|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Altmann S.L. — Band Theory of Solids: An Introduction from the Point of View of Symmetry |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Hoffmann 22 212 247
Hole states 149 159
Holes 149 151
Holes, effective mass 151
Holes, velocity 151
Holohedric point group 57
Hume — Rothery 199
Hume — Rothery, rules 199
Impurities and surface states 227
Impurities and surface states, Koster and Slater method 235
Insulator 140 149
Interplanar distance 70
Intrinsic semiconductivity 158
Intrinsic semiconductor 140
Invariant subgroup 25 (2—1.6)
Inversion operator 103
Inversion operator, effect on Bloch functions 103 (6—1.9)
Irreducibility test 38 (2—5.1)
Irreducible representation 37
Irreducible representation, conjugate 211 P12—4.6
Irreducible representation, dimension 38
Irreducible representation, faithful 216
Irreducible representation, number 37 38
Irreducible representation, orthogonality relations 38 (2—5.2) (2—5.3)
Irreducible representation, relation to degeneracy 37
Irreducible representation, test for irreducibility 38 (2—5.1)
Jahn — Teller effect 205
Jansen 45
Janssen 63
Jerome 211
Jones 101 199
k space 12
k space, quantization 12 94
k space, volume per state 13 (1—3.25)
k vectors 11
k vectors, equivalent 91
k vectors, group 107
k vectors, quantization 11 (1—3.20) 94
k vectors, quasi-continuous distribution inside Brillouin zone 94
Kelly 63 85
Ket 79
kinetic energy 9 188
Kinetic energy, for vibrating crystal 188(11—2.10)
Kinetic energy, invariance under translations 189
Kittel 22 165
KKR method 183
Kleinmann 183
Knox 63 119
Kohn — Korringa — Rostoker method 183
Koster and Slater method 235
Koster and Slater method, localized perturbation 239
Kronecker delta 38 (2—5.2) 80
Kventsel 212 240
Landau 45 203 212
Lapiccirella 158 195
Lattice 49
Lattice planes 64 78
Lattice, synonymous with Bravais lattice 52
Lattice, with basis 49
Lax 44
LCAO 177
Lennard — Jones 240
Levine 247
Lifshitz 45 203 212
Linear chain 137
Linear chain, alternation 200 212
Linear chain, bases and irreducible representations 152 (8—8.1H8—8—3)
Linear chain, Brillouin zone 100 P5—7.5 137
Linear chain, electron-phonon interactions 203
Linear chain, energy bands 139 F8—4.2
Linear chain, energy bands, forbidden contacts 139 F8—4.3
Linear chain, energy bands, forbidden gaps 138
Linear chain, N atoms, tight binding calculation 175
Linear chain, N atoms, tight binding calculation, eigenvalues 176 (10—2.26)
Linear chain, Peierls instability 200
Linear chain, reconstruction 200
Linear chain, six atoms 120
Linear chain, six atoms, bands 127
Linear chain, six atoms, bases of the representations 125 T7—3.1
Linear chain, six atoms, Brillouin zone 126 F7—3.1
Linear chain, six atoms, classes 122 T7—1.1
Linear chain, six atoms, energy levels 177 T10—2.1 177
Linear chain, six atoms, irreducible representations 127 T7—3.3
Linear chain, six atoms, isomorphism with 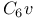 122 122
Linear chain, six atoms, representations of invariant subgroup 124 T7—2.1
Linear chain, six atoms, small representations 138 T8—4.2
Linear chain, six atoms, stars and groups of k 137 T8—4.1
Linear chain, surface states 240 244
Linear chain, tight-binding calculation 175
Linear combination of atomic orbitals 173
Linear independence 31 (2—3.8)
Linear operators 33
Linear variational method 167
Littlewood 202
Local potential 181
Lodge 158 195
Loewdin 225 226
Loewdin orbitals 222
Loewdin orbitals, close formula 224 (13—3.20)
Longitudinal oscillation 196
Longuet — Higgins 212
Loucks 183
Lukes 247
Matrix (representative) 34
Matrix element 168
Matrix function 224
Matrix, direct sum 35
Matrix, invariant 37
Matrix, trace 37
McKie 63
McWeeny 44 240
Mermin 22 63 85 165
Metallic electrons 7
Miller indices 71 F4—4.2
Miller indices, properties 72
Miller indices, relation to reciprocal vectors 72 (4—4.11)
Momentum 9 10
Momentum, eigenfunctions 9 10
Momentum, operator 9 10
Momentum, quantization 11
Momentum, vector 84
Momentum, vector, not parallel to velocity 136
Mott 101
N-type semiconductors 159
Nearly free-electron method 167
Nearly free-electron method, band gap 171 (10—1.33)
Nearly free-electron method, form of wave function 168(10—1.10)
Noble metal 161 164
Noble metal, d band 164
Noble metal, s band 164
Non-linear operator 33
Non-symmorphic space group 62
Normal coordinates 187 190
Normal coordinates, as translation eigenvectors 191 (11—2.20)
Normal mode of vibration 186 191
Normal mode of vibration, longitudinal 196
Normal mode of vibration, transverse 196
Normalization 79 (4—9.5)
One-dimensional chain see also linear chain
One-dimensional chain, Brillouin zone 100 P5—7.5
Open surfaces 49
Operator, configuration space 28
Operator, function space 28 29
Operator, function space, isomorphic to configuration space operators 30 (2—2.8)
Operator, function space, wrong form 45
Operator, products 27 53
Operator, transformation 30 (2—2.13)
Optic bands 196
Optic branches 196
OPW see orthogonalized plane waves method
| Orbital degeneracy 12
Orbital state 13
Orbits in k space 148
Orthogonality 79 (4—9.4)
Orthogonality, of irreducible representations 38
Orthogonalized plane waves method 178
Orthogonalized plane waves method, orthogonalized plane waves 179 (10—3.6)
Orthogonalized plane waves method, wave function 179 (10—3.12)
Orthonormal functions 80 (4—9.9)
Orthonormal vectors 65 (4—1.5) (4—1.6)
Orthonormality 79
Oscillator force constant 186
Ovchinnikov 212
Overlap integral 168
P point group 57
P point group, of space group 60
P-type semiconductor 159
Papaconstantopoulos 162 183
PARRY 212
Passive picture 28
Passive picture, never used in this book 28
Pattern (crystal) 46
Peierls 200 211
Peierls instability 200
Peierls instability, linear chain 200
Peierls instability, lowering of Fermi energy 201 (12—2.1)
Peierls instability, quasi linear chain 205
Peierls instability, total energy balance 202
Peierls instability, vibronic interactions 203
Peierls transition 201
Period 19
Periodic boundary conditions 8 F1—2.1
Periodic boundary conditions, in a lattice 87
Periodic boundary conditions, in a one—dimensional lattice 87 F5—1.1
Periodic boundary conditions, order of the translation group 88 (5—1.3)
Periodic boundary conditions, three-dimensional form 9
Periodic functions 65
Periodic functions, are periodic in the lattice 65
Periodic functions, expansion in Fourier series 81 (4—9.17)
Periodic functions, in any lattice 68 (4—2.12)
Periodically repeated scheme 143
periodicity 47
Periodicity, it is fully determined by translation lattice 64
Periodicity, its relation to translation symmetry 47
Phase changes 199
Phase changes, relation to Fermi surface 199
phase velocity 19 (1—8.8)
Phillips 183
Phonon drag 194
Phonon spectrum 195
Phonon spectrum, cusps 196
Phonon spectrum, for silicon 195 F11—4.1
Phonons 192
Plane group 53
Plane staeks 69
Plane waves 18 18 65 77
Plane waves, as translation eigenfunctions 100 P5—7.3
Plane waves, corresponding to lattice planes 78
Plane waves, in the lattice 84 (4—10.2)
Plane waves, momentum of 84 (4—10.3)
Plane waves, normalized 79 (4—9.6) 84
Plane waves, of the lattice 84(4—10.1)
Plane waves, orthogonal over crystal volume 100 P5—7.4
Plane waves, orthonormality 80 (4—9.9)
Plane waves, propagation vector 11 77
Planes (crystal) 70
Planes (crystal), equation in Miller indices 71 (4—4.7)
Planes (crystal), equation in the normal 70 (4—4.2)
Planes (crystal), of the lattice 78
Point group 57
Point group, leaves Bravais lattice invariant 57 58
Point group, relation to space group 60
Polyacetylene 206 F12—3.1
Polyene chain 206
Polyene chain, degeneracy due to glide 207 209
Polyene chain, double Brillouin zone 208 209 F12—3.3
Polyene chain, glide plane 206
Polyene chain, Peierls instability 209
Polyene chain, reconstruction 210 F12—3.4
Position vectors 64
Position vectors, always given in direct components 68 73
Position vectors, are expressed in terms of the crystal lattice 66
Position vectors, as vectors in or of the lattice 68 (4—2.8) (4—2.9)
potential energy 9
Potential energy, for vibrating crystal 188(11—2.11)
Potential energy, for vibrating crystal, invariance under translations 189
Potential field 166
Potential field, local 181
Primitive cell 48
Primitive cell, as a maximal set of translationally inequivalent points 49
Primitive cell, centred 50 92
Primitive cell, construction as maximal sets of translationally inequivalent points 50
Primitive cell, contains only one lattice point per cell 53
Primitive cell, open polyhedron property 49
Primitive cell, standard 51
Primitive cell, standard and centred have same extension 51
Primitive cell, with a basis 50 53
Primitive vectors 48
Projection operator 38 (2—5.4)
Projection operator, for plane waves 179 (10—3.10)
Propagation vector 11 77
Pseudo Hamiltonian 180 (10—4.6)
Pseudo wave function 180 (10—4.2)
Pseudomomentum 99
Pseudopotential 180 (10—4.8)
Pseudopotential method 180
Quasi linear chain 205 see
Quasi-continuous 94
Reciprocal lattice 74
Reciprocal lattice, blind to any basis in direct lattice 75
Reciprocal lattice, cannot have a basis 75
Reciprocal lattice, correct relation to the direct lattice 74
Reciprocal lattice, entirely determined by translational lattice 74
Reciprocal lattice, of face—centred cubic lattice 76 F4—7.1
Reciprocal lattice, the k vectors in its primitive cell label all representations of T 91
Reciprocal vectors 67
Reciprocal vectors, construction 69 (4—3.3) (4—3.5) (4—3.6)
Reciprocal vectors, definition in crystallography 67 (4—2.4) (4—2.5)
Reciprocal vectors, definition in solid—state theory 68 (4—2.6) (4—2.7)
Reciprocal vectors, direction in terms of plane stack 72 (4—4.11)
Reciprocal vectors, error to be avoided in getting moduli 74
Reciprocal vectors, in the lattice 75 (4—6.3)
Reciprocal vectors, modulus in terms of interplanar spacing 72 (4—4.12)
Reciprocal vectors, of the lattice 75 (4—6.4)
Reciprocal vectors, relation to plane stacks 72 (4—4.11) (4—4.12)
Reciprocal vectors, used to denote directions 73
Reconstruction of surface 235
Reduced coordinates 189
Reduced zone scheme 142
Reduction of a representation 35
Reduction of a representation, number of times an irreducible is contained 269 (15—12.19)
Reflections 53
Relaxation time 185
Representation 35 see
Representation, conjugate 211 P12—4.6 251
Representation, irreducible 37
Representation, partition over irreducibles 38 269
Representation, reduction 36
Resolvent 241
Rigid band model 198
Rosenberg 22 165 197
s band 162 164
s band, in noble metal 164
s band, in transition metal 164
Salem 212
Scattering electron-phonon 192
Scattering of electron by rigid crystal 193
Schroedinger equation 9 (1—3.1)
Schroedinger group 30
Schulz 211
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте