|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Petrie A., Sabin C. — Medical Statistics at a Glance |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
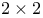 table 61 62—63 table 61 62—63
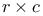 contingency table 64 65—66 contingency table 64 65—66
 67 69 67 69
 (alpha) 44 (alpha) 44
 (beta) 44 (beta) 44
+/- symbol 87
a priori probability 20 109
Addition rule 20
Adjusted 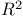 76 76
Agreement assessing 93—95
Agreement, limits of 93-94
All subsets model selection 80
Allocation, bias 31 34
Allocation, random see “Randomization”
Allocation, systematic 34
Allocation, treatment 34
Alternative hypothesis 42
Altman's nomogram 84 85—86 119
Analysis of covariance 75
Analysis of variance, F-ratio 55 57 72
Analysis of variance, Kruskal — Wallistest 56 57
Analysis of variance, non-parametric 56 57
Analysis of variance, one-way 55—57
Analysis of variance, repeated measures 101-102
Analysis of variance, table 71 76 121 125
anova see “Analysis of variance”
Area under the curve (AUC) 101 102 103
Arithmetic mean 16 (see also “Mean”)
ASCII format 10
Assessment bias 31 34
Association in contingency table 64 65—66
Association in correlation 67
Assumptions, checking 82—83
Autocorrelation 105
Autocorrelation coefficient of lag k 105
Autocorrelation function, partial 105
Automatic selection procedures 80
Autoregressive models 105
Average 16—17
Backwards selection 80
Bar chart 14 15
Bartlett's test 56 82
Bayes theorem 109
Bayesian methods 109—111
Bias 31 93 96
Bimodal distribution 14
Binary (dichotomous) variables 8
Binary (dichotomous) variables in logistic regression 78
Binary (dichotomous) variables in meta-analysis 98
Binary (dichotomous) variables in multiple regression 75
Binary (dichotomous) variables, dependent 80
Binary (dichotomous) variables, explanatory 80
Binomial distribution 23 58
Binomial distribution, normal approximation of 23 58
Blinding 34 96
Blocked randomization 34
Blocking 32
Bonferroni correction 45
Box (box-and-whisker) plot 14 18 82 121
British Standards Institution repeatability coefficient 93 95
Carry-over effects 32
Case-control studies 31 40—41
Case-control studies matched 40 41
Case-control studies unmatched 40—41
cases 40
Cases incident 40
Cases prevalent 40
Categorical data (variables) 8
Categorical data, assessing agreement of 93 94
Categorical data, coding 10 11
Categorical data, error checking 12
Categorical data, graphical display of 14
Categorical data, more than two categories 64—66
Categorical data, multiple regression with 75
Causality in observational studies 30
Censored data 9 106
Censored data, left- 106
Censored data, right- 106
Central limit theorem 26
Chi-squared (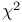 ) distribution 22 112 113 ) distribution 22 112 113
Chi-squared (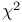 ) test for covariates (model Chi-square) 79 ) test for covariates (model Chi-square) 79
Chi-squared (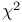 ) test for trend in proportions 66—65 66 ) test for trend in proportions 66—65 66
Chi-squared (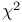 ) test for two proportions, independent data 61 62—63 ) test for two proportions, independent data 61 62—63
Chi-squared (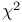 ) test for two proportions, paired data 62 63 ) test for two proportions, paired data 62 63
Chi-squared (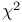 ) test in ) test in 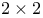 table 61 62—63 table 61 62—63
Chi-squared (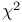 ) test in ) test in 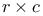 table 64 65—66 table 64 65—66
CI see “Confidence intervals”
Classification table 79
Clinical practice, applying results 97
Clinical trials 34—35 36
Clinical trials, avoiding bias in 34
Clinical trials, blinding in 34
Clinical trials, critical appraisal 96
Clinical trials, cross over designs in 32 33
Clinical trials, endpoints 34
Clinical trials, ethical issues 35
Clinical trials, intention-to-treat analysis 35
Clinical trials, on-treatment analysis 35
Clinical trials, parallel designs in 32 33
Clinical trials, phase I/II/III 34
Clinical trials, placebos in 34
Clinical trials, profile 36
Clinical trials, protocol 35
Clinical trials, size of 35 84—86
Cluster randomization 34
Clustered column (bar) chart 14
Cochrane Collaboration 98
Coding data 10 11
Coding missing values 11
Coefficient logistic regression 78
Coefficient of variation 19
Coefficient partial regression 75 76
Coefficient regression 70
Coefficient repeatability/reproducibility 93 95
Cohen's kappa ( ) 93 94 ) 93 94
Cohort studies 31
Cohort studies, dynamic 37
Cohort studies, fixed 37
Cohort studies, historical 37
Collinearity 76
Column (bar) chart 14 15
Complete randomized design 32
Conditional probability 20 109
Confidence intervals (CI) 28—29 87
Confidence intervals (CI) 95% 28
Confidence intervals (CI) for correlation coefficient 68 69
Confidence intervals (CI) for difference in two means 52
Confidence intervals (CI) for difference in two medians 53
Confidence intervals (CI) for difference in two proportions independent groups 61 62
Confidence intervals (CI) for difference in two proportions paired groups 62 63
Confidence intervals (CI) for mean 28 29 46
Confidence intervals (CI) for mean difference 49—50 51
Confidence intervals (CI) for median 47 112 115
Confidence intervals (CI) for median difference 49 50—51
Confidence intervals (CI) for odds ratio 41
