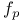|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Hendrik Wade Bode Ч Network Analysis and Feedback Amplifier Design |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Regenerative amplifiers 53
Regulating broad-band amplifier 509Ч529
Regulating broad-band amplifier, high frequency characteristic for 517Ч529
Regulating broad-band amplifier, lower cut-off characteristic for 509Ч517 see
Regulator circuits for speed, voltage or frequency control 43
Regulator circuits, to compensate for temperature and repeater spacing irregularities 518Ч519 523
Relations between real and imaginary components of network functions 303Ч336
Relations between real and imaginary components of network functions, applications of formulae for 304Ч305
Relations between real and imaginary components of network functions, graphical computation of 337Ч345
Relations between real and imaginary components of network functions, tabulation of 335Ч336
Relative importance of tubes and circuit in limiting feedback 476Ч477
Relative sensitivity 62Ч63 66 73
Relative sensitivity in multiple loop circuits 83
Relative sensitivity, ratio of return difference to 84Ч86
Representation of impedance functions see УPhysical representationФ
Residual attenuation distortion with linear minimum phase shift characteristic 322Ч327
Residue of a function at a pole 145 296 305
Resistance and reacrance for minimum resistance and reactance networks 205Ч206
Resistance and reacrance, relation between 204
Resistance efficiency, definition 376
Resistance efficiency, reduction for transition region 377
Resistance integral condition 362 394Ч396 431Ч435
Resistance integral condition for four-terminal interstage gain 435Ч436 438 440
Resistance integral condition theorem 280Ч283
Resistance reduction of passive impedances 170Ч173 226 236
Resistance reduction theorem 172
Resistance reduction, extension to active impedances 189
Resistance reduction, for plate or grid-leak-conductance in interstage design 173
Resistance, minimum 172
Resistance, negative 185Ч188
Resistance, terminating 227
Resonant and anti-resonant networks 174 178 183 495
Resonant and anti-resonant networks, Q and element value limitations in 503
Resonant circuit, the single 18Ч19
Return difference and impedance 68Ч69
Return difference and impedance measurements 75
Return difference and impedance sensitivity 47Ч48 54Ч60
Return difference and impedance, relative 84Ч86
Return difference for bilateral elements 50Ч52 71
Return difference for open- or short-circuited elements 7 69
Return difference for reference k 49Ч50 66 186
Return difference for two elements 75Ч78
Return difference for zero reference 50 66 186
Return difference, definition 47Ч49
Return difference, plot 151Ч153
Return loss in reflection coefficient theory 365Ч367
Return ratio 47Ч48 65 186
Return ratio for bilateral elements 50 71
Return ratio for reference value k 51 95
Return ratio for zero reference 48
Return ratio, definition 48Ч49
Return ratio, plot 154Ч156 160Ч163 476
Return voltage 48
Return voltage and tube variations 46Ч47
Return voltage difference see УReturn differenceФ
Riemann surface 297
Roots of  , and , and 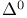 109Ч113 134 152 157 164 109Ч113 134 152 157 164
Scott, R.F. and Matthews, G.B. 54
Screen-grid type tube 1 16 361 384
Self-admittance of a node 11
Self-biasing units in a cathode 510Ч513
Self-immittance 48
Self-impedance 11 48
Semi-infinite constant slope characteristic 338 341Ч344
Semicircular integration path 143Ч144 365Ч367
Sensitivity 47Ч48 52Ч60 63 71 84Ч86
Sensitivity, definition 47
Sensitivity, general formula for 53Ч54
Sensitivity, relation of, to return difference 54Ч60
Sensitivity, relative see УRelative sensitivityФ
Series feedback amplifier 86 463 485Ч486 517Ч529
Series feedback amplifier in coaxial repeaters 361 388
Series feedback amplifier, impedance of 73
Shaw, R.C. 485
Shea, T.E. 1 78 80 83
Short-circuit stable networks 19 189Ч191 203 206 227 279
Shot effect 35
Shunt feedback amplifier 86 459 462
Shunt feedback amplifier, impedance of 73
Signal-to-noise ratio 34 384 386Ч387 390 393 490
Signal-to-noise ratio, relation of modulation and signal level to 390
Signal-to-noise ratio, volume performance and signal level to 391
Simulation of resistance characteristic by ladder line 376
Singing see УStabilityФ
Single loop amplifiers, absolutely stable 288 451Ч487 489 see
Single loop amplifiers, definition of 451
Single loop amplifiers, illustrative feedback designs for 489Ч529
Singularities 27Ч28 144 147 152
Singularities at infinity 301
Singularities, branch point 279 300Ч301
Singularities, essential 300
Singularities, logarithmic 28 278Ч279 300
Six-terminal network 35
Sources, current and voltage 13
Sources, energizing 10 190
Stability 44 49 154 226 245Ч246 486
Stability and physical realizability 103Ч136
Stability and the roots of  109Ч111 109Ч111
Stability of passive networks 132Ч134
Stability, correction of loop characteristics to produce 470
Stability, effect of changes in tube gain on 453
Stability, effect of excess phase on 386
Stability, index of 158
Stability, limitations on network functions resulting from requirements for 103Ч136
Stability, limiting gain and phase margin for 453
Stability, relation of, to singing 107
Stability, relation of, to steady-state characteristics 109Ч110
Stability, relation of, to transients 107
Stability, relation of, to zero impedance or return difference 69
Stability, requirements derived from the energy functions 132Ч134
Stability, requirements on the roots of  109Ч110 137 109Ч110 137
Stability, type of, absolute or unconditional 162Ч164 288 453
Stability, type of, conditional or Nyquist 162Ч164 289 452
Stability, type of, open- or short-circuit 189
Stable amplifier circuits 419 475 see
Stage gain and phase 403
Stages of an amplifier, increase in the number of 496 see
Staggered grid circuit designs 515
Starr, A.T. 271
Steady-state characteristics 300
Steady-state characteristics, relation of stability to 109Ч110
Steady-state solution for the-mesh equations 7 18
Step-type cut-off 465 476 see
Stiffness 5
Stored energy functions T and V 127 171 216
Straight-line approximation method 337Ч339
Strieby, M.E. 285 309
Subsidiary feedback path 158 489
Superposition theorem 1
Superposition, principle of 20
Surplus factors in equalizer expansions 258Ч260
Susceptance reduction 173Ч177 234 see
Symmetrical interstage networks 438Ч440
Symmetrical lattice network see УLattice networkФ
Symmetrical minors 113
Symmetrical minors, roots of 116
Symmetrical minors, upper cut-off characteristic 517
Synthesis vs analysis of networks for feedback amplifiers 103
T and  networks 268Ч269 networks 268Ч269
T-plot 154Ч156 160Ч163 476
Tandem configurations 229 237 251
Television transmission 309
Terman, F.E. 1 31Ч32 78 80 83 326 373
Thermal agitation 35
TheveninТs theorem 11 387Ч389
TheveninТs theorem in active circuits 76Ч78
TheveninТs theorem, generalized 78 80
Townsend, E.J. 137
Transconductance 14 47Ч48 156 186 385 387 403 451 457 459 477 483 495 518
Transconductance product 451
| Transfer constant 230Ч233
Transfer impedance as a function of a single element 9Ч10 223
Transfer impedance as a passive network parameter 227Ч230
Transfer impedance in terms of external impedance measurements 266Ч268 432
Transfer impedance, active 244Ч246
Transfer impedance, all-pass 239Ч242
Transfer impedance, choice of parameters in 265Ч266
Transfer impedance, complementary characteristic for a general 249
Transfer impedance, constituents of a general 246Ч248 252Ч253 260
Transfer impedance, construction of a general 230Ч233
Transfer impedance, driving-point and 8Ч9 24
Transfer impedance, loss and phase reduction of 236Ч238
Transfer impedance, minimum phase shift 238 242Ч244
Transfer impedance, partial product expansion of a 250Ч258
Transfer impedance, reconstruction of a, from a knowledge of either component 261Ч263
Transfer impedance, representation by lattices 258Ч259
Transfer impedance, surplus factors in 258Ч260
Transformations from low-pass to band-pass interstages 418
Transformations, frequency see УFrequency transformationsФ
Transformer as interstage network 427Ч428
Transformer characteristic 36
Transformer for crossing terminals 40
Transformer with lattice and bridge circuits 271
Transformer, equivalent T 183
Transformer, potentiometer terms 389Ч390 519
Transformer, tuned 369
Transients 30 107 110
Transimpedance 6 7 48 see
Transit time 1 457 481 485
Transit time frequency, 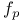 485 485
transmission line 222Ч223 298Ч299
Transmission, definition 77
Trap circuit 290Ч291 420Ч421 497Ч498 507Ч509
Tube see УVacuum tubeФ
Two-terminal impedance of Brune type 182Ч185
Two-terminal interstage of specified phase margin 418Ч425
Two-terminal interstage with maximum constant gain 406 408Ч415
Two-terminal interstage with variable gain 415Ч417
Two-terminal interstage, band-pass 418
Two-terminal interstage, gain 403Ч406
Two-terminal interstage, general theorems on 403Ч407
Two-terminal interstage, ideal 411Ч412
Two-terminal interstage, simple types of 425Ч427
Two-terminal network see УDriving-point impedanceФ
