|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Czanderna, Madey, Powell Ч Beam Effects, Surface Topography, and Depth Profiling in Surface Analysis (Methods of Surface Characterization) |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
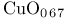 400 402 403 400 402 403
Acronyms and abbreviations in surface analysis 273 274 356
Adatom yields 148
Adatoms 44Ч149
Adsorption, residual gases 394; see also УChemisorptionФ
Adventitious carbon see УCarbon adventitiousФ
AES 39 103 140 150 157 202 203 208 210 221Ч224 243 357 359 361 363Ч365 386 398 400 407
AES advantages 365
AES artifacts 132
AES, charging in see УCharging effectsФ
AES, compared with other techniques 115
Alloy compositional changes 206Ч211
Altered layer see УZone mixingФ
Aluminum 130 196
Aluminum alloys 164
Aluminum gallium arsenide 129 164 198 201 387
Aluminum oxidation by electron beam and water 53
Aluminum oxide 15 17 51 130
Aluminum windows in XPS 3 5
Aluminum, secondary electrons from 4Ч6
Aluminum, XPS spectrum of 16
Amorphization see УIon beamsФ
Analysis of materials or devices 355
Angular mapping 362
Angular resolved XPS 107
Argon (Ar), bombardment 101 106 112Ч114 117 118 126 129 130 131 135Ч138 141 143Ч150 155Ч158 162 164 65 168 174 176 179 192 195 199 203 206Ч212 216Ч225 231Ч239 378 397Ч411
ASTM standards 86 255
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) 173 189Ч191 199 307Ч334
Atomic relaxation 14
Atoms in solids, binding energy see УChemical bond
Attractive pairpotentials see УInteraction potentialsФ
Auger electron spectroscopy 39; see also УAESФ
Auger neutralization 107
Auger parameter 18Ч20
Auger stimulated desorption 23 45
Auger, deexcitation 107
Auger, electron emission 108
Backscattering in SDP 10
Backscattering in XPS 13
Backscattering of electrons 4
Ballistic (mixing) regime see УBinary collisionsФ
Beam damage in AES 39Ч87
Beam damage in SDP see УSputter depth profiling (SPD) damage
Beam damage in XPS 20Ч35
Beam rastering see УIon beams rasteringФ
Benzene damage 30
Berylium 189
Binary scattering 107 110 118Ч122 134 366Ч378
Binding energies in SDP 23 41Ч45 124 139 202 371 375
Binding energies in XPS 2 13Ч18
Binding energy artifacts 8
Binding energy scale calibration 18
Bindingenergy absolute 18
Bombardment induced light emission (BLE) 356 359 361
Bond stretching 139
Boron oxide decomposition 51
Cadmium sulfide 45 47
Cadmium telluride 47 164
Calcium fluoride decomposition 51
Calcium surface depletion in AES 63
Calibration ofspectrometers 18
Carbon adventitious 14 15 203 224 227
Carbon AES spectra 44
Carbon binding energy 14
Carbon carbide formation 225
Carbon monoxide 42 44 48
carbon nanotube 316
Carbon ubiquitous 14 15
Cascade mixing 107 116 119 121 376
Catalysts 402 409
Cazaux model for charging 29 60 79
Cazaux nomogram for X-ray dose 21
Cesium (Cs) ion beams 110 129 198 378
Channeling in SDP see also Sputter depth profiling(SPD) singlecrystalsФ
Channeling of surfaces 1 10
Charge neutralization see УCharging effectsФ УResonance
Charging effects in SDP 389Ч392
Charging effects in UPS 1 13
Charging effects in XPS 1Ч13 34
Charging effects on insulators 12 16 34 58Ч60
Charging effects with thin conducting layers 12 13
Charging effects, AES 13 40 58Ч60 92 93
Charging effects, andionic conductivity 9
Charging effects, Auger parameter and 8Ч20
Charging effects, compensation of 6 10Ч17
Charging effects, differential 8Ч10 12
Charging effects, positive charge accumulation 3
Charging effects, with monochromatic X-rays 3 10 13
Chemical bond breaking 23 25 41Ч15 70 87 88 139 159Ч163 202
Chemical reactions, electron induced 39 40
Chemical reactions, ion beam induced 201Ч226
Chemical reactions, photon induced 20Ч23 34
Chemical structure changes 40
Chemisorption  on Si 48 on Si 48
Chemisorption 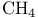 on Si 48 on Si 48
Chemisorption CO on lr (110), ESD of 42
Chemisorption CO on Si 48
Chemisorption CO on Si (111), ESD of 44
Chromate decomposition 51Ч53
Chromium oxidation 409
Chromium-nickel multilayers 169Ч171 174 175 196 199 200 241Ч247 398
Clean surfaces 202 211 224 227
Clusters 144Ч149
Coatings industries (AFM) 327
Cobalt silicides 223
Collision cascade in SDP 102 107 108 119 174 202 367
Color changes in AES 65Ч68
Compositional changes 40 201Ч226
Configuration coordinates 24
Contaminant effects 20Ч23 34 39 40 201Ч226
copper 239 240
Copper oxides 398 400
Copper sulfate decomposition 25Ч27
Copper, alloys 226; see also УSpecific alloysФ
Copper, argon bombardment 131 144Ч147 168 176
Copper, depth profiles 245
Copper, nanotopography 144Ч148 168
Copper-gold alloys 398 400
Copper-indium-diselenide 212
Copper-lithium alloys 207
Copper-nickel alloys 207
Copper-titanium alloys 209
Copper-zirconium alloys 209
Core level states 42
Crater shapes 239 240 391Ч393
Crater-wall profiling 362 364
Cross section for electron-induced damage 55Ч57
Cross section for x-ray induced damage 23 24
Damage flux levels 28 54Ч58 106 163 164
Damage to surfaces by electrons 39Ч87
Damage to surfaces by ion beams 100 139Ч168
Damage to surfaces by photons 20Ч35
Damage to surfaces threshold by electrons 54Ч58
Data storage industries 325 326
Decomposition of surfaces and films 49Ч53; see also УDamage to surfacesФ
Defect annihilation 40 149 154 168
Defect metastability 167
Defect production in AES 40
Defect production in SDP 106 108 118Ч122 139Ч168 176 202 209 253
Defect production in XPS 23
Definitions in surface analysis 103
Depth analysis 356
Depth distribution, simulations 135Ч138
Depth of sampling 125
Depth profile(s) see УSputter depth profiling (SPD)Ф
Depth profiling see also УSputter depth profiling (SPD)Ф
Depth profiling artifacts 100
Depth profiling by sputtering 98Ч100; see also УSputter depth profiling (SPD)Ф
Depth profiling cratering 99 239 240 391Ч393
Depth profiling erosion rate 101 175 381
| Depth profiling ideal 98
Depth profiling in AES 103
Depth profiling in SIMS 103
Depth profiling in XPS 103
Depth profiling instrumentation 358 360 379 381
Depth profiling principles 98Ч103 357Ч360
Depth profiling resolution 99 103
Depth resolution analysis method 241Ч247
Depth resolution angle of incidence 235 237 240
Depth resolution beam energy 231Ч239
Depth resolution beam inhomogeneities 393
Depth resolution calibration standards 396
Depth resolution current density effect 233
Depth resolution definition 94 395
Depth resolution in sputter depth profiling 99 227Ч249 254 394Ч396
Depth resolution limiting 101 103 247Ч249 388
Depth resolution model surfaces 230 396
Depth resolution nature of sample 227Ч231 389Ч391 396
Depth resolution nickel-chromium multilayers 229 232 233 235 239 243Ч247
Depth resolution rotation, with and without 242Ч247
Depth resolution time of bombardment 228
Depth resolution total ion dose 234
Depth resolution Zalar rotation 228Ч247
Depth resolution, degradation in 231 387
Depth resolution, Gaussian error function 395
Depth resolution, grazing incidence 240
Depth resolution, instrumental factors 239Ч247 391Ч393
Depth resolution, ion beam effects 231Ч239; see also УZone of mixingФ
Desorption, electron stimulated see УESDФ
Detect recombination 120Ч123 147Ч149 154 168 202
Detection limits in surface analysis 396 397
Deuterium trapping 115 117
Diamond tool edge 330
Differential sputtering 103 202 203 228
Differential surface charging 8
Diffusion, surface enhanced 163Ч166
Diffusional mixing 122 123 163Ч166
Dissociative ionization 56
Dose (ion) 103
Dose (ion), distinction from ion fluence 104
Dose (ion), magnitudes 104 105
Doses, critical electron for damage 57
EID see УESDФ
Ejected particles blocking and channeling 124 125
Ejected particles surface structural influences 131
Electrochemical science 329
Electromigration in insulators 60Ч64 82
Electron beam charging of insulators 92 93
Electron beam damage in surface analysis 87 93Ч96
Electron beam damage reduction 86
Electron beam effects in AES 39Ч87
Electron beam effects in AES, coated surfaces 69Ч71
Electron beam effects in AES, contaminated surfaces 69 72
Electron beam effects in AES, decomposition 69 70
Electron beam effects in AES, first order kinetics for damage 86
Electron beam effects in AES, induced changes 71Ч74
Electron beam effects in AES, of glasses 74Ч82
Electron beam effects in AES, oxidized surfaces 69
Electron beam effects in AES, physical effects 65Ч68
Electron beam effects in AES, polymers, AES 74
Electron beam, enhanced sputtering 83
Electron beam, induced changes 71
Electron beam, induced decomposition 67
Electron beam, induced heating 64Ч65
Electron beam, interactions 41 53 88Ч92
Electron emission 108
Electron energy loss spectroscopy 39 140 150 154 221
Electron flood gun 7
Electron induced ion desorption see УESDФ
Electron microscopy, beam damage 87
Electron probe microanalysis 39
Electron stimulated adsorption see УESAФ
Electron stimulated desorption see УESDФ
Electronic interactions 111
Electronic thermalization 22
Electronic-excitation processes 41 49 55
Elemental analysis 356
Energy scale calibration in XPS 13
Erbiumsilicide 221
Erosion rate see УSputter depth profiling (SPD) erosion
ESA 45Ч49
ESA in oxidation of layers and films 53 54
ESA of  , ,  amd CO on Si (111) 48 amd CO on Si (111) 48
ESA of CdS (0001) with  45 45
ESA of semiconductor surfaces 47
ESA, mechanisms for 45
ESD 25 41Ч45 70 87 88
ESD of alkali halides and alkaline earths 49
ESD of carbon 73
ESD of chlorine in 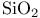 82 82
ESD of glasses 49Ч51 73
ESD of surface layers 49Ч53 73
ESD of thin films 49Ч53
ESD, fundamentals of 87 88
ESD, ion angular distributions 45
ESD, oxygen ion desorption 49
ESD, silicon ion desorption 77
ESD, sodium ion desorption 78 79
ESDIAD 45
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) 141
F-center formation 25Ч27
Fast atom bombardment (FAB) 359
Fermi level referenced XPS 16
First order kinetics and electron beam damage 86
Flood gun for charge neutralization 2 20 34
Fluence (ion) 103
Fluence (ion), distinction from ion dose 104
Fluence (ion), magnitudes 104 105
Fluorine compounds 19
Fluropolymers 203 205
Gallium arsenide 47 84 106 129 135 150 153 155Ч157 164 168 189 192 198 213 309 387 405
Gallium phosphide 198
Germanium 150 153 168
Gibbsian segregation 132 206
Glasses, damage 93 94
Glasses, electron beam effects 41 74Ч80
Glasses, float 71 72
Glasses, mobile ions 74 219
Glasses, phosphosilicate 51 179 218
Glasses, soda-silicate 76 179 218
Glasses, sodium 60 219
Glasses, susceptible to damage 85 218Ч221
Glasses, titanium doped 220
Glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy (GDOES) 359 361
Glow dischrage mass spectrometry (GDMS) 359 361
Gold, binding energy in 14
Gold, defect production 156
Gold, nanotopography 144 145
Gold, topography development 177 182 195
Gold, XPS spectrum of 4 16 17
Gold-copper alloys 208 226
Gold-palladium alloys 203Ч205
Grain boundary interdiffusion 398
graphite 117 150 189 205
Heating in AES 40 64 65
Helium(He) implantation see УTrappingФ
Helium(He) ion bombardment 112Ч114 117 118 132 144Ч148 150 168 194
Helium(He) trapping 112Ч114
Hemispherical energy analyzer 3
Hydrocarbon contamination 66Ч68
Hydrogen (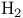 ), ion bombardment 141 150 162 194 212 ), ion bombardment 141 150 162 194 212
Implantation see УIon beams trapping
Indium 140Ч143
Indium antimonide 187
Indium arsenide 198
Indium phosphide 140Ч143 165 168 182Ч186 189 192 198 212 232 235Ч237 405
Information depths in surface analysis 373Ч376
Inorganic materials, radiation damage 25
Instrumentation 2 358 360 379Ч381
Insulators, charging 12 16 34 58Ч60
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



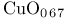
 on Si
on Si 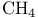 on Si
on Si  amd CO on Si (111)
amd CO on Si (111) 
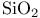
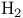 ), ion bombardment
), ion bombardment