Confidence intervals (CI) for predictive values 91
Confidence intervals (CI) for proportion 28 29 58
Confidence intervals (CI) for regression coefficient 73
Confidence intervals (CI) for relative risk 38 39
Confidence intervals (CI) for slope of regression line 73 74
Confidence intervals (CI) in meta-analysis 98—99 100
Confidence intervals (CI) vs hypothesis tests 43
Confidence intervals (CI), interpretation of 28—29 46 52 96
Confidence intervals (CI), multipliers for calculation of 112 113
Confidence intervals (CI), power and 44
Confidence limits 28
Confounding 31
Consent, informed 35
CONSORT statement 35 36
Contingency tables 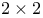 61 62—63 61 62—63
| Contingency tables rxc 64 65—66
Contingency tables, ordered categones in 65
Continuity correction 47 58
Continuous numerical data 8 14
Continuous probability distributions 20—21 22—23
Continuous time series 104
Control group 31
Controls 31 34 96
Controls in case-control studies 40
Controls, positive/negative 34
Correlation 67—69
Correlation coefficient assumptions 67
Correlation coefficient, confidence interval for 68 69
Correlation coefficient, hypothesis test of 68 69
Correlation coefficient, misuse of 67
Correlation coefficient, non-parametric 68
Correlation coefficient, Pearson 67—68 69 113 117 124
Correlation coefficient, Spearman's rank 68 69 113 117 124
Correlation coefficient, square of 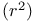 71 72 73—74 71 72 73—74
Correlation, auto- 105
Correlation, linear 67—68
Correlation, serial 104 105
Correlogram 105
Counts 23
Covariance, analysis of 75
Covariate 75
Cox proportional hazards regression model 107 108
Critical appraisal 96
Cross-over designs 32 33
Cross-sectional studies 30—31
Cross-sectional studies, repeated 30 31
Cut-off values 91 92
Cyclic variation 104 105
DATA 8—9
Data, censored 9 106
Data, coding 10 11
Data, derived 9
Data, describing 16—19
Data, entry 10—11
Data, error checking 12 13
Data, graphical display of 14—15
Data, missing 11 12
Data, presentation 87—89
Data, transformations 24—25
Data, types 8—9
Dates, checking 12
Dates, entering 10—11
Deciles 18
Degrees of freedom (df) 22 29
Delimiter 10
Dependent (outcome, response) variables 70
Dependent (outcome, response) variables, binary 80
Dependent (outcome, response) variables, numerical 80
Describing data 16—19
Design, study 30—33
Design, study, cross-over 32 33
Design, study, factorial 32—33
Design, study, parallel 32 33
Design, study, randomized 32
df (degrees of freedom) 22 29
Diagnostic tests 90—92
Diagnostic tests in Bayesian framework 109—111
Diagrams 87
Dichotomous variables see “Binary variables”
Discrete numerical data 8 14
Discrete time series 104
Discriminant analysis 80—81
Distribution-free tests see “Non parametric tests”
Distributions, bimodal 14
Distributions, continuous 20—21 22—23
Distributions, discrete 20 23
Distributions, empirical 14 20
Distributions, frequency 14 20
Distributions, probability 20
Distributions, sampling 26—27
Distributions, skewed 14 15
Distributions, symmetrical 14 16
Distributions, theoretical 20—23
Distributions, unimodal 14
Dot plot 14 15
Double-blind trial 34
Dummy variables 75
Duncan's test 55
Effect (of interest) 44 87
Effect (of interest) in meta-analysis 98
Effect (of interest) in sample size calculation 84
Effect (of interest), importance of 96
Effect (of interest), power of test and 44
Efficacy, treatment 34
Empirical frequency distributions 14 20
Endpoints 34
Endpoints primary 34
Endpoints secondary 34
Epidemiological studies 30
Errors checking 12 13
Errors in hypothesis testing 44—45
Errors residual (unexplained variation) 55 71
Errors typing 12
Ethical committee 35
Evidence-based medicine (EBM) 96—97 98
Exclusion criteria 35
Expected frequencies 61 63 64 66
Experimental studies 30 31
Experimental units 32
Explanatory (independent, predictor) variables 70
Explanatory (independent, predictor) variables in logistic regression 78
Explanatory (independent, predictor) variables in multiple regression 75—76
Explanatory (independent, predictor) variables, categorical 75
Explanatory (independent, predictor) variables, numerical 80
Exponential model 107
F-distribution 22 112 114
F-ratio 55 57 72
F-test 55 72
F-test in multiple regression 76
F-test to compare variances 82 83
Factorial study designs 32—33
Fagan's nomogram 110
False negatives 90
False positives 90
Fisher's Exact Test 61
Fitted value 70 72
Fixed-effect model 98
Follow-up 37
Follow-up, losses to 37 38
Forest plot 98 100
Forms, multiple 10
Forwards selection 80
Frame, sampling 26
Free format data 10
frequency 14 61 64
Frequency distributions 14 20
Frequency, observed and expected 61 62 64 65—66
Frequency, relative 14
Frequentist probability 20 109
Gaussian distribution see “Normal distribution”
Geometric mean 76 17
Gold-standard test 90
Goodness-of-fit 71 72 76
Gradient of regression line 70
Graphical display 14—15
Graphical display, identifying outliers 15
Graphical display, one variable 14
Graphical display, two variables 14—15
Hazard 106—107
Hazard, ratio 107
Hazard, relative 107
Healthy entrant effect 31 37
Helsinki Declaration 35
Heterogeneity of variance 82 98
Heterogeneity, clinical 99
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



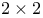 table
table 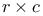 contingency table
contingency table 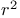
 (alpha)
(alpha)  (beta)
(beta) 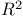
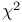 ) distribution
) distribution  )
)