|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bishop Y.M.M., Feinberg S.E., Holland P.W. Ч Discrete Multivariate Analysis, Theory and Practice |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Rearranging data, relabeling 102Ч105
Regularity conditions see УBirchТs results for MLEsФ
Reinfiirt, D. 284 306 537
Relatives, high order 34
Rho(p) measuring association 381Ч385
Ries, P.N. 142 143 540
Risk, expected squarred error 313Ч335
Risk, for comparing Bayesian estimators 406Ч408
Risk, ratios, limiting 414Ч416
Risk, relative 11 (see also УCross-product ratioФ)
Robbins, H 403 540
Romig, H.G 436 540
Roscoe, J.T. 410 540
Rosen, B. 368 540
Rourke, R.E.K. 331 332 436 538
Roy, S.N. 84 540
Rudolf, G J 64 344 455 540
Samejima, F. 344 540
Sampling design, constraints on models 36
Sampling design, stratified 29Ч30
Sampling distribution 62Ч64 185 212
Sampling distribution, effect on model selection 70Ч71 (see also УBinomial distributionФ УHypergeometric УMultinomial УPoisson
Sampling models, search for 315Ч317
Sanathanan, L. 237 255 540
Sandler, I 200 201 202 205 538
Saturated models 9
Savage, I.R. 178 186 540
Schoener, T.W. 164 540
Scoring categorical variables 360
Scott, W.A 369 540
Search procedures see УStepwise model selectionФ
Sekar, C.C. 233 234 235 540
Selesnick, H.L. 107 108 109 540
Sensitivity 20Ч21 48
Separability, dealing with 184Ч187
Separability, in 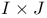 tables 182Ч183 tables 182Ч183
Separability, in many dimensions 212Ч216
Separability, semi- 194
Shepard, R.N 298 540
SideLV. 230 542
Silvey, S.D. 370 531
Simplicity in model building 312Ч315
Skarin, A.T 124 125 248 540
Smith, A.F.M. 403 538
Smith, D.H 210 242 241 540
Smith, H. 142 141 540
Smoothed counts see УCell values smoothingФ
SMR (Standard Mortality Ratio) see УRates standard
Smyllie, H.C. 400 511
Sonquist, J.A. 160 540
Spagnuolo, M. 116 111 111 541
Sparse multinomials 410Ч413
Specificity 20Ч22 48
Square tables 281Ч309 320Ч324 339Ч342 347
Standard deviation and stochastic order 476Ч477
Standardization see УFitting iterative classical УRatesФ
Star, S.A 117 118 160 541
Starmer, F 284 106 108 151 354 516
Stationarity, of transition probabilities 261Ч267 269
Stein, C. 403 404 409 541
Stephan, F.F. 84 533
Stepwise model selection 165Ч167
Steyn, H.S 144 451 454 541
Stochastic order, Chernoff Ч Pratt theory for 479Ч484
Stochastic order, definition of 475Ч476
Stochastic order, methods for determining 476Ч477
Stochastic order, of exponential variables 477Ч478
Stochastic order, of moments 485Ч486 (see also УStochastic sequenceФ)
Stochastic sequence, Chernoff Ч Pratt theory for 479Ч480
Stochastic sequence, convergence of 463Ч475
Stochastic sequence, determining order of 476Ч478
Stochastic sequence, formal structure of 480Ч482 (see also УStochastic orderФ)
Stouffer, S. 137 138 160 541
Structural models, definition of 9Ч10
Structural models, uses of 11
Stuart, A. 284 541
Suchman, E.A. 117 118 160 541
Sufficient statistics 64Ч67
Sufficient statistics, for three-dimensional models 66
Sufficient statistics, general derivation of 68Ч69
Sufficient statistics, minimal set of 66
Sufficient statistics, minimal set of, and direct estimates 78
Summary statistics see УAssociation measures УChi УFrequency of УRatesФ УSufficient
Suppressing parameters 332Ч337
Sutherland, M 409 412 429 411 411 516 541
Svalastoga, K 100 209 210 228 120 427 541
Symmetry, exact 260
Symmetry, in association measures 376
Symmetry, in square tables 258 282Ч286 299Ч306 347Ч348
Symmetry, quasi- 286Ч292 303 296
| Symmetry, relative 260
Synergism see УWorcester modelФ
t see УTschuprowТs measure of associationФ
Taback, M.A.M. 90 517
Tallis, G.M 288 541
Taranta, A 116 117 118 541
Taylor expansion 460Ч461
Testing, and fitting 317Ч324
Testing, simplifying structure before 150
Testing, use of asymptotic variances for 498Ч499 (see also УInteractionФ УPartitioning
Tetrahedron, of reference 50
Thayer, D.T. 402 522
Theil, H 151 541
Thomas, G.B.Jr. 416 518
Thompson, V. 221 224 225
Transformations, variance-stabilizing 366Ч371 491Ч492 УArcsine УLogit УFreeman УProbit
Transition probabilities 262Ч269
Transition probabilities, single sequence 270Ч273
tree structures 360
triangular arrays see УIncomplete arraysФ
Trinomial distribution, for risk of pseudo-Bayesian estimators 417Ч419
Truett, J. 159 160 541
Trybula, S 407 541
Tschuprow, A.A. 385
TschuprowТs measure of association, T 385Ч387
TSS (total sum of squares) 390
Tukey, J.W. 117 112 119 159 167 168 492 511 534 518 541
U, as collection of u-terms 62
U, as measure of association 389Ч392
u-terms, definition 17Ч18
u-terms, generalized notation 61Ч62
u-terms, interpretation of 29Ч30 32Ч34
u-terms, relationship to cross-product ratios 17Ч18
u-terms, standardized estimates of 141Ч146 153 156
u-terms, variance of 494Ч497 (see also УLog-linear modelФ УLinear
Unsaturated models 9
V, CramerТs measure of association 386Ч387
Vandaele, W. 401 542
VanEeden, C. 412 541
Variance, asymptotic 498Ч499
Variance, asymptotic, for confidence intervals 499Ч500
Variance, asymptotic, for hypothesis testing 488Ч499
Variance, for capture-recapture problem 233 240Ч242 248Ч254
Variance, for distance measures 518Ч519
Variance, methods for computing 248Ч251 (see also УDelta methodФ)
Variance, stabilizing transformations 491Ч492 500Ч501
Variation, measures of 389Ч393
Varner, R.N 244 262 517
Vechio, T.J. 22 541
Vidmar, N. 201 206 541
Waite, H. 178 541
Waiting times 467Ч468
Wald, A. 352
Walker, S.H. 259 360 541
Wallace, D.L. 316 317 318 529
Watson, G.S 178 403 405 521 532 541
Weeks, D.L. 215 541
Werner, A 233 535
White, H.C. 191 192 541
Wilks, S.S. 405 541
Williams, D.R. 211 541
Williams, O.D. 353 536
Williams, R.M.Jr. 122 138 160 541
Willick, D.H. 386 387 388 391 541
Wilson, E.B. 527 541
Winsor, C.P. 225 226 541
Wittes, J.T. 230 240 247 252 253 541 542
Worcester model 111
Worcester, J. 96 111 112 141 542
WSS (within-group sum of squares) 390
Y see Association УYuleФ
Yarnold, J. 140 542
Yates, F. 124 542
Yee, A.H. 275 542
Yerushalmy, J. 132 542
Youtz, C. 137 368 492 539
Yuasa, S. 102 103 538
Yule, G.U. 375 377 378 381 382 542
YuleТs Q as measure of association 378Ч380 501
YuleТs Y as measure of colligation 378Ч380
Zacks.S. 65 485 542
Zangwill, W.I. 251 225 542
Zelen, M. 365 366 452 542
Zellner, A 261 353 403 522 542
Zero entries, deviations in cells with 140
Zero entries, diagonals with, in square tables 296Ч299
Zero entries, invalidating model 72
Zero entries, random, defined 59 177
Zero entries, structural 31 59 93 177
Zero entries, unrepeated events in Markov chains 275Ч276 (see also УConfigurationФ)
Zorb, G. 245
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 tables
tables