Type J open-wire carrier telephone system 499Ч502
Type of feedback circuits, balanced bridge 37Ч38 73 85 464
Type of feedback circuits, cathode 39Ч40 86 361 400
Type of feedback circuits, double loop 56
Type of feedback circuits, general 35Ч39
Type of feedback circuits, hybrid coil, high and low side 38 464 499
Type of feedback circuits, local 41 95Ч101
Type of feedback circuits, local, series and shunt 42
Type of feedback circuits, multiple loop 42 45
Type of feedback circuits, series 36Ч37 39Ч41 73 86 361 463 485Ч486
Type of feedback circuits, shunt 36Ч37 39 73 86 504
Type of feedback circuits, single loop 41 46Ч47 55 61 86 451Ч487
Unfolded loop 505
Uniform dissipation, definition 216
Uniform dissipation, frequency transformation for 217
Unilateral element see УVacuum tubeФ
Unit amplitude, definition 131
Unit slope, definition 315
Unsymmetrical minors 113
Unsymmetrical minors, roots of 116
Vacuum tube 1 6Ч7 13Ч14 31Ч81 186 451 462 494
Vacuum tube, amplification 6
Vacuum tube, currents and voltages 6Ч7
Vacuum tube, distortion 79Ч80
Vacuum tube, elements 6
Vacuum tube, figure-of-merit 477
Vacuum tube, grid-plate coupling 7
Vacuum tube, impedances 6Ч7
Vacuum tube, linear or non-linear 43
Vacuum tube, mutual impedance 6 67
Vacuum tube, parasitic capacities see УParasitic capacityФ
Vacuum tube, phase reversal 7 48
Vacuum tube, plate generator, apparent or equivalent 6
Vacuum tube, reference value 78Ч79
Vacuum tube, return difference 77
Vacuum tube, transconductance see УTransconductanceФ
Vacuum tube, transimmittance 48Ч49 56
Vacuum tube, transimpedance 6Ч7
Vacuum tube, variations in gain, return voltage as index of effect of 46Ч47
Vacuum tubes in tandem 7 31Ч81
Vacuum tubes working into their own parasitic capacities 457Ч458 477
Vacuum tubes, optimum number of 478Ч480
Vacuum tubes, to furnish negative resistances 187
Variable cut-off characteristic, mean and extreme values of 520Ч521
Variable cut-off characteristic, required changes in loss and phase margins of 519Ч520
Variable cut-off characteristic, simulation by circuit with regulator 527Ч529 see
Variable cut-off characteristic, theoretical 519Ч521
Variable loop gain in the useful band 456
Variable phase margin over cut-off region 456
Variations in a network characteristic produced by changes in a single element 223Ч225
Video amplifier interstage 326
Voice-frequency band 43
Voltage equations, branch 4
Voltage equilibrium 4 10
Voltage equivalent plate generator 7
Voltage generator of zero internal impedance 188Ч189
Voltage of frequency f 22
Voltage source 1 10 13 190
Voltage, complex, exponential or sinusoidal 8Ч9 18Ч23 29Ч30
Voltage, driving 4Ч10 29
Voltage, input and output 31 34
Voltage, instantaneous 8
Voltage, node 2Ч3
Voltage, steady-state 15 30
Volume limiter 490
Volume performance 387Ч392 399Ч401 486
Volume performance in illustrative design 392
Volume performance per repeater link 392
Volume performance requirement 391Ч392
Volume performance vs external gain 396 399
Volume performance, characteristics, definition 387
Volume performance, compromise between feedback and 390 463
Ware, L.A. 151
Wave filter 1
Wave filter for input and output circuits 369 372Ч378
Wave filter for interstage networks 417
Wave filter, dissipative 217
Wave filter, image impedance 326
Wave filter, representation by lattices 234Ч235
Wave filter, simple circuits approximating the impedance of a 312Ч315
Webster, A.G. 126
Weighting factor for computing phase 313
Wentz, J.F. 285 309
West, J.M. 392 489
Wheatstone bridge, inverse network for 197
Wheatstone bridge, unfolded lattice as a 231 243
Wheeler, H.A. 408 428
Whittaker, E.T. 126
Wiener, N. 242 303
Zero gain intercept of asymptote 460
Zero reacrance or phase characteristic 294
Zero reference for an element 48Ч49
Zeros and poles in equalizer design 249Ч262
Zeros and poles in general physical network characteristics 105Ч106 111 120Ч123 134 276Ч277
Zeros and poles in phase reduction 365
Zeros and poles in pure reactances 215
Zeros and poles in transfer impedance functions 230Ч240
Zeros and poles of impedance and admittance 24Ч28
Zeros and poles of resonant circuit impedance 26Ч27
Zeros and poles on real frequency axis 105 111Ч113 171Ч178
Zeros and poles, interchange of 196
Zeros and poles, location of, on complex plane 105
Zeros and poles, translation of, for parasitic dissipation 217Ч218
Zeros for stable networks 134
Zeros in an illustrative circuit 115Ч120
Zeros of  on real frequency axis 111Ч113 on real frequency axis 111Ч113
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 , and
, and 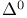
 networks
networks