377
Interstage network in a non-feedback video amplifier 305
Interstage phase 488
Introduction of surplus factors 258Ч260
Inverse network for active impedance 199
Inverse network for Wheatstone bridge 197
Inverse network relationship 231 233 241
Inverse network structures 13 see
Inverse network, analytic 198
Inverse network, definition 196
Inverse network, structural 197Ч198
Iterative parameters 229
Johnson, K.S. 122
Kendall, B.W. 499
Knopp, K. 441
Kreer, J.G. 151 489
Kva rating 182Ч185 382
Ladder circuits 243 326
Lattice network equalizer circuits 270Ч271
Lattice network equivalents 266Ч270
Lattice network filters 326
Lattice network for four-terminal interstages 440
Lattice network with ideal transformer 231
Lattice network, all-pass 237
Lattice network, bridged-T equivalent of 271
Lattice network, construction of branch impedances in 231Ч233
Lattice network, conversion to bridged-T 444
Lattice network, interchange of branches in 237
Lattice network, representation of transfer impedance by 230Ч235
Lattice network, symmetrical 231Ч233
Leakage inductance of hybrid coils 500
Leakage inductance of transformer 374Ч375 464
Lee, Y.W. 242 303
Linear phase shift systems, in general 322Ч327
Linear phase shift with prescribed discrimination 331Ч334
Linear phase shift with vestigial side-band 333
Linear phase shift, in useful range 310
LiouvilleТs theorem 200
Llewellyn, F.B. 158
Local feedback 41Ч42
Local feedback, cathode circuit 451
Local feedback, computation 95Ч99
Local feedback, parasitic capacity 283Ч285 291 451
Local feedback, paths 43 482 512
Local feedback, properties 99Ч102
Logarithmic derivative, integral of 147
Logarithmic frequency scale 287 338 344
Loop characteristic see УLoop cut-off characteristicsФ
Loop cut-off characteristics with maximum obtainable feedback 464Ч468
Loop cut-off characteristics with multiple  paths 452 paths 452
Loop cut-off characteristics, alternative high frequency 471Ч476
Loop cut-off characteristics, asymptotic 458Ч464
Loop cut-off characteristics, basic 410
Loop cut-off characteristics, contribution of tubes and circuits to 476Ч477
Loop cut-off characteristics, corrected vs uncorrected 468Ч471
Loop cut-off characteristics, cut-off interval in 453
Loop cut-off characteristics, excess phase compensation in 480Ч486
Loop cut-off characteristics, frequency ratios for ideal phase corresponding to 465 468 484
Loop cut-off characteristics, general design procedure for simulating 486Ч488
Loop cut-off characteristics, horizontal step 465
Loop cut-off characteristics, ideal 454Ч458 470Ч471 475 491Ч492 505 507
Loop cut-off characteristics, margins for 453
Loop cut-off characteristics, variable 456
Loop dimensions 481
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 for four-terminal interstage
for four-terminal interstage 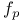
 -circuitФ
-circuitФ -circuit
-circuit 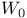 reference
reference