|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Czanderna, Madey, Powell Ч Beam Effects, Surface Topography, and Depth Profiling in Surface Analysis (Methods of Surface Characterization) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Insulators, electromigration 60Ч63
Insulators, SDP 403Ч405
Interaction potentials, Born Mayer 149
Interaction potentials, Moliere 149
Interferometer microscopes see УOptical profiling techniquesФ
Interstitial-vacancypairs 120
Ion beam-solid interactions 103 105 108Ч140
Ion beams 104 252Ч255
Ion beams in surface analysis 98Ч102
Ion beams, amorphization of surfaces 139 159Ч163 202
Ion beams, angle of incidence 104 215 231
Ion beams, applications 251 252
Ion beams, clean surfaces 202 211 221 224
Ion beams, combined beam effects 249Ч251
Ion beams, compositional changes from 201Ч226
Ion beams, current density 101 104 231 380
Ion beams, damage 100 109 154Ч163 202
Ion beams, desorption induced 213
Ion beams, diffusion enhancement 122 202
Ion beams, Duoplasmatron source 379
Ion beams, energetic impact 99 104 198
Ion beams, energy loss 109 112
Ion beams, enhanced erosion 250
Ion beams, etching 109
Ion beams, full width at half-maximum (FWHM) 104
Ion beams, gases see УSpecific noble or reactive gasФ
Ion beams, liquid metal ion source 379
Ion beams, mean projectile range 112
Ion beams, neutralization of 106 110
Ion beams, penetration and trapping 103 111 112 202 377
Ion beams, penetration depths 159Ч163
Ion beams, preferential sputtering 206 214 371
Ion beams, production of 378Ч381
Ion beams, redeposition 100 202 240
Ion beams, reflection of 110
Ion beams, reionization of 110
Ion beams, retarded erosion 250
Ion beams, scattering 109 110
Ion beams, segregation enhancement 122 202 203 211
Ion beams, sources 379Ч381
Ion beams, substrate interactions 116
Ion beams, topics not covered 102
Ion beams, trapping 100 105 107 110 202
Ion desorption see УESDФ
Ion etching see УIon beams etchingФ
ion implantation see УSputter depth profiling trapping
Ion induced photon emission 108
Ion scattering spectrometry see УISSФ
Ion-induced electron emission 108
Ionic crystals, F-centers 25Ч27
Iridium 177 182
Iron-boron alloys 210
Iron-chromium alloys 398 399
Iron-titanium alloys 398
ISO/TC 201. Subcommittee on Terminology 104
Isotopic studies in SDP 397 402 403
ISS 102 103 115 140 150 152 157 202Ч204 207 210 357 359 363 386 397Ч400 402 403
Kapton, AES damage 75
Knock-in effects see УSputter depth profiling (SPD) principlesФ
Krypton, ion bombardment 127 155Ч158 164 168 212 231 236
Laser interferometers see УScanned probe microscopiesФ
Lateral resolution 86
Lattice dynamics see УSimulationsФ
Lattice imperfections see УDefect productionФ
Layer-by-layer sputtering (removal) 100 123 125 139 252 388
Lead-tin alloys 209
Leadsulfide 156
LEED 39 140 150
LEIS see УISSФ
Linear cascade(s) 107 119 124 367Ч369
Lithium fluoride 156 168
Low energy electron diffraction see УLEEDФ
Low energy ion scattering see УISSФ
Magnesium 130 189
Magnesium oxide 130
Magnetic force microscope see УScanned probe microscopiesФ
Many body potentials see УSimulationsФ
Mechanical parts industries (AFM) 328
Medium energy ion scattering 102 157
Melting in AES 40
Mercury cadmium telluride 135 201
Metal oxides 213Ч221
Metal phosphates 223Ч225
Microanalyses in AES 83
Microelectronic industries 326
Molecular dynamics calculations see УSimulationsФ
Molecular measuring machine 312
Moliere potential 149
Molybdenum 70 117
Molybdenum, carbide formation 70
Molybdenum, disulfide 221 222
Nanotopography see УSputter depth profiling (SPD) topography
Neon(Ne) ion bombardment 111 117 118 126 144Ч150 155Ч158 164 168 192 231Ч239 378
Neutral beam bombardment 205
Neutral desorption 108
Neutralization see УCharging and Ion beamsФ
Nickel alloy decomposition 69 70 200
Nickel chromium alloys 210 229 398
Nickel oxidation by ESA 53 54
Nickel silicide modification 221
Nickel silver multilayers 166 208 398
Niobium oxides 67 214Ч218
Nitrogen (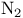 ) ion beams 212 378 ) ion beams 212 378
Noble gas bombardment 378; see also УArgon bombardmentФ УHelium ion УNeon ion УKrypton УXenon
Nomarski microscope 306
Nuclear backscattering 102 371Ч373;
Nuclear reaction analysis (NRA) 363
Optical elements industries 327
Optical profiling techniques 302Ч307
Optical profiling techniques advantages 302
Optical profiling techniques feature heights 303
Optical profiling techniques interferometry 302
Optical profiling techniques optical homogeneity 305
Optical profiling techniques sensitivity 303
Optical profiling techniques speed 303
Optical profiling techniques topographic map 305
Optical profiling techniques types 303 304
Optical profiling techniques, Nomarski type 306
Organic materials, adventitious carbon 14 15 203 224 227
Organic materials, biomolecules 203
Organic materials, cross linking 204
Organic materials, dehydrogenation 204
Organic materials, molecular ions 204
Oxidation with SPMs 332
Oxidation, electron beam enhanced see УESAФ
Oxidation, ion beam enhanced see УSputter depth profiling (SPD)Ф
Oxide compositional changes 213Ч221
Oxygen (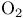 ), ion beams 118 129 174 186 198 199 378 ), ion beams 118 129 174 186 198 199 378
Palladium 177 182 210 329 331
Palladium, carbon on 15
Peak interference 202 203
Peak shape changes in AES 44 85
Peak shape changes in in x-ray absorption data 141Ч145
Perovskites 217 218
Phosphates see УMetal phosphatesФ
Phosphorus in Si SDP 405 407
Phosphosilicate glasses 51 82 218
Photodegradation of polymers 30
Photoemission, internal 21
Photon absorption processes 20
Photon damage to polymers 29Ч34
Photon induced x-ray emission (PIXE) 363
Photon-stimulated desorption 22 25 45
Platinum 143Ч148 168 210
Platinum, ethylene diamine chloride 28
polycarbonate 30 31 33
Polyethylene 30 203
Polyethyleneterephthalate 11 12 30 205
Polymer-metal interfaces 402Ч403
Polymers 11 23 29 74Ч76 85 203 327
| Polymethylmethacrylate 204
Polypropylene 11 30 402 403
Polypyrrole, AES 75
polystyrene 30
Polyurethane 203
Polyvinylchloride 30Ч33 204
Potassium chloride 296 297
Preferential sputtering see УIon beamsФ
Probe shape see УScanned probe microscopiesФ
Quantitative analysis in AES 85
Radiation absorption 25
Radiation enhanced diffusion or segregation 103 165 202 223 377 387
Raman 155 159
RBS 102 155 212 223 363 412
Recoil implantation 119 121 132
Recommendations for using electron beams 85Ч86
Reconstruction see УSiliconФ
Redeposition see УIon beams Sputter depth profiling
Reflection electron microscopy 278
Reflection high-energy diffraction (RHEED) 140 150 153 157
Reflection of ions see УIon beams reflection
Relaxation of bonds 142
Resolution, depth see УDepth resolutionФ
Resonance ionization and neutralization 107
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry see УRBSФ
Sampling depth see also УInformation depthФ
Sampling depth in AES 203
Sampling depth in ISS 203
Sampling depth in XPS 203
Scanned probe microscopies 307Ч334 339 340
Scanned probe microscopies, AFM 173 189Ч191 199 307 309Ч311 313Ч326 339 340
Scanned probe microscopies, applications 320 325
Scanned probe microscopies, calibration 311
Scanned probe microscopies, carbon nanotube 316
Scanned probe microscopies, characterization 311
Scanned probe microscopies, commercial instruments 313
Scanned probe microscopies, critical dimensions 318
Scanned probe microscopies, defects 337Ч339
Scanned probe microscopies, displacement calibration 311 314
Scanned probe microscopies, eddy current microscopy 322
Scanned probe microscopies, electrical methods 320 324
Scanned probe microscopies, force-based methods 320Ч323
Scanned probe microscopies, future directions of techniques 330Ч334
Scanned probe microscopies, height versus spatial wavelength 339
Scanned probe microscopies, high resolution instruments 315
Scanned probe microscopies, history of 307
Scanned probe microscopies, hysteresis 311
Scanned probe microscopies, instrumentation future 330Ч334
Scanned probe microscopies, intercomparisons 334Ч339
Scanned probe microscopies, laser interferometers 311 314
Scanned probe microscopies, lateral resolution 315 316
Scanned probe microscopies, magnetic force microscope 321
Scanned probe microscopies, molecular measuring machine 312
Scanned probe microscopies, optical 320 323
Scanned probe microscopies, phase shifting profiler 334Ч337
Scanned probe microscopies, probe shape 318
Scanned probe microscopies, scanning near-field microscope 323
Scanned probe microscopies, scanning near-field microscope, optical microscope 323 324
Scanned probe microscopies, semiconductor structures 316
Scanned probe microscopies, silicon nanoedge 319
Scanned probe microscopies, silicon spike wafer 319
Scanned probe microscopies, specimens for calibration 314
Scanned probe microscopies, standards 311 314
Scanned probe microscopies, STM 307Ч309 312Ч320 339 340
Scanned probe microscopies, thermal 320 324
Scanned probe microscopies, topagrafmer 307
Scanned probe microscopies, types other than STM and AFM 319Ч325
Scanning near-field microscope see УScanned probe microscopiesФ
Scanning near-field optical microscope see УScanned probe microscopiesФ
Scanning, acoustic microscopy 365 412
Scanning, Auger microscopy 407 408
Scanning, tunneling microscopy 140Ч149 157 173Ч191 307 334; STMФ
Schottky defect 26
Schottky diodes 167 213
Secondary electron emission 6 13 16
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) 102 103 202 357 397 401Ч103 408Ч411
Segregation see УIon beams segregation УSputter segregation
SEM 278 294 307 318
Semiconductor sputter depth profiling 405Ч408
Semiconductor surface enrichment 203 211
Shadow cones 228
Sigmund formulae 126Ч128 134 367Ч372
Signal-to-noise ratio 86
Silicate glasses, ion mobility 74
Silicon dioxide 10 12 5 49Ч51 82 83 101 130 168 179 197 212 217 398
Silicon, amorphous 141 159Ч163
Silicon, boron in 168
Silicon, bromides 211
Silicon, cones on 183 186
Silicon, depth profile of 101
Silicon, displaced atoms 135
Silicon, electron-induced oxidation 53
Silicon, enrichment in alloys 221
Silicon, ESA of 458
Silicon, etch pits 177
Silicon, fluorine in 34 212
Silicon, hydride loss 141 143
Silicon, implanted with l* 126 127
Silicon, ion desorption from glass 77
Silicon, nanoedge tip, STM 317
Silicon, nanotopography 144 145
Silicon, oxidation of 211 315
Silicon, reconstruction 165 168 309
Silicon, sputtering yield 130 376
Silicon, stepped, STM 309
Silicon, topography 177 183 190 191 196 240 334Ч336
Silicon, trapping in 117 118
Silicones 203
Silver 177 182 186Ч188
Silver iodide 8Ч10
Silver-copper alloys 128
Silver-nickel multilayers 164 166 208
Simulations of ion beam damage 149Ч151 226 227
Simulations, binary collision 138
Simulations, depth distribution 135
Simulations, depth of origin 136 138
Simulations, ejection mechanisms 136
Simulations, erosion rate 137
Simulations, molecular dynamics 135Ч138
Simulations, Monte Carlo 135Ч138 226
Simulations, preferential sputtering 137 226
Simulations, sputtering yields 135Ч138
Simulations, zone of mixing 136 388
Single knock-on regime 368
SNMS 359 363 386 411
Sodium chlorate 27Ч29
Sodium glasses 60Ч64 78Ч82
Sodium surface depletion 390
Spike regime 107 119 368Ч370
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) 80Ч85 98Ч102 252Ч255 357Ч412
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) advantages 100
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) alloys see УSpecific combinationsФ
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) altered layers see УZone of mixingФ
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) applications 397Ч411
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) binary collisons 100 107 110 118Ч122 134
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) changes in properties 105
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) compositional changes 131Ч133 201Ч226
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) consumptive methods 362
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) corroded surfaces 398
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) depth scale 382Ч386
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) dynamic range 393
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) ejection of particles 101 102 105
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) energy transfer 112 366Ч371
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) enhance reactivity 100 105 202
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) experimental arrangement 358 360 379Ч381
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) field-induced migration 390 391
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) incident ion effects 106
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) layer-by-layer removal 100 123 125 139 252 388
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) limitations 100
Sputter depth profiling (SDP) methods 359 360
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



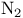 ) ion beams
) ion beams 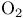 ), ion beams
), ion beams