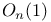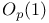|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bishop Y.M.M., Feinberg S.E., Holland P.W. — Discrete Multivariate Analysis, Theory and Practice |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
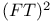 see “Freeman — Tukey” see “Freeman — Tukey”
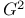 see “Likelihood ratio statistic see “Likelihood ratio statistic
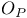 , , 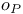 notation see “Stochastic order” “Stochastic notation see “Stochastic order” “Stochastic
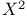 see “Pearson’s chi square” see “Pearson’s chi square”
Abelson, R.P 359 531
Additive models 23—24 (see also “Partitioning chi square” “Lancaster’s
Agreement, measures of 393—400 501—502 measures
AID see “Automatic interaction detection”
Aitchison, J. 370 531
Altham, P 393 403531
Anderson, T.W 260 262 265 267 274 531
Andrewartha, H.G. 234 531
Angular transformation for binomial 367—369 491—492 “Transformations variance-stabilizing”)
Anomalies in data 332—337
Anscombe, F.J. 454 531
Arcsin transformation 367—369 491—492
Armitage, P. 400 531
Association, measures of, asymptotic variances for 374 501—502
Association, measures of, for 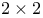 tables 376—385 tables 376—385
Association, measures of, for IxJ tables 385—393
Association, measures of, geometry of 383—385
Association, measures of, interpretability of 374—375
Association, measures of, norming 375—376
Association, measures of, sensitivity to margins 375 392—393 measures “Correlation “u-terms”)
Association, measures of, symmetry 376
Association, surface of constant 52—53
Asymptotic theory 457—530 (see also “Bayes estimators”)
Automatic interaction detection 360
Bahadur, R.R. 415
BAN (best asymptotic normal) 58 126 349 352 518
Bartlett, M.S 63 83 87 270 357 363 368 531
Bayes estimators 404—410
Bayes estimators, asymptotic results for 410—416
Bayes estimators, risk function of 406—407
Bayes estimators, small sample results for 416—419 421—424
Beard, J.H. 90 537
Beck, A 230 531
Bennett, B.M. 400 531
Benson, L. 99 531
Berelson, B. 265 537
Bergerson, H.W. 340
Berkson, J. 126 347 355 358 531
Bhapkar, V.P. 284 306 352 353 531 532
Bhat.B.R 370 532
Binomial distribution, angular transformation for 332—337 367—369 491—492
Binomial distribution, asymptotic distribution of powers 478—479 488
Binomial distribution, asymptotic normality of 464—465
Binomial distribution, behavior of minimax estimators for 416—417
Binomial distribution, estimation of proportion 437
Binomial distribution, estimation of sample size 437—438
Binomial distribution, moments of 436—437
Binomial distribution, negative 316—317 339—340 452—454 500
Binomial distribution, orders of 477
Binomial distribution, variance of squared proportions 485
Binomial distribution, variance stabilization for 491—492 (see also “Sampling distributions”)
Birch, M.W. 3764 69 94 146 161 365 366 446 509 511 532
Birch’s results for MLEs, uniqueness of 69
Birch’s results for MLEs, uniqueness of, regularity conditions for 509—511
Bishop, Y.M.M. 7 41 105 106 124 125 134 135 148 150 178 193 196 197 198 401 532
Black, M.M. 102 103 538
Blackwell, D. 532
Blendis, L.M 400 531
Bloch, D. 403 532
Block-diagonal table 182
Block-stairway table 194—198
Block-triangular table 194—198
Bock, R D. 84 142 344 360 532
Bootstrap-Bayes estimators see “Pseudo-Bayes estimators”
Bortkiewicz, L.V. 325 532
Bose, RC 182 532
Bowker, A.H 283 284 532
Braungart, R G. 379 380 532
Breaking-apart see “Rearranging data”
Brown, D.R 85 532
BSS (between-group sum of squares) 390
Bush, N. 182 534
Bush, R 260 262 532
Byars, J.A. 410 540
Cameron, W.R 178 532
Capture-recapture models, incomplete tables and 233 237—239 246—247
Capture-recapture models, incomplete tables and, general 246—254
Capture-recapture models, incomplete tables and, interpreting dependencies in 230 255
Capture-recapture models, incomplete tables and, three-sample 237—245
Capture-recapture models, incomplete tables and, two-sample 231—237
Cassedy, J.H. 362 532
Caussinus, H. 178 284 286 287 289 294 298 532
Cell values, elementary 13 61
Cell values, nonelementary 61
Cell values, smoothing 123 401—433
Cell values, standardized residual 136—139
Cell values, sums of 61 (see also “Configuration” “Zero
Chains, Markov for different strata 277—279
Chains, Markov, order of 269—270
Chapman, D.C. 237 532
Chase, G.R 524 532
Chatfield, C 275 532
Chen, W.Y 178 532
Chernoff — Pratt theory see “Stochastic order” “Stochastic
Chernoff, H 475 480 523 533
Chi square distribution, percentage points of 527 (see also “Chi square statistic”)
Chi square statistic, see also “Minimum logit 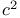 ” “Neyman’s “Pearson’s ” “Neyman’s “Pearson’s
