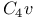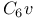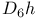|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Altmann S.L. — Band Theory of Solids: An Introduction from the Point of View of Symmetry |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
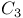 42 42
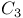 , operations 42 F2—7.1 , operations 42 F2—7.1
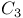 , representations 43 T2—7.1 , representations 43 T2—7.1
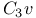 , as the group of ammonia 213 , as the group of ammonia 213
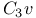 , character table 44 T2—7.2 , character table 44 T2—7.2
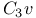 , operations 44 F2—7.2 , operations 44 F2—7.2
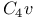 106 106
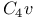 , character table 111 T6—3.2 , character table 111 T6—3.2
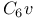 40 40
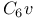 , character table 41 T2—6.1 , character table 41 T2—6.1
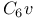 , operations 40 F2—6.1 , operations 40 F2—6.1
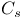 109 109
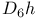 40 40
Abelian group 42
Acceptor levels 159
Acoustic bands 196
Acoustic branches 196
Active picture 28
Alloys 198
Alloys, rigid band model 198
Altmann 45 63 119 183 195 204 212 226
Ammonia 214
Amplitude 20
Antoncik 183
Apostol 212
Arfken 85
Ashcroft 22 63 85 165
Atkins 23 45
Augmented plane wave method 183
Austin 183
Austin — Heine — Sham pseudopotential 182 (10—4.15)
Austin — Heine — Sham pseudopotential, form of wave equation 181 (10—4.9)
Baldea 212
Band 17 95 see
Band gap 138
Band gap, Fermi level in it for semiconductors 159
Band gap, nearly free-electron method value 171 (10—1.33)
Band gap, states in it 227
Band gap, type I 173
Band gap, type II 173
Band label 99
bands 17 99
Bands, antibonding 232
Bands, bonding 232
Bands, condition for two bands to touch or cross at given k 111 116
Bands, conduction 140 158
Bands, continuity over the Brillouin zone 112
Bands, degeneracies 113 115
Bands, guesswork of trends 114
Bands, inversion symmetry with respect to k 118 (6—5.6)
Bands, periodicity of energy in reciprocal space 112 (6—4.1)
Bands, relation to free atomic levels 100 F5—6.1
Bands, valence 158
Bases 35 see
Bases of space group representations 103
Bases of space group representations, condition for same k to be repeated in same basis 111
Bases of space group representations, generated by k vectors 104
Bases of space group representations, group of the k vector 107
Bases of space group representations, importance of use of bases of invariant subgroup T 104
Bases of space group representations, separate all k vectors of Brillouin zone in disjoint sets 104
Bases of space group representations, small representations 110
Basis of a crystal pattern 50
Basis of a representation 35
Basis of a representation, direct sum 35
Basis of a representation, irreducible 37
Basis of a representation, reduction 36
Bassani 183
benzene 39
Benzene, energy levels 42 F2—6.2
Binary rotations 53
Blakemore 22 165
Bloch functions 97 (5—6.3)
Bloch functions, as eigenfunctions of the translations 97 (5—6.2)
Bloch functions, as modulated plane waves 98 (5—6.9)
Bloch functions, asymptotic relation to atomic states 99
Bloch functions, asymptotic relation to plane waves 99
Bloch functions, definition depends on form of translation representative 98
Bloch functions, effect of space group operators 102 (6—1.1)
Bloch functions, form for the wrong translation representatives 100 P5—7.2
Bloch sums 174 (10—2.6)
Bloch sums, for a lattice with basis 246 P14—5.8
