|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Rencher A.C., Barnett V., Bradley R.A. (Ed) Ч Multivariate Statistical Inference and Applications |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Multivariate inferential procedures 1Ч2
Multivariate normal distribution 37Ч59
Multivariate normal distribution and quadratic form 48Ч49
Multivariate normal distribution, central limit theorem 51
Multivariate normal distribution, conditional distribution 47Ч48
Multivariate normal distribution, constant density ellipsoid 40Ч41
Multivariate normal distribution, contour plot 40Ч42
Multivariate normal distribution, estimation of  and and 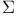 49Ч51 49Ч51
Multivariate normal distribution, estimation of  and and 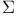 , properties of estimators 52Ч56 , properties of estimators 52Ч56
Multivariate normal distribution, estimation of 51Ч52 51Ч52
Multivariate normal distribution, generating data from 42
Multivariate normal distribution, independence and zero covariance 46Ч47
Multivariate normal distribution, likelihood function 49
Multivariate normal distribution, linear functions of 45Ч46
Multivariate normal distribution, marginal distribution 46
Multivariate normal distribution, moment generating function of 44Ч47
Multivariate normal distribution, moments of 42Ч43
Multivariate normal distribution, properties of 43Ч49
Multivariate normal distribution, tests for multivariate normality 43
Multivariate normal distribution, transformations to achieve multivariate normality 56Ч57
Multivariate normal distribution, transformations to achieve multivariate normality and Wishart distribution 53Ч56
Multivariate normality, tests for 43
Multivariate regression see УRegression multivariateФ
Multivariate t-distribution 56
Nonparametric tests for several mean vectors 194
Nonparametric tests for two mean vectors 113
Normal distribution, multivariate normal see УMultivariate normal distributionФ
Normal distribution, univariate normal 37Ч38
Normal distribution, univariate normal, standard normal 37
Normality, tests for 43
O matrix 401
Orthogonal matrix 410
Orthogonal vectors 410
Outliers 43 301Ч303 373
Paired observation test 97Ч99
Partial F 177 211 214Ч215 217 219 248Ч249 252
Perron Ч Frobenius theorem 414
Physiological data 224
PillaiТs test 292 295 296
PillaiТs test, F-approximations 130
PillaiТs test, table of critical values 431Ч437
PillaiТs tests 130Ч131 292 295Ч296
Positive definite matrix 408
Power of a test 104Ч108
Power of a test, noncentrality parameter 104
Principal component regression 363Ч370
Principal components 337Ч376
Principal components and correspondence analysis 373
Principal components and eigenvalues 338 341
Principal components and eigenvectors 338
Principal components and factor analysis 361 377
Principal components and maximum variance 338
Principal components and minimum variance 339
Principal components and multidimensional scaling 373
Principal components and projections 340
Principal components and regression 363Ч370
Principal components and regression, biased regression 363
Principal components and regression, latent root regression 363 370
Principal components and regression, principal component regression 363Ч370
Principal components and regression, principal component regression, using correlation matrix 364 367Ч370
Principal components and regression, principal component regression, using covariance matrix 364Ч367
Principal components and regression, ridge regression 363
Principal components as rotation of axes 343Ч344
Principal components from covariance matrix (S) 338Ч344 348Ч355 357Ч363
Principal components of singular matrix 342
Principal components with grouped data 371Ч372
Principal components with grouped data, common principal components 371Ч372
Principal components with grouped data, comparing principal components 371Ч372
Principal components, common principal components 371Ч372
Principal components, correlations of 341Ч342
Principal components, definition 338
Principal components, discarding components 347Ч352
Principal components, discarding components, average eigenvalue 348
Principal components, discarding components, bootstrap 352
Principal components, discarding components, cross validation 352
Principal components, discarding components, jackknife 352
Principal components, discarding components, percent of variance 347
Principal components, discarding components, rank of 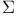 352 352
Principal components, discarding components, scree graph 348Ч349
Principal components, discarding components, tests of significance 349Ч351
Principal components, empirical orthogonal functions 337
Principal components, from correlation matrix (R) 342 344Ч349 351 353Ч359 364 367Ч370
Principal components, from correlation matrix (R), properties of 344Ч345
Principal components, generalized principal components 340
Principal components, influence of each observation 372Ч373
Principal components, interpretation 353Ч363
Principal components, interpretation, correlations 361Ч363
Principal components, Karhunen Ч Loeve expansion 337
Principal components, large variance of a variable, effect of 342
Principal components, last few principal components 352Ч353
Principal components, leverage of each observation 372
Principal components, number of components to retain see УPrincipal components discarding
Principal components, orthogonality of 339
Principal components, outliers 373
Principal components, percent of variance 341
Principal components, plotting of 340
Principal components, principal component regression 363Ч370
Principal components, principal curves 373
Principal components, principal points 373
Principal components, projection pursuit 340
Principal components, properties of 341Ч343
Principal components, proportion of variance 341
Principal components, robust principal components 373
Principal components, rotation 359Ч361
Principal components, scale invariance, lack of 342
Principal components, sensitivity analysis 355
Principal components, size and shape 355
Principal components, special patterns in S or R 353Ч359
Principal components, special patterns in S or R, equal correlations 354 358Ч359
Principal components, special patterns in S or R, equal variances and covariances 354 357Ч358
Principal components, special patterns in S or R, sensitivity analysis 355
Principal components, special patterns in S or R, size and shape 355
Principal components, tests of significance 349Ч351
Principal components, variance and eigenvalues 341
Principal components, variance of principal component 341
Principal components, variance, large variance, effect of 342
Principal components, variance, proportion of 341
Principal components, variance, total 341
Principal curves 373
Principal points 373
Probe word data 22
Projection pursuit 340
Projections 340
Quadratic classification rule 232Ч233
Quadratic form 48Ч49 404
Quadratic form, lack-of-fit tests 300
Quadratic form, leverage 301
Quadratic form, outliers 301Ч303
Quadratic form, residuals 300Ч301
Random xТs 303Ч305
Random xТs, confidence intervals 305
Random xТs, estimation of the  Тs and Тs and 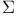 304Ч305 304Ч305
Random xТs, estimation of the  Тs and Тs and 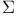 , beta weights 305 , beta weights 305
Random xТs, estimation of the  Тs and Тs and 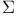 , correlations 305 , correlations 305
Random xТs, model 303Ч304
Random xТs, tests of hypotheses 305
Repeated measures 121 183 246 296
Robust estimation in classification analysis 235
Robust estimation in regression 307
Robust estimation of canonical variates 333
Robust estimation of correlation matrices 29Ч30
Robust estimation of covariance matrices 29Ч31
Robust estimation of discriminant functions 223Ч227
Robust estimation of mean vectors 28Ч31
Robust estimation of means 28
Robust estimation of principal components 373
Robust estimation, affine equivariance of (scale invariance) 30
Robust estimation, breakdown point 30
Robust estimation, contaminated normal 28
Robust estimation, mean deviation 28
| Robust estimators 307
Rotation see УFactor analysisФ
RoyТs test 291Ч292 295 296
RoyТs test (union-intersection) 127Ч129 291Ч296
RoyТs test (union-intersection), table of critical values 435Ч437
RoyТs test, subset of the xТs 293Ч295
RoyТs test, union-intersection test see УRoyТs testФ
RoyТs test, WilksТ 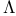 290Ч291 294 296 290Ч291 294 296
Seemingly unrelated regression 306
Seemingly unrelated regressions 306
Selection of variables 111 177 217Ч221
Selection of variables in classification analysis 247Ч251
Selection of variables in higher order designs 218Ч219
Selection of variables in regression 307
Selection of variables, all possible subsets 218
Selection of variables, bias 219Ч221
Selection of variables, stepwise discriminant analysis 217Ч221
Selection of variables, using discriminant functions 217
Singular value decomposition 26Ч27 315Ч316
Size and shape 355
Soils data 103
Specific variance 379
Spectral decomposition 412
Squared multiple correlation see У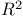 Ф Ф
SSE 269
SSR 271
Standardized vector 45
Stepdown test 110Ч111
Stepwise discriminant analysis 177Ч178 217Ч221
Subset selection 307
Subvector(s) 12Ч14
Subvector(s), conditional distribution 47
Subvector(s), covariance matrix of 13
Subvector(s), distribution of 46Ч48
Subvector(s), independence of 14
Subvector(s), mean of 13
Subvector(s), paired observation 116
Subvector(s), sum of 14
Subvector(s), tests on 108Ч112 174Ч178
Sufficient statistic 52Ч53
t-ests, definition of t-statistic 61
t-ests, likelihood ratio 62Ч65 86
t-ests, one sample 61Ч65
t-ests, properties of 62
t-ests, two samples 85Ч86
t-ests, two samples, comparing means when variances are unequal 99Ч100
Tests of hypotheses 289Ч300 305
Tests of hypotheses and missing data 299Ч300
Tests of hypotheses for additional information 108Ч110
Tests of hypotheses for an individual  297 297
Tests of hypotheses for elliptically contoured distributions 112Ч113
Tests of hypotheses for linear combinations in ANOVA and MANOVA 163Ч171
Tests of hypotheses for linear combinations in multivariate regression 295Ч297
Tests of hypotheses for linear combinations in univariate regression 272Ч273
Tests of hypotheses for linear combinations one sample 72Ч72 79Ч80 83Ч85
Tests of hypotheses for linear combinations one sample, for 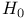 : \mu_1 = \mu_2 = . . . = \mu_p$ 83Ч85 : \mu_1 = \mu_2 = . . . = \mu_p$ 83Ч85
Tests of hypotheses for linear combinations, two samples 94Ч95
Tests of hypotheses for principal components 349Ч351
Tests of hypotheses in discriminant analysis 207Ч210
Tests of hypotheses in regression, multivariate 289Ч299
Tests of hypotheses in regression, univariate 271Ч274
Tests of hypotheses on a subvector 108Ч112 174Ч178
Tests of hypotheses,  -tests see У -tests see У -testsФ -testsФ
Tests of hypotheses, 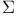 known 60Ч61 known 60Ч61
Tests of hypotheses, 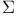 unknown 65Ч74 unknown 65Ч74
Tests of hypotheses, 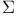 unknown, several mean vectors 121Ч134 unknown, several mean vectors 121Ч134
Tests of hypotheses, 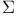 unknown, two mean vectors, unknown, two mean vectors,  85Ч92 85Ч92
Tests of hypotheses, 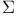 unknown, two mean vectors, unknown, two mean vectors,  , 100Ч104 , 100Ч104
Tests of hypotheses, accepting 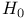 65 65
Tests of hypotheses, analysis of covariance, multivariate see УAnalysis of covariance multivariateФ
Tests of hypotheses, analysis of covariance, univariate see УAnalysis of covariance univariateФ
Tests of hypotheses, canonical correlation 320Ч326
Tests of hypotheses, covariance matrices, BoxТs M-test 138Ч140
Tests of hypotheses, covariance matrices, equality of 138Ч140
Tests of hypotheses, covariance matrices, table of critical values 446Ч447
Tests of hypotheses, E matrix 285 286 290
Tests of hypotheses, equality of covariance matrices 138Ч140
Tests of hypotheses, experimentwise error rate 82 95
Tests of hypotheses, general linear hypotheses 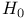 : CB = O and : CB = O and 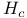 : CBM=O 295Ч297 : CBM=O 295Ч297
Tests of hypotheses, H matrix 290 293 296
Tests of hypotheses, individual variables 80Ч83 95
Tests of hypotheses, individual variables, Bonferroni tests for 80Ч83 95
Tests of hypotheses, individual variables, Bonferroni tests for, modifications of 80Ч82
Tests of hypotheses, individual variables, Bonferroni tests for, protected tests 95
Tests of hypotheses, individual variables, Bonferroni tests for, simultaneous tests for 80 94
Tests of hypotheses, individual variables, Bonferroni tests for, table of critical values 78
Tests of hypotheses, Lawley Ч Hotelling test 292 295 296
Tests of hypotheses, likelihood ratio test see УWilksТ 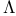 Ф Ф
Tests of hypotheses, likelihood ratio tests see УLikelihood ratio testФ
Tests of hypotheses, MANOVA see УMultivariate analysis of variance mean vectorsФ
Tests of hypotheses, MANOVA, likelihood ratio test 71Ч72 91Ч92
Tests of hypotheses, Mests see Уt-testsФ
Tests of hypotheses, nonparametric tests for several mean vectors 194
Tests of hypotheses, nonparametric tests for two mean vectors 113
Tests of hypotheses, overall regression test 289Ч293
Tests of hypotheses, overall regression test in terms of canonical correlations 323
Tests of hypotheses, paired observation test 97Ч99
Tests of hypotheses, partial F-test 110
Tests of hypotheses, power of tests 292Ч293
Tests of hypotheses, protected tests 95
Tests of hypotheses, robust versions of  -ests 114 -ests 114
Tests of hypotheses, simultaneous tests 80 94 146Ч148 150 274
Tests of hypotheses, stepdown test 110Ч111
Tests of hypotheses, union-intersection test 72Ч74
Total variance 8Ч9 341 382
Trace of a matrix 410
Transformation of a random variable, distribution of 38Ч40
Transformation of a random variable, distribution of, Jacobian 39
Two-sample test for mean vectors 87Ч92
Two-sample test for mean vectors, comparing mean vectors when  100Ч104 100Ч104
Unbalanced data 152 155Ч160 168Ч174
Unbalanced data, contrasts 156Ч160
Unbalanced data, contrasts, Bonferroni confidence intervals 157
Unbalanced data, contrasts, simultaneous confidence intervals 156Ч157
Unbalanced data, discriminant functions 157
Unbalanced data, one-way model 155Ч160
Unbalanced data, tests on individual variables 157
Unbalanced data, two-way model 168Ч174
Unbalanced data, two-way model, constrained model 169Ч171
Univariate analysis of variance see УAnalysis of variance univariateФ
Univariate normal distribution 37Ч38
Variables see also УRandom variablesФ
variables, categorical 2
Variables, commensurate 1
Variables, correlated 1
Variables, standardized 11
Variance inflation factor 21
Variance matrix see УCovariance matrixФ
Variance, generalized 8Ч9
Variance, population 3
Variance, sample 3
Variance, sample, unbiased 3
Variance, total 8 341 382
Variance-covariance matrix see УCovariance matrixФ
Varimax rotation 388
Vector(s), 0 vector 401
Vector(s), definition 399
Vector(s), differentiation 414Ч415
Vector(s), distance between two vectors 22Ч23
Vector(s), distance from origin 402
Vector(s), j vector 400
Vector(s), length of 402
Vector(s), linear independence and dependence of 406
Vector(s), normalized 402
Vector(s), orthogonal vectors 410
Vector(s), partitioned 12Ч14
Vector(s), product of 401Ч402
Vector(s), random 1 (see also УRandom vectorsФ)
Vector(s), standardized vector 45
Vector(s), subvectors 12Ч14 (see also УSubvector(s)Ф)
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 and
and 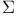

 Тs and
Тs and 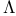
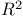 Ф
Ф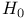 : \mu_1 = \mu_2 = . . . = \mu_p$
: \mu_1 = \mu_2 = . . . = \mu_p$  -tests
-tests 
 ,
, 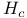 : CBM=O
: CBM=O 