Chi square statistic, association measures based on 310—332 385—387
Chi square statistic, asymptotic distribution, under null hypothesis 472—473 516—518
Chi square statistic, asymptotic distribution, under null hypothesis, “under alternative hypothesis” 329—330 473—474 518
Chi square statistic, comparing several 330—332
Closed-form estimates see “Direct estimates”
Cochran, W.G. 63 146 307 366 533
Cochran’s Q test 307—309
Cochran’s test for combined tables 146—147
Cohen, J 395 396 533 534
Cohen, J.E. 152 153 213 533
Cohen’s measure of agreement, K 395—397
Cole, N.W. 403 539
Coleman, J.S 397 533
Collapsing, general definition of 47
Collapsing, general theorem for 47—48
Collapsing, illustration of 41—43
Collapsing, theorem for 3-way array 39—40
Collapsing, two-way tables 27—28
Colton, T. 230 542
Combination of 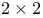 tables 365—366 (see also “Mantel” “Haensel “Collapsing”) tables 365—366 (see also “Mantel” “Haensel “Collapsing”)
Combining categories 27—29 (see also “Collapsing”)
Complete data, fitting incomplete models to 111—114 (see also “Incomplete arrays” “Comprehensive
Complete tables, definition of 58
Comprehensive model, definition 38 66—67
Computer programs 7
Conditional distribution for Poisson variates 440—441 (see also “Incomplete tables”)
Conditional distribution, exact theory for 364—366
Conditional tests, for interaction 148 364—366
Conditional tests, for marginal homogeneity 293—296 307—309
Confidence interval, asymptotic for cell probability, p 478
Confidence interval, asymptotic for measures of association 374 380 382
Confidence interval, asymptotic, use of asymptotic variances for 499—500 (see also “Variance asymptotic”)
Configuration, correspondence of, with u-terms 66
Configuration, definition of 61
Configuration, empty cells in 90
Configuration, of same order, degrees of freedom 119—122
Connectivity see “Separability”
Conover, J. 124 533
Constructing tables 25—26
Contingency tables 57
Continuous variables 360
Contrasts see “Linear contrasts”
Convergence in distribution 463—465 467—475
Convergence in distribution and 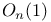 478—479 478—479
Convergence in distribution and 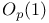 474 474
Convergence in distribution and probability 477—479
Convergence in probability 465—467
Convergence of moments 484—486
Cormack, R.C 229 248 533
| Cornfield, J. 359 360 365 366 533 541
Correlation coefficient, association measures based on 380—385
Correlation coefficient, chi square and 382
Correlation coefficient, partial, related to collapsing 41
Correlation coefficient, related to cross product 14—15
Correlation coefficient, variance stabilization of 500—501
Cox, D.R 1 143 358 359 360 365 368 533
Craddock, J.M 140 533
Craig, A.T. 65 536
Craig, W. 275 276 277 533
Cramer, H 348 386 393 486 533
Cramer’s measure of association, V 386—387
Crittenden, L.B. 178 532
Cross-product ratio, as loglinear contrast 15 26—27
Cross-product ratio, association measures based on 377—380 393
Cross-product ratio, asymptotic variance of 377 494—497
Cross-product ratio, definition of 13
Cross-product ratio, functions of 379 601
Cross-product ratio, interpretation of 14—15
Cross-product ratio, properties of 14 377
Cross-product ratio, related to correlation coefficient 15
Cross-product ratio, related to u-terms 17—18
Cross-validation of models 319—320
Cyclic descent, method of see “Fitting iterative
D-association see “Separability”
D-separability see “Separability”
Darroch, J.N. 85 101 229 240 247 248 249 250 289 533
Das Gupta, P. 240 246 247 533
Das.T. 191 192 533
Davis, J.A. 373 533
Davis, P.J 411 533
Dawber, T.R 358 533
Degrees of freedom, adjusting, for empty cells 115—119
Degrees of freedom, for closed-form models 121—122
Degrees of freedom, for complete tables 25 35 66 114—122
Degrees of freedom, for marginal homogeneity 287 294 307
Degrees of freedom, for quasi-independence 187—188
Degrees of freedom, for quasi-loglinear models 216—220
Degrees of freedom, for quasi-symmetry 287 303
Degrees of freedom, for symmetry 283 301—302
Delta method, for binomial distribution 481—482
Delta method, for calculating asymptotic distributions 486—502
Delta method, for capture-recapture problem 249—250
Delta method, multivariate theorem 492—497
Delta method, one-dimensional theorem 487—490
Deming — Stephan procedure see “Fitting iterative
Deming, W.E. 84 233 234 235 247 533 540
Deutsch, K.W 178 540
Devinney, L.C 137 138 160 541
Dickey, J.M 404 533 534
Direct estimates, difference between models with 129—130
Direct estimates, equivalence to iterative 74 201—202
Direct estimates, for multiway incomplete tables 217221—223 248
Direct estimates, for quasi-independence 192—201
Direct estimates, in three or four dimensions 74—75
Direct estimates, partitioning 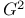 for models with 170—171 for models with 170—171
Direct estimates, rules for detecting 76—77
Direct estimates, theorems for detecting 78—82
Dirichlet distribution 405—406
Disagreement 398—399 (see also “Agreement”)
Distributions see “Sampling distributions”
Duncan, D.B. 359 360 541
e, approximating 460—462
Eccleston, J. 215 534
Eckler, A.R 340 341 342534
Efron, B. 403 534
Einhorn, H. 360 534
Elston, R.C 182 534
Empirical — Bayes see “Pseudo-Bayes”
Empty cells see “Zero entries”
Entropy, maximum, theorem relating to linear models 346 (see also “Information theory”)
Error, prediction, measures of reduction in 387—389
Estimability, compared with connectedness 215
Estimability, of parameters in incomplete table 219—220
Estimation see “BAN” “Bayes “Information “Maximum “Minimum methods” “Minimum
Everett, B.S. 396 534
Exact theory, for 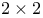 tables 364—365 tables 364—365
Exact theory, for combined tables 365—366
Exact theory, practicability of 366
Exponential distribution, as limit of long waiting times 467—468
Exponential distribution, distribution of minimum 477—478
Feller, W. 261 428 464 469 524
Fienberg, S.E 50 52 53 54 55 85 99 164 178 186 193 196 197 198 210 221 222 224 221 229 210 234 231 404 401 402
Fienberg, S.E. 413 414 416 417 418 421 422 423 425 429 433 496 532 534 541
Finney, D.J 367 371 534
Fisher, R.A. 58 63 328 364 365 367 453 489 527 534
Fitting, iterative proportional, classical usage 97—102 337 392
Fitting, iterative proportional, convergence of 85—87 94—95 289
Fitting, iterative proportional, for asymptotic variances 250—251 253—254
Fitting, iterative proportional, for MLEs 83
Fitting, iterative proportional, for quasi-symmetry 289
Fitting, iterative proportional, general algorithm 91—97
Fitting, iterative proportional, in three dimensions 84—85
Fitting, iterative proportional, incomplete tables 188—192 217
Fitting, iterative proportional, initial estimates 92—95
Fitting, iterative proportional, properties of 83
Fitting, iterative proportional, stopping rules 95—96 (see also “Maximum likelihood estimates”)
Fleiss, J.L 1 396 400 534
Flood, C.R 140 533
Foa, U. 297 298 299 534
Four-fold table (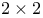 table), definition of 11—12 table), definition of 11—12
Four-fold table (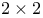 table), descriptive parameters of 13—14 table), descriptive parameters of 13—14
Four-fold table (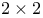 table), geometry of 49—55 383—385 table), geometry of 49—55 383—385
Francis, W.N 331 537
Frank, M 220 221 534
Freeman — Tukey, chi square 130 137 513—516
Freeman — Tukey, chi square, transformation for binomial 367—368 492
Freeman — Tukey, chi square, transformation for Poisson 137 492
Freeman — Tukey, chi square, transformation, residuals for 130 137—140 334—337
Freeman, M.F 137 367 492 534
Frei, E 371
Freidlander, D 97 98 534
Frequency of frequencies 337—342 (see also “Sampling distributions”)
Fryer, J.G 306 535
Gafarian, A.V 524 539
Gage, N.L 275 542
Gart, J 353 365 366 535
Gaudet, H 265 537
Geiger, H 233 535
Geometry, of Bayes estimators 408—410
Geometry, of measures for 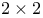 tables 49—55 383—385 tables 49—55 383—385
Gilbert, J.R 52 53 54 55 384 534
Gini, C 389 390 535
Gini’s definition of variation 389—390
Girshick, M.A 532
Glass, D.V 100 206 209 320 427 535
Goldman, A 132 535
Good, I.J 1 337 338 345 346 403 406 425 535
Goodman, L.A 84 127 137 143 146 148 166 169 177 178 182 183 190 193 196 200 201 207 209 225 226 227 228 260 262 265 266 267 270 320 322 323 353 373 374 375 376 380 387 388 389 391 393 502 531 535 536
Goodness-of-fit, asymptotic distribution of test statistics for 513—529
Goodness-of-fit, asymptotic equivalence of 3 statistics 513—514
Goodness-of-fit, fitting and testing for 317—324
Goodness-of-fit, for sampling distributions 315—317
Goodness-of-fit, multinomial general theory of 507—508
Goodness-of-fit, of internal cells 136—141
Goodness-of-fit, too good a fit 324—329
Goodness-of-fit, when model is false 329—332 (see also “Chi square” “Likelihood “Neyman’s “Pearson’s
Greenhouse, S.W 124 538
Grizzle, J.E 124 284 306 308 353 354 536
Gross, R 369 402 536
Gumbel, E.J 327 536
Haberman, S 7 64 65 70 84 85 178185 189 193 208 216 250 452 536
Haenszel, W 146 367 538
Haight, F.A 435 536
Haldane, J.B.S 442 536
Halkka, O 224 536
Halperin, M 178 538
Hansen frequencies, asymptotic distribution of 489
Hansen, E.W 489 536
Harris, J.A 183 184 204 205 536
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



 ,
,  notation
notation 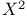
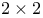 tables
tables  ”
” tables
tables