|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Johnstone P.T. — Sketches of an Elephant: A Topos Theory Compendium |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Locale, stably locally compact C4.1.11
Locale, strongly compact C3.4.1
Locale, strongly Hausdorff C1.2.17
Locale, strongly zero-dimensional D4.5.2(d)
Localic groupoid C5.2.11
Localic groupoid, algebraically connected C5.3.7
Localic groupoid, atomic C5.2.11
Localic groupoid, etale-complete C5.3.16
Localic groupoid, open C5.2.11
Localic groupoid, proper C5.2.11
Localic reflection A4.6.12
Localization (of cartesian category) A4.3.1
Localization (of topos) C3.6.12
Loewenheim-Skolem Theorem D2.3.10
Logic,  -cartesian D2.3.6 -cartesian D2.3.6
Logic,  -first-order D3.1.19 -first-order D3.1.19
Logic, cartesian D1.3.4
Logic, classical D1.3.3
Logic, coherent D1.3.1
Logic, disjunctive D1.3.6
Logic, first-order D1.3.1
Logic, infinitary D1.3.1
Logic, regular D1.3.1
Logical category A1.4.1
Logical functor A2.1.1
Logos A1.4.10
Los’s Theorem D2.4.11
MacNeille completion C2.5.8(e)
MacNeille section D4.7.4
Mal’cev operation D4.2.13
Map (in allegory) A3.1.3
Martin-Loef type theory D4.4.1
Measure (on topos) B4.5.8
Measure (on topos), probability B4.5.12
Model (of sketch) D2.1.1(c)
Model (of theory) B4.2.1(c) D1.2.10(b) D4.1.5
Model (of theory), conservative D3.2.6
Model (of theory), finitely presented D2.4.1
Model (of theory), free D5.3.5
Model (of theory), functionally complete D3.1.3
Model (of theory), generic B4.2.1(b) D1.4.5 D3.1.1
Model (of theory), term C3.6.3(c)
Model (of theory), ultraproduct of D2.4.11
Modification B1.1.2
Modular law A3.1.5
Monad (in 2-category) B1.1.7
Monad (in 2-category), idempotent B1.1.9
Monad (in 2-category), KZ- B1.1.11
Monad (in 2-category), symmetric B4.5.6
Monoid, free D5.3.3
Morita equivalence D1.4.9 D1.4.13
Morita equivalence for localic groupoids C5.3.1
Morleyization D1.5.13
Morphism of allegories A3.2.10
Morphism of diagrams B2.3.11
Morphism of fibrations B1.3.6
Morphism of profunctors B2.7.1
Morphism of sites C2.3.1 C2.3.7
Morphism of sketches D2.1.1(b)
Morphism of structures D1.2.1
Morphism, cartesian B1.3.3
Morphism, characteristic A1.6.1
Morphism, descent B1.5.5
Morphism, effective descent B1.5.5
Morphism, elementary D1.2.10(a)
Morphism, etale C1.3.3
Morphism, fully monic B1.1.19
Morphism, geometric A4.1.1
Morphism, horizontal B1.3.1
Morphism, pre-descent B1.5.5
Morphism, pre-geometric A4.1.13
Morphism, prone B1.3.3
Morphism, supine B1.3.3
Morphism, vertical B1.3.1
Name (of relation) A2.1.1 A3.4.5
Natural number object A2.5.1
Natural number object, Freyd D5.1.1
Natural number object, Lawvere D5.1.1
Natural number object, Peano D5.1.1
Natural number object, standard D5.1.7
Natural number object, weak D4.2.12
Natural transformation, 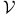 -enriched B2.1.1 -enriched B2.1.1
Natural transformation, indexed B1.2.1
Natural transformation, internal B2.3.1(c)
Natural transformation, lax B1.1.2
Natural transformation, locally internal B2.2.1
Natural transformation, pseudo- B1.1.2
Natural transformation, strong B2.1.6
Negation (of subobject) A1.4.13
Nerve (of internal category) B2.3.2
Nucleus C1.1.13
Nucleus, closed C1.1.16(b)
Nucleus, dense C1.1.16(c)
Nucleus, double-negation C1. 1.16(c)
Nucleus, fibrewise closed C1.1.22
Nucleus, fibrewise dense C1.1.22
Nucleus, flat C1.1.16(d)
Nucleus, open C1.1.16(a)
Nucleus, strongly dense C1.1.22
Nucleus, weakly closed C1.1.22
Numeral D5.5.4
Numeral, K-finite D5.5.9
Object classifier B3.2.9 B4.2.9 D3.2.1
Object of components B2.5.5
Object of generators B3.1.7
Object of morphisms B2.3.1(a)
Object of objects B2.3.1(a)
Object, 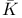 -finite D5.4.22 -finite D5.4.22
Object,  -presentable D2.3.1 -presentable D2.3.1
Object, choice D4.5.5
Object, coarse A2.6.11
Object, cocomplete B1.1.16
Object, coherent D3.3.4
Object, compact D3.3.2
Object, consistent D3.4.5
Object, decidable A1.4.15
Object, decidably well-ordered D5.1.6
Object, Dedekind-finite A1.6.10 D5.1.4
Object, exponentiable A1.5.1
Object, finitely presentable C4.2.1 D2.3.1
Object, generic D3.2.1
Object, Higgs D4.5.10
Object, indecomposable A1.1.10
Object, internally projective D4.5.1(b)
Object, irreducible (for coverage) C2.2.18(a)
Object, Kuratowski-finite D1.1.7(k) D5.4.1(b)
Object, list A2.5.15 D4.1.4
Object, natural number A2.5.1
Object, order able C5.4.8
Object, power A2.1.1 A3.4.5
Object, projective A1.1.10 A1.3.8
Object, quasi-initial A1.5.14
Object, R-finite D5.5.12
Object, real number D4.7.4
Object, separated A4.3.4
Object, simplicial B2.3.2
Object, solid A2.6.6
Object, stable D3.3.4
Object, strict (initial) A1.4.1
Object, subterminal A1.5.10
Object, supercoherent D3.3.10
Object, supercompact D3.3.10
Object, thin A2.6.6
Object, well-ordered D4.5.9
Object, well-supported A1.3.8
Opfibration B1.3.7(a)
Opfibration in 2-category B4.4.1
Opfibration, discrete B2.5.1
Oplax functor B1.1.2
Oplax limit B1.1.6
| Orbital D5.5.1
Orbital, acyclic D5.5.3
Orbital, K-finite D5.5.9
Orbital, Ordered wedge D4.7.15
Orbital, thick D4.7.15
Ore condition A2.1.11(h)
Partial map A2.4.6 A3.4.10
Partial map, representable A2.4.6
Partial product A1.5.7
Partial product, contravariant B4.4.13
Partial product, covariant B4.4.13
Partial surjection A4.6.1
Peano postulates A2.5.9 D4.3.17(c) D5.1.1
Pierce representation B4.4.23
Pitts’s Theorem C2.3.17
Point (of locale) C1.2.1
Point (of locale), focal C1.5.6
Point (of topos) C2.2.12
Poset, complete B2.3.9
Poset, conditionally complete D4.7.7
Poset, continuous C4.1.1(b)
Poset, Dedekind-complete D4.7.7
Poset, directed B2.6.2
Poset, DM-separated D4.7.15
Poset, inductive D4.5.14
Poset, internal B2.3.8
Posite C1.1.16(e)
Positivization A1.4.5
Power object A2.1.1 A3.4.5
Power object, weak A2.6.1
Pre-bound D3.2.3
Pre-descent condition B1.5.2
Pre-geometric morphism A4.1.13
Pre-logos A1.4.1
Pre-stack B1.5.2
Preframe C1. 1.3
Preorder A1.1.5
Presheaf A2.1.8 C1.3.1(a)
Presheaf, flat B3.2.3
Pretopology A2.1.9
Pretopos A1.4.8
Pretopos,  - A1.4.19 - A1.4.19
Pretopos,  - A1.4.19 - A1.4.19
Product, 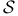 -indexed B1.4.2 -indexed B1.4.2
Profunctor (internal) B2.7.1
Profunctor (internal), unit B2.7.2
Profunctor comonad C4.2.16
Progenitor B3.1.7
Propositions-as-types paradigm D4.2.1
Protocategory A1.1.5
Protomorphism A1.1.5
Pseudo-complement A1.4.13
Pseudofunctor B1.1.2
Pseudofunctor, strictly unital B1.1.2
Pseudonatural transformation B1.1.2
Pullback-stability theorem for atomic morphisms C3.5.12
Pullback-stability theorem for coherent morphisms C2.4.7
Pullback-stability theorem for connected locally connected morphisms C3.3.15
Pullback-stability theorem for connected tidy morphisms C3.4.15
Pullback-stability theorem for exponentiable morphisms B4.3.5
Pullback-stability theorem for fibrations B4.4.3
Pullback-stability theorem for hyperconnected morphisms B3.3.7 C2.4.11
Pullback-stability theorem for local maps C3.6.7(iv)
Pullback-stability theorem for localic morphisms B3.3.6
Pullback-stability theorem for locally connected morphisms C3.3.15
Pullback-stability theorem for open maps C3.1.11 C3.1.23 C3.1.27
Pullback-stability theorem for proper maps C3.2.6 C3.2.21
Pullback-stability theorem for tidy morphisms C3.4.7
Pullback-stability theorem for totally connected morphisms C3.6.18
Pure-entire factorization C3.4.13
Quasitopos A2.6.1
Quasitopos, Grothendieck C2.2.13
Quasitopos, solid A2.6.5
Real number object, Cantor D4.7.12
Real number object, Cauchy D4.7.12
Real number object, Dedekind D4.7.4
Real number object, formal D4.7.5
Real number object, MacNeille D4.7.4
Real number object, semicontinuous D4.7.2
Rectangular diagram category B1.3.12
Recursion data D5.1.9
Recursive function, partial D5.1.6
Recursive function, primitive A2.5.4
Recursor D4.2.11(a)
Reflection A1.1.1
Reflector A1.1.1
Reflector, cartesian A4.3.1
Reflexive pair A1.1.2
Regular category A1.3.3
Regular category, capital A1.3.8
Regular category, effective A1.3.6
Regular category, quasi-effective C2.2.13
Regularization A1.3.9
Relation A1.3.6 A2.1.1 A3.1.1
Relation symbol D1.1.1 D4.1.1
Relation, apartness D4.7.6
Relation, entire D4.5.5
Relation, equivalence A1.3.6
Relation, name of A2.1.1
Relation, opposite A3.1.3
Relation, reflexive A1.3.6
Relation, symmetric A1.3.6
Relation, transitive A1.3.6
Ring, indecomposable B4.4.23
Ring, local D1.1.7(g)
Ring, reduced D3.1.11(b)
Ring, separably real-closed local D4.7.10
Ring, von Neumann regular D3.1.11(b)
Rule of inference D1.3.1
Rule of inference of 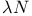 -calculus D4.2.11(b) -calculus D4.2.11(b)
Rule of inference of  -calculus D4.2.2 -calculus D4.2.2
Rule of inference of  -calculus D4.4.5 -calculus D4.4.5
Rule of inference of 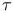 -calculus D4.3.1 -calculus D4.3.1
Rule of inference, cut D1.3.1(a)
Rule of inference, equality D1.3.1(b) D4.2.2
Rule of inference, substitution D1.3.1(a)
Rule of inference, weakening D1.3.1 (a)
Ryll-Nardzewski’s criterion D3.4.6
Scone A2.1.12
Scott topology C4.1.3
Section, Dedekind D4.7.4
Section, lower D4.7.1
Section, MacNeille D4.7.4
Semilattice C1.1.3
Semilattice, complete join- C1.1.3
Semilattice, continuous C4.1.1(c)
Semilattice, free C1.1.3 D5.4.9
Semilattice, Heyting A1.5.11
Semilattice, join- C1.1.3
Semilattice, meet- C1.1.3
Sentence D1.1.3
Separating family A1.2.4 B2.4.1
Separator A1.2.4 B2.4.1
Separator, strong A3.4.10
Sequent D1.1.5
Sequent calculus D1.3.1
Sequent, cartesian D1.1.7(m) D1.3.4
Sequent, coherent D1.1.5
Sequent, derivable D1.3.1
Sequent, disjunctive D1.3.6
Sequent, first-order D1.1.5
Sequent, geometric D1.1.5
Sequent, Horn D1.1.5
Sequent, provable D1.3.1
Sequent, regular D1.1.5
Sequent, satisfied in M D1.2.12(a)
Sheaf for a closure operation A4.3.4
Sheaf on a locale C1.3.1(b)
Sheaf on a site A2.1.9 C2.1.2
Sheaf on a space A2.1.8
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 -cartesian
-cartesian 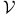 -enriched
-enriched 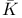 -finite
-finite  -
-  -
- 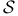 -indexed
-indexed 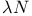 -calculus
-calculus  -calculus
-calculus  -calculus
-calculus 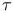 -calculus
-calculus