Bloch sums, for linear chain 175 (10—2.12)
Bloch sums, use in tight-binding method 174 (10—2.7)
Boas 85
Body-centred cubic lattice 52 F3—3.2 77 84
Boon 45
Born-von Karman boundary conditions 8
Born-von Karman boundary conditions, in a periodic lattice 87
Bouckaert 119
Boundary conditions, Born-von Karman 8
Boundary conditions, box 21 P1—9.6—P1—9.9 249
Boundary conditions, periodic 11
Bozovic 212
Bra 79
Bradley 63 119
Bragg reflection 132
Bragg reflection, its relation to group velocity 136 see
Bragg scattering 193
Brass alloy phases 199
Brass alloy phases, Hume — Rothery rules 199
Brass alloy phases, Jones theory 199
Bravais lattice 51
Bravais lattice, must be a lattice without basis 53
Bravais lattice, of crystal pattern 52
Bravais lattice, synonymous with lattice and translational lattice 52
Bra—ket 79 (4—9.3)
Brillouin 101
Brillouin zone 92
Brillouin zone, all operations of P are covering operations 93
Brillouin zone, as centred primitive cell of the reciprocal lattice 92
Brillouin zone, basic domain 115
Brillouin zone, construction 143
Brillouin zone, folding back 147
Brillouin zone, for one-dimensional chain 100 P5—7.5
Brillouin zone, it has inversion symmetry from conjugator 118
Brillouin zone, it has no geometrical symmetry of its own 93 116
Brillouin zone, number of states inside 94 96
Brillouin zone, of higher order 141
Brillouin zone, open polyhedron property 93
Brillouin zone, permitted k vectors inside label all energy eigenstates 94
Brillouin zone, properties of faces 131
Brillouin zone, properties of faces, cusps 134
Brillouin zone, properties of faces, cusps, relation to group velocity 136
Brillouin zone, properties of faces, energy derivatives 133 (8—2.8)
Brillouin zone, properties of faces, k vectors 132
Brillouin zone, quantization of k vectors inside 95 F5—5.1
Brillouin zone, three—dimensional definition 143
Buerger 63
Bullett 183
Burns 63
Cell functions 98
Cell functions, asymptotic relation to atomic states 99
Celli 183
Cellular method 183
Centred primitive cell 50 92
CHARACTER 37 (2—4.17)
Character table 109 T6—3.1
Circular frequency 19 (1—8.7)
Circular wave number 19 (1—8.6)
class 24
Cochran 197
Cohen 183
Conduction band 140 158
Conductivity 184
Conductivity, relation to Fermi surface 185 (11—1.6)
Conductor 140
Configuration space 26
Configuration space operator 28
Conjugate element 24
Conjugate representations 251 P2—7.6
| Conjugator operator 32 (2—3.11)
Conjugator operator, commutes with symmetry operations 33
Conjugator operator, inverts k vector of Bloch functions 118 (6—5.1)
Conjugator operator, it is non linear 33
copper 161
Copper, band structure 162 F9—2.1
Copper, Brillouin zone 157 F9—1.3
Copper, crystal structure 162
Copper, density of states 162 F9—2.1
Copper, details 165 P9—4.2 P9—4.3
Copper, Fermi surface 163 F9—2.2 164
Copper, free-electron energies 165 P9—4.4
Core electrons 7
Cornwell 45
Cotton 45
Cottrell 22 183 200 212
Coulson 240
Covering operation 26
Cox 22
Cracknell 63 119
Crystal lattice 52 64
Crystal pattern 46
Crystal structure 46
Crystal vibrations 186
Current density 184
Cyclic groups 42 P2—7.3 215 250
Cyclic groups, partition space into disjoint cells 214 216
Cyclic groups, properties 215
Cyclic groups, their representations are faithful 216
d band 162
d band, in noble metal 164
d band, in transition metal 164
Dangling bond 230
De Haas — Van Alphen effect 148
Degeneracy 31
Density of states 14
Density of states, for free electrons 15(1—5.7)
Density of states, free-electron gas 16 Fl—5.1
Diamond crystal pattern 153 154
Diamond crystal pattern, bond lengths 165 P9—4.1
Diamond crystal pattern, Bravais lattice 154
Diamond crystal pattern, point group 154
Diamond crystal pattern, space group 155
Dimmock 183
Direct product 25 (2—1.7) (2—1.8)
Direct product, basis 204 (12—2.12)
Direct product, character 210 (12—4.3)
Direct product, matrix 204
Direct product, representations 38
Direct product, symmetrized 210
Direct sum, of bases 35
Direct sum, of matrices 35
Displacement vector 188
Donor levels 159
Electron density 14
Electron-phonon interactions 203
Electron-phonon scattering 192
Electrons 149
Electrons, relation to holes 149
Energy as a function of k 92 112
Energy as a function of k, contacts or crossings at given k 111
Energy as a function of k, inversion symmetry in reciprocal space 118
Energy as a function of k, periodicity in reciprocal space 112 (6—4.1)
Energy as a function of k, symmetry in reciprocal space due to the star 115
Energy eigenvalues 31 (2—3.3)
Energy eigenvalues, are labelled by k vector 92
Energy level surfaces 135
Energy level surfaces, discontinuities at the Brillouin zone edge 145 F8—7.1
Equivalent functions 213 215(13—1.7)
Equivalent functions, close formula 219(13—1.33)
Equivalent functions, construction 218 (13—1.20)
Equivalent functions, orthogonal for different cells 218
Equivalent k vectors 91
Exchange integral 176 (10—2.15) 231
Exchange interactions 166
Extended zone scheme 143 141
Extrinsic semiconductivity 159
Extrinsic semiconductor 140
Face-centred cubic lattice 76 F4—7.1
Face-centred cubic lattice, Brillouin zone 131 F8—1.1
Face-centred cubic lattice, its reciprocal 76 F4—7.1 84
Faithful representations 216
Falicov 44 212
Fermi energy 13 146
Fermi energy, for free electrons 16 (1—6.4)
Fermi sphere 14
Fermi surface 14
Fermi surface, displacement under electric field 185 F (11—1.1)
Fermi surface, experimental determination 148
Fermi surface, extremal cross-sections 148
Fermi surface, for simple square lattice 147 F8—7.2 148
fermions 13
First Brillouin zone see Brillouin zone
Flores 247
Folding back 147
Forbidden energy gap 138
Fourier coefficients 81 (4—9.19)
Fourier series 78 81
Fourier series, for lattice with basis 82 (4—9.25)
Fractional translation 55
Free-electron approximatio 167
Function products, transformation properties 204(12—2.12) 266 269
Function space operator 28 29
Function space operator, isomorphic to configuration space operators 30(2—2.8)
Function space operator, wrong form 45
Function transformation 28
Function transformation, wrong form 45
Functional transformations 29
G, a group 24
G, a space group 56
Garcia Moliner 247
General k vector 116
General k vector, bands cannot touch or cross at them 116
Glazer 63
Glide reflection 55
Gold 63 119 212
Green function 237
Green function, explicit form 239 (14—3.30)
Group 24
Group of the k vector 107
Group of the k vector, varies over star 110
Group velocity 20 (1—8.13)
Group velocity, from energy gradient 135 (8—3.2)
Group velocity, it is normal to level surfaces of energy 135 F8—3.1
Group velocity, not always parallel to momentum 135
Group, associative condition 24 (2—1.2)
Group, closure 24
Group, conjugate element 24
Group, identity 24 (2—1.3)
Group, inverse element 24(2—1.4)
Group, product of elements 24
Groves 63 85
Hamcrmcsh 45
Hamiltonian 9
Hamiltonian, vibronic 203(12—2.8)
Harmonic approximation 188
Harmonic oscillations 186
harmonic oscillator 186
Harmonic oscillator, eigenvalues 186 (11—2.3)
Harmonic oscillator, quantum mechanical Hamiltonian 186 (11—2.1)
Harris 212
Harrison 183
Hash 67
Heine 44 181 183
Hermite functions 186
Herring 183
Hexagonal close-packed structure 83 F4—9.1
Hexagonal close-packed structure, phase change 211 P12—4.5
Hexagonal close-packed structure, two dimensional (lattice) 73 F4—5.1
Hiickel approximation 177
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



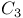
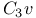 , as the group of ammonia
, as the group of ammonia