|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Heath T. Ч A History of Greek Mathematics, Vol. 2 |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Pythagoras, motto 25 141
Pythagoras, Proclus on discoveries of 84Ч85 90 119 141 154
Pythagoras, theorem of Pythagoras 142 144Ч149
Pythagoras, theorem of Pythagoras, how discovered? 147Ч149
Pythagoras, theorem of Pythagoras, Pappus's extension ii. 369Ч371
Pythagoras, travels 4Ч5
Pythagoras, travels, story of bribed pupil 24Ч25
Pythagoreans 2 11 220
Pythagoreans, 'all things are numbers' 67Ч69
Pythagoreans, 'friendly' numbers 75
Pythagoreans, 'number' of an object 69
Pythagoreans, 'number' of an object, 'number in the heaven' 68
Pythagoreans, 1 is odd-even 71
Pythagoreans, 10 the 'perfect' number 75
Pythagoreans, a Pythagorean first taught for money 22
Pythagoreans, astronomical system (non-geocentric) 163Ч165
Pythagoreans, classification of numbers 72Ч74
Pythagoreans, construction of regular pentagon 160Ч162
Pythagoreans, definition of unit 69
Pythagoreans, definitions 166
Pythagoreans, discovered the incommensurable 65 90Ч91 154
Pythagoreans, discovered the incommensurable, with reference to 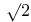 155 168 155 168
Pythagoreans, figured numbers 69
Pythagoreans, first cases of indeterminate analysis 80 91 96Ч97
Pythagoreans, first to advance mathematics 66
Pythagoreans, geometrical theorems attributed to 143Ч154
Pythagoreans, invented application of areas and geometrical algebra 150Ч154
Pythagoreans, oblong numbers 82Ч83 108 114
Pythagoreans, on order of planets ii. 242
Pythagoreans, quadrivium 11
Pythagoreans, side- and diameter-numbers giving approximations to 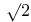 2 91Ч93 2 91Ч93
Pythagoreans, sum of angles of triangle =2R 135 143
Pythagoreans, theory of proportion only applicable to commensurables 153 155 167 216
Qay en heru, height (of pyramid) 127
Quadratic equation, numerical solutions ii. 344 ii. ii.
Quadratic equation, solved by Pythagorean application of areas 150Ч152 167 394Ч396 422Ч423
Quadratrix 2 23 171 182 218 219 225Ч230 ii.
Quadrivium of Pythagoreans 11
Quinary system of numerals 26
Quintilian ii. 207
Qusta b. Luqa, translator of Euclid 362 ii.
Rangabe, A.R. 49Ч50
Ratdolt, Erhard, first edition of Euclid 364Ч365
Reductio ad absurdum 372
Reductio ad absurdum, already used by Pythagoreans 168
Reduction (of a problem) 372
Reflection, equality of angles of incidence and reflection 442 ii. ii.
Refraction 6Ч7 444
Refraction, first attempt at a law (Ptolemy) ii. 294
Regiomontanus 369 ii. ii.
Regula Nicomachi 111
Rhabdas, Nicolas 40 ii. ii.
Rhind Papyrus, algebra in ii. 440Ч441
Rhind Papyrus, mensuration in 122Ч128
Right-angled triangle, inscribed by Thales in circle 131
Right-angled triangle, theorem of Eucl. I. 47
Right-angled triangle, theorem of Eucl. I., attributed to Pythagoras 142 144Ч145
Right-angled triangle, theorem of Eucl. I., supposed Indian origin of 145Ч146
Right-angled triangles in rational numbers, Diophantus's problems on ii. 507Ч514
Right-angled triangles in rational numbers, Indian examples 146
Right-angled triangles in rational numbers, Pythagoras's formula 80
Right-angled triangles in rational numbers, Pythagoras's formula, Euclid's 81Ч82 405
Right-angled triangles in rational numbers, Pythagoras's formula, Plato's 81
Right-angled triangles in rational numbers, triangle (3,4,5) known to Egyptians 122
Robertson, Abram ii. 27
Rodet, L. 234
Rodolphus Pius ii. 26
Rudio, F. 173 184 187Ч191 ii.
Rudolph of Bruges ii. 292
Ruelle, Ch.Em. ii. 538
Ruestow, F.W. ii. 309
Ruler-and-compasses restriction 175Ч176
Sachs, Eva 209n.
Salaminian table 48 50Ч51
Salinon ii. 23 ii.
Sar (Babylonian for 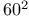 ) 28 ii. ) 28 ii.
Satapatha Brahmana 146
Savile, Sir H., on Euclid 360 369
Scalene, of an oblique , cone ii. 134
Scalene, of an odd number (Plato) 292
Scalene, of certain solid numbers 107
Scalene, of triangles 142
Schiaparelli, G. 317 330 ii.
Schmidt, W. ii. 308 309 310
Schoene, H. ii. 308
Schoene, R. ii. 308 317
Scholiast to Charmides 14 53
Schulz, O. ii. 455
Scopinas ii. 1
Se-qet, 'that which makes the nature' (of pyramid) = cotangent of angle of slope 127Ч128 130 131
Secondary numbers 72
Sectio canonis 17 215 444
Seelhoff, P. 75n.
Seleucus ii. 3
Semicircle, angle in, is right (Thales) 131 133Ч137
Senkereh, Tables 28 29
Senti, base (of pyramid) 127
Serenus ii. 519Ч526
Serenus, on section of cone ii. 522Ч526
Serenus, on section of cylinder ii. 519Ч522
Sesostris (Ramses II) 121
Sexagesimal system of numerals and fractions 28Ч29
Sexagesimal system of numerals and fractions, sexagesimal fractions in Greek 44Ч45 59 61Ч63 233 ii.
Sextius 220
Sicily 8
Simon, M. 200
Simplicius, commentary on Euclid 358 ii.
Simplicius, extract from Eudemus on Hippocrates's quadrature of lunes 171 182Ч199
Simplicius, on Antiphon 221Ч222
Simplicius, on Eudoxus's theory of concentric spheres 329
Simplicius, on mechanical works of Archimedes ii. 24 ii.
Simson, R., edition of Euclid's Data 421
Simson, R., edition of Euclid's Elements 365 369
Simson, R., on Euclid's Porisms 435Ч436
Simson, R., restoration of plane loci of Apollonius ii. 185 ii.
Simus of Posidonia 86
Sines, tables of ii. 253 ii.
Sinus rectus, sinus versus 367
Smith, D.E. 49 138n.
Solids, five regular, all five investigated by Theaetetus 159 162 212 217
Solids, five regular, content of ii. 335 ii.
Solids, five regular, discovery attributed to Pythagoras or Pythagoreans 84 141 158Ч160 168
Solids, five regular, discovery attributed to Pythagoras or Pythagoreans, alternatively (as regards octahedron and icosahedron) to Theaetetus 162
Solids, five regular, Euclid's constructions for 415Ч419
Solids, five regular, Pappus's constructions ii. 368Ч369
Solids, five regular, Plato on 158Ч160
Solon 4 48
Sophists, taught mathematics 23
Sosigenes 316 329
Soss = sussu = 60 (Babylonian) 28 ii.
Speusippus 72 73 75 ii.
Speusippus, on Pythagorean numbers 76 318
Speusippus, on the five regular solids 318
Sphaeric 11Ч12
Sphaeric, earlier text-book presupposed in Autolycus 349Ч350
Sphaeric, Sphaerica of Menelaus ii. 252Ч253 260 261Ч273
Sphaeric, Sphaerica of Theodosius ii. 245 246Ч252
Sphaeric, treatises on, by Autolycus and Euclid 348Ч352 440Ч441
Sphere-making 18
| Sphere-making, Archimedes on ii. 17Ч18
Spiric sections ii. 203Ч206
Sporus 226
Sporus, criticisms on quadratrix 229Ч230
Sporus, duplication of cube 266Ч268
Square numbers 69
Square numbers, 8 times a triangular number +1 = square 84 ii.
Square numbers, any square is sum of two triangular numbers 83Ч84
Square numbers, formation by adding successive gnomons (odd numbers) 77
Square root, extraction of 60Ч63
Square root, extraction of, ex. in sexagesimal fractions (scholiast to Euclid) 63
Square root, extraction of, ex. in sexagesimal fractions (Theon) 61Ч62
Square root, extraction of, method of approximating to surds ii. 51Ч52 ii. ii. ii.
Ssade, Phoenician sibilant became 900 32
Stadium of Zeno 276Ч277 281Ч283
Star-pentagon, or pentagram, of Pythagoreans 161Ч162
Stereographic projection (Ptolemy) ii. 292
Stevin, S. ii. 455
Strabo 121 ii. ii.
Strato ii. 1
Subcontrary (=harmonic) mean, defined 85
Subtraction in Greek notation 52
Surds see "Approximations"
Surds, Theaetetus's generalization 203Ч204 205 209 304
Surds, Theodorus on 22Ч23 155Ч156 203Ч209 304
Surface-Loci 219 ii.
Surface-Loci, Euclid's 439Ч440 ii. ii.
Surya-Siddhanta ii. 253
Sussu = soss (Babylonian for 60) 28 ii.
Synesius of Cyrene ii. 293
Synthesis 371Ч372
Synthesis, defined by Pappus ii. 400
Syracuse 8
Table of chords 45 ii. ii.
Taittiriya Samhita 146
Tannery, P. 15 44 87 89 119 132 180 182 184 188 196n. 232 279 326 440 ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. 546 ii. ii. ii.
Teles on secondary education 21
Teos inscription 32 34
Tetrads of Apollonius 40
Tetrahedron, construction 416 ii.
Tetrahedron, volume of ii. 335
Thabit b. Qurra, of Apollonius's Conics V-VII ii. 127
Thabit b. Qurra, of Archimedes's Liber assumptorum ii. 22
Thabit b. Qurra, of Menelaus's Elements of Geometry ii. 260
Thabit b. Qurra, of Ptolemy ii. 274Ч275
Thabit b. Qurra, translator of Euclid 362 363
Thales 2 4 67
Thales, astronomy 137Ч139 ii.
Thales, definition of number 69
Thales, geometrical theorems attributed to 130Ч137
Thales, introduced geometry into Greece 128
Thales, measurement of distance of ship from shore 131Ч133
Thales, measurement of height of pyramid 129Ч130
Thales, one of Seven Wise Men 128 142
Thales, predicted solar eclipse 137Ч138
Theaetetus 2 119 170
Theaetetus, investigated regular solids 159 162 212 217
Theaetetus, on irrationals 209Ч212 216Ч217
Theaetetus, on surds 22Ч23 155 203Ч204 205 209 304
Themistius 221 223 224
Theodorus of Cyrene, on surds 22Ч23 203Ч209 304
Theodorus of Cyrene, taught mathematics 22Ч23
Theodosius ii. 245Ч246
Theodosius, no trigonometry in ii. 250
Theodosius, other works ii. 246
Theodosius, Sphaerica 349Ч350 ii.
Theologumena arithmetices 96 97 318
Theon of Alexandria, commentary on Syntaxis 58 60 ii. ii.
Theon of Alexandria, edition of Euclid's Elements 360Ч361 ii.
Theon of Alexandria, examples of multiplication and division 58 59Ч60
Theon of Alexandria, extraction of square root 61Ч63
Theon of Alexandria, of optics 441 ii.
Theon of Smyrna 12 72 73 74 75 76 79 83 87 ii.
Theon of Smyrna, forms of numbers which cannot be squares 112Ч113
Theon of Smyrna, on 'side-' and 'diameter-numbers' 91Ч93 112
Theon of Smyrna, treatise of ii. 238Ч244
Theophrastus 158 163
Theophrastus, on Plato's view of the earth 315
Theudius 320Ч321
Theuth, Egyptian god, reputed inventor of mathematics 121
Thevenot, M. ii. 308
Thrasyllus 97 176 177 ii. ii.
Thucydides ii. 207
Thymaridas, 'rectilinear' = prime numbers 72
Thymaridas, definition of unit 69
Timaeus of Locri 86
Tittel ii. 300 301 304
Tore (or anchor-ring), sections of (Perseus) ii. 203Ч206
Tore (or anchor-ring), use by Archytas 219 247Ч249
Tore (or anchor-ring), volume of (Dionysodorus and Heron) ii. 218Ч219 ii.
Torelli, J. ii. 27
Transversal, lemmas relating to quadrilateral and transversal (Pappus) ii. 419Ч420
Transversal, Menelaus's theorem for spherical and plane triangles ii. 266Ч270
Triangle, spherical, propositions analogous to Euclid's on plane triangles ii. 262Ч265
Triangle, spherical, sum of angles greater than two right angles ii. 264
Triangle, theorem about sum of angles Pythagorean 135 143
Triangle, theorem about sum of angles Pythagorean, Geminus and Aristotle on 135Ч136
Triangular numbers 15 69
Triangular numbers, 8 times triangular number +1 = a square 84 ii.
Triangular numbers, formation 76Ч77
Trigonometry ii. 5 ii. ii. ii. ii. ii.
Trisection of any angle, Pappus on ii. 385Ч386
Trisection of any angle, solutions 235Ч244
Tschirnhausen, E.W. 200
Tycho Brahe 317 ii. ii.
Tzifra (=0) ii. 547
Ukha-thebt (side of base in pyramid) 126 127
Unit, definitions (Pythagoreans, Euclid, Thymaridas, Chrysippus) 69
Usener, H. 184 188
Valla, G., translator of extracts from Euclid 365
Valla, G., translator of extracts from Euclid, and from Archimedes ii. 26
van Roomen, A. ii. 182
Van Schooten, F. 75n. ii.
Venatorius, Thomas Gechauff, ed. princeps of Archimedes ii. 27
Venturi, G. ii. 308
Vieta 200 223 ii. ii. ii. ii.
Vigesimal system (of numerals) 26
Vincent, A.J.H. 50 436 ii. ii. ii.
Vitruvius 18 147 174 213 ii. ii.
Vitruvius and Heron ii. 302Ч303
Viviani, V. ii. 261
Vogt, H. 156n. 203n.
von Braunmuehl, A. ii. 268Ч269n. ii. ii.
Wescher, C. ii. 309
Wilamowitz-Moellendorff, U. v. 158n. 245 ii.
Xenocrates 24 319
Xenocrates, upheld 'indivisible lines' 181
Xenocrates, works on Numbers 319
Xenophon, on arithmetic in education 19
Xylander (W. Holzmann) ii. 454Ч455 ii.
Yahya b. Khalid b. Barmak ii. 274
Zamberti, B., translator of Euclid 365 441
Zeno of Elea 271Ч273
Zeno of Elea, arguments on motion 273Ч283
Zeno of Sidon on Eucl. I. 1 359 ii.
Zenodorus ii. 207Ч213
Zero in Babylonian notation 29
Zero in Babylonian notation, O in Ptolemy 39 54
Zeuthen, H.G. 190 206Ч209 210Ч211 398 437 ii. ii. ii. ii. ii. ii.
Zodiac circle, obliquity discovered by Oenopides 138 174 ii.
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



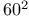 )
)