|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Fowler R.H. Ч Statistical Mechanics: The Theory of Properties of Matter in Equilibrium |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Schottky 176 345 355 366 417 436 783
Schottky and Waibel 401
Schottky effect, in electron emission 355 Ч 356
Schr dinger 17 125 724 dinger 17 125 724
Schr dingerТs equation, for harmonic oscillators 18 20 dingerТs equation, for harmonic oscillators 18 20
Schr dingerТs equation, for structureless particles 53 dingerТs equation, for structureless particles 53
Schubin see УTamm and S.Ф
Schultze see УVillars and S.Ф
Schuster 611
Seebeck effect, defined 412
Seebeck effect, defined statistical theory of 413 Ч 418
Seitz 333; see УWigner and S.Ф
SellmeyerТs formula 441
Semenoff 718
Semi-conductors, composite, general theory of 425 Ч 429
Semi-conductors, composite, general theory of, contact potentials for 401 Ч 403
Semi-conductors, composite, general theory of, electrical conductivity of 418 Ч 421
Semi-conductors, composite, general theory of, impurity 390 Ч 391
Semi-conductors, composite, general theory of, metals and insulators, defined 388 Ч 390
Semi-conductors, composite, general theory of, thermoelectric effects in 418 Ч 421
Semi-conductors, composite, general theory of, work functions for 401 Ч 403
Sheratt and Griffiths 94
Shilling see УPartington and S.Ф
Short range forces, ordering effect of 798 Ч 800
Shot effect 783 Ч 785
Sidgwick 312
Silverman see УBarnes and S.Ф
Simon see УKiirti and S.Ф; see УLange and S.Ф
Simon and Ruhemann 814
Simon and Swain 131
Simon, Mendelssohn and Ruhemann 222
Skinner and Appleyard 679
Slater 322 333 397
Slater and Kirkwood 292 305
Smekal 1
smith see УLewis (G. N.) and S.Ф
Snow 99 223
Solids, dielectric constant of polar 816 Ч 825
Solids, dielectric constant of polar, emission and absorption of radiation by 739 Ч 740
Solids, dielectