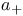Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Fraisse R. — Theory of Relations
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Theory of RelationsАвтор: Fraisse R. Аннотация: Relation theory originates with Hausdorff (Mengenlehre 1914) and Sierpinski (Nombres transfinis, 1928) with the study of order types, specially among chains = total orders = linear orders. One of its first important problems was partially solved by Dushnik, Miller 1940 who, starting from the chain of reals, obtained an infinite strictly decreasing sequence of chains (of continuum power) with respect to embeddability. In 1948 I conjectured that every strictly decreasing sequence of denumerable chains is finite. This was affirmatively proved by Laver (1968), in the more general case of denumerable unions of scattered chains (ie: which do not embed the chain Q of rationals), by using the barrier and the better orderin gof Nash-Williams (1965 to 68).
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2000Количество страниц: 456Добавлена в каталог: 19.11.2008Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Maximalist extension theorem, maximalist = existentially closed relation 11.2.4 11.2.6 Maximalist extension theorem, maximalist subset 11.2.3 Maximum (Max), minimum (Min) ordinal 1.2.1 Maximum (Max), minimum (Min) ordinal, element in a poset 1.6.1 Maximum right (or left) indecomposable interval 6.3.3 Mc KAY, Ramsey numbers 3.1.4 3.1.5 MILLER (Arnold), 5.2 5.11.2 MILLER (E.W.), decreasing sequence 5.5.2 9.5.5 MILLER (E.W.), dimension 4.9 MILLER (E.W.), partition theorem 3.3.2 3.3.3 MILNER, better quasi-ordering 7.7.10 MILNER, finitely free poset 4.7.2 MILNER, linear augmentation 2.15.1 Minimal bad sequence 4.2.2 Minimal bad sequence, barrier sequence 7.2.3 Minimal bad sequence, with respect to forerunning 7.3.5 Minimal for its age (relation) 10.7 MISLOVE, topologically scattered poset 6.7.4 MOEHRING, computation of posets 2.14 Monochromatic set 3.1.1 3.1.3 Monomorphic relation 9.6 Monomorphy threshold 13.10.6 Monotonic extracted sequence 3.1.2 MOORE, maximal chain axiom 2.2.4 MOSTOWSKI, dependent choice 1.8 MOSTOWSKI, set theory 1.1.8 10.11.1 Multicolor theorem 3.4.3 Multiplicity function (Ramsey) 3.1.7 Multirelation 1.7 N = 1.2.4 1.6.1 n-amalgamable, amalgamable over a relational system A.2.3 n-element set (or subset) 1.2.3 n-set-transitive group 12.3.3 n-set-transitive group, set-transitive group theorem (Cameron) 13.8 n-transitive group 12.3.3 n-tuple 1.2.3 NASH.WILLIAMS, barrier partition theorem 7.1.4 NASH.WILLIAMS, better partial ordering 7.7 NASH.WILLIAMS, forerunning 7.3.1 NASH.WILLIAMS, minimal bad sequence 7.2.4 NASH.WILLIAMS, separation theorem 3.2.4 Natural number = integer 1.2.3 Natural sum 6 4.8.2 Negation 1.7.4 Net = directed poset 2.13 Non symmetric Ramsey number 3.1.5 Non-amalgamation for trees 2.11.6 Non-classical ultraproduct and ultrapower 11.8 Non-embeddability rank 10.4.3 Non-embeddability rank, non-richness rank 10.4.3 Normal form (Cantor) 1.3.5 Normal ultraproduct and ultrapower 11.8 Older relation 10.1.3 Older relation, 10.4.1 Older relation, A-older relation 11.1.2 Open set 6.6.1 6.6.4 Operator (free) 9.3 Operator (free), (k,p)-operator 10.10.2 Orbit 12.3.2 A.2.8 Order type 1.7.7 Orderable set, ordering axiom 2.4.4 Ordered pair = couple 1.1.2 Ordinal 1.2.1 Ordinal power ( 1.3.3 Ordinal power ( 2.6.3 Ordinal power ( 2.6.1 2.6.2 Ordinal, ordinal 1.2.4 Ordinal, ordinals 1.6.5 Ordinal-indexed sequence = 1.2.2 P (property) A.4.1 PABION, prehomogeneous relation 12.7.1 PAILLET, free interpret ability and concatenation 9.2.3 Pair = unordered pair 1.1 Paradoxes concerning the empty base 10.10.4 PARIKH, maximal augmented chain theorem 4.11.2 Partial operator 9.3.4 Partial ordering = poset 1.6 Partial ordering of words 4.1.3 Partition in slices 2.10.2 Partition lemma and theorem, Dushnik — Miller 3.3.2 3.3.3 Partition lemma and theorem, Erdoes 3.3.4 Partition lemma and theorem, Erdoes — Rado 3.3.5 Partition of the continuum 1.5.3 Partition theorem for barriers (Nash-Williams) 7.1.4 Peano 1.2.10 PELCZYNSKI, continuous image of a compact 6.10.4 Perfect barrier sequence 7.2.2 Perfect set (topology) 6.6.5 PERLES, finitely free poset 4.14.1 Perpendicular sum of posets ( 9.9.2 Pigeon-hole principle 1.1.1 PINCUS, ordering axiom 2.4.4 PIWAKOWSKI, Ramsey numbers 3.1.6 Poizat 4.3.3 4.5.3 Polychromatic Ramsey number 3.8.4 POSA, edge-indivisible graph A.5.2 Poset = partial ordering 1.6 Poset = partial ordering, poset of antichains 6.7.3 Poset = partial ordering, scattered poset 6.5 Poset = partial ordering, topologically scattered poset 6.7 POUZET, age-inexhaustible system A.3.3 POUZET, Cameron's theorem 13.8.3 POUZET, cofinal height 2.12 POUZET, cofinal subset 2.7.2 POUZET, cofinality of a finitely free poset 4.12 POUZET, criterion prehomogeneous relation 12.9 POUZET, criterion richrelation 11.4 12.3.7 POUZET, directed well partial ordering 4.13 6.5.1—6.5.3 POUZET, equivalence between finitely free scattered and topologically scattered poset 6.7.4 6.8.2 7.1.3 7.1.7 7.6.6 7.7.7 7.7.8 8.6.8 POUZET, finite number of bounds 13.2.3 POUZET, inexhaustible relation 10.6 POUZET, infective operator 9.3.6 9.6.3 POUZET, lexicographically ordered set 3.2.1—3.2.3 POUZET, linear augmentation 2.15.1 POUZET, multicolor theorem 3.4.3 POUZET, orbit and inexhaustible age A.3.2 POUZET, orbits 12.4.1(2) POUZET, partition in slices 2.10.2 POUZET, profile increase theorem 3.6 4.5.3(3) 4.5.3(4) 4.6.2 4.9.5 4.11.2 10.9.5 POUZET, relation minimal for an age 10.7 POUZET, representatives of an age 10.2.4 POUZET, set 2.9.4 POUZET, thresholds 13.10 POUZET, tournament and monomorphy 9.7 POWELL, hereditarily transitive set = ordinal 1.2.8 Power (ordinals) 1.3.3 Power of a barrier 7.1.8 Power set ( 1.1 Precede (relational system) A.4.5 Precedes in a barrier ( 7.1.5 Predecessor 1.2 Prehomogeneous relation 12.7 PRIKRY, Ramsey set 3.7.1 Prime-ideal axiom = ultrafilter axiom 2.13 Product between alephs 1.6.8 Product between cardinals 1.4.5 Product between ordinals: 1.3.2 Product, cartesian notation 1.1.2 Product, generalization 1.1.9 Product, Hessenberg based product 9.9.2 Product, natural product 4.8.2 Profile, bounded profile 10.9.7 Profile, profile increase theorem 3.6 10.9.5 Projection filter 10.1 Property P(, ) A.4.1 Pseudo-amalgamable age, pseudo-amalgamation theorem 12.6 Pseudo-homogeneous relation 12.5 Q = set or chain of rationals 1.6.1 2.1 Quasi-ordering 1.6 Quaternary (dihedral) relation 9.2.2 Quotient 1.3.2 R = set or chain of reals 1.6.1 2.1 RADO, coherence lemma 2.4.3 RADO, partition theorem 3.3.5 RADO, poset 4.4.2 7.6.4 RADO, Rado graph A.1.5 RADO, Ramsey numbers 3.8.1 RADO, Ramsey set 3.7.1 RADO, well partial ordering of words 4.5.2 RADO, with Dushnik, Miller 3.3.3 RADZISZOWSKI, Ramsey numbers 3.1.4—3.1.6 RAMSEY, connection with Galvin 3.2.2 RAMSEY, connection with Nash-Williams 7.1.4 RAMSEY, multiplicity function 3.1.7 RAMSEY, polychromatic Ramsey number 3.8.4 RAMSEY, Ramsey class A.4 RAMSEY, Ramsey number 3.1.4 RAMSEY, Ramsey number and polynomial coefficient 3.8.5 RAMSEY, Ramsey sequence and set 3.7.1 RAMSEY, theorem, finitary form 3.1.3 RAMSEY, theorem, infinitary form 3.1.1 Range (Rng) 1.1.2 Rank, aleph rank 1.6.6 Rank, fundamental 1.4.2 Rank, lexicographic 3.2.1 Rank, neighborhood 6.2.4 Rank, non-embeddability and non-richness rank 10.4.3—10.4.5 Ranking function 7.3.3 rational 2.1 Rational, rational ordinal 4.8.2 RAUZY, bivalent tableau 8.4 RAWLINS, computation of posets 2.14 REAL 2.1 Real, transfinite real 4.8.2 Realization of a 11.5 Recursion, definition 1.2.10 Reduced tree — reduct 2.11.4 Reduction threshold 13.10.1 13.11.2 Reflection (permutation group 13.6.2 Regular aleph 2.8.1 Regular aleph, regular cardinal 2.8.4 Reinforcement see "Augmentation" rel-age 11.1.2 Relation 1.7 Relation, A-relation 11.1.1 Relation, binary relation 1.6 Relational system 12.3.1 Remainder 1.3.2 Represent, representative of an age 10.2.1 Restriction, barrier 7.1.1 Restriction, barrier sequence 7.2.2 Restriction, cut 2.6.5 Restriction, function 1.1.4 Restriction, relation 1.7.1 Retro-ordinal 1.7.5 RIBENBOIM, stratified poset 2.10.1 Rich for its age (relation) 10.5 Rich relation 10.3 Right bound of a cut 2.6.5 Right indecomposable chain 6.3.1 ROBERTS, Ramsey numbers 3.1.5 ROBINSON, maximalist relation 11.2.6 ROBINSON, saturated relation 11.3.4 ROEDL, indivisible graph A.4.11 ROSENBERG, Sperner's lemma 3.8.2 ROSENSTEIN, decreasing sequence of chains 5.5.4 ROSENSTEIN, forerunning 7.3.1 7.3.4 ROSENSTEIN, separation by functions 5.5.3 ROTHSCHILD, Ramsey numbers 3.1.6 Row (in a tableau) 8.4 RUBIN, range subpotent with the domain 1.1.8 RUDIN, continuous image of a compact 6.10.4 S-indivisible relational system A.5.1 SABBAGH, existence of a supremum chain 8.2.2 SANCHEZ-FLORES, Ramsey numbers 3.1.6 3.8.1 Saturated relation 11.3.4 Saturated relation, saturated subset 11.3.1 SAUER, age-inexhaustible system A.3.3 SAUER, canonical partition A.5.3 SAUER, condition for indivisibility A.4.5 SAUER, divisibility and squares A.4.10 SAUER, indivisible homogeneous graphs A.4.11 SAUER, partition and up edges A.5.5 SAUER, property P A.4.1 SAUER, strongly amalgamable age A.3.5 SAUER, weak indivisibility A.4.3 Scattered chain 6.1 Scattered chain, scattered poset 6.5 Scattered chain, strongly scattered chain 6.2.3 Scattered chain, topologically scattered chain 6.7.2 Scattered chain, topologically scattered poset 6.7 Scheme of foundation 1.2.7 Scheme of induction for finite sets 1.1.1 Scheme of substitution 1.2.4 SCHMERL, homogeneous posets A.1.7 SCHROEDER, equimorphism 5.1.2 SCHROEDER, equipotence theorem 1.1.5 1.6.8 SCHUR, numbers 3.8.3 SCOTT, definition of cardinality 1.4.4 SEMADINI, continuous image of a compact 6.10.4 Separation lemma 2.3.3 Separation lemma, separation by injective functions 5.5.3 Separation scheme 1.1 Separation theorem (Nash-Williams) 3.2.4 Sequence, 1.2.5 Sequence, ordinal-indexed sequence, 1.2.2 Set of integers ( 1.2.4 SHELAH, adjacent elements and reduction threshold 13.10.1 13.11 SHEPHERDSON, accessibility axiom 2.8.9 SIERPINSKI, counterexample 3.3.1 SIERPINSKI, decreasing sequence of chains 5.5.4 SIERPINSKI, generalized continuum hypothesis 1.9.3 SIERPINSKI, poset 2.2.7 SIERPINSKI, separation by injective functions 5.5.3 SIKORSKI, rational ordinal 4.8.2 SILVER, Ramsey set 3.7.1 SIMMONS, saturated relation 11.3.4 Simple convergence topology, on integers 6.6.1 Simple convergence topology, on intervals 6.6.4 Singleton relation 10.8 Singular aleph 2.8.1 Singular aleph, singular cardinal 2.8.4 Skeleton A.1 Skolem 10.1.7 Slice 2.10.2 SOCHOR 1.1.8 Solid family 11.5.1 Solid family, morphism 11.6 Solid family, relation 11.5.3 SOLOVAY, Suslin axiom 5.8 Specification of a rel-age, specify 11.1.3 SPECKER, age without any rich representative 10.5.4 SPECKER, chain 5.9.2 SPENCER, Ramsey number 3.1.6 SPERNER, mutually incomparable subsets 3.8.2 Square of a barrier 7.1.8 Square of a relational system A.2.9 STANTON, non-unimodal profile 3.6.1 Stratified poset = weak ordering 2.10.1 Strong embedding property A.3.5 Strong interval of a poset 9.8 Strongly amalgamable age or set 12.2 A.2.1 Strongly inexhaustible system A.3.5 Strongly scattered chain 6.2.3 Subpotence 1.1.4 Substitution scheme 1.2.4 Succeeds, successive element in a barrier ( 7.1.5 Successor aleph 1.6.5 Successor barrier (forerunning) 7.3.1 Successor barrier (forerunning), successor barrier sequence 7.3.3
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



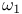 -sequence of denumerable posets
-sequence of denumerable posets 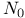 = chain of integers (synonymous with
= chain of integers (synonymous with 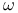 )
) 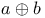 , product
, product 
 -older relation
-older relation 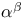 )
)  )
)  ,
, 
 )
) 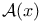
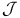 of initial intervals
of initial intervals 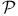 )
) 
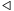 )
) 


 -family
-family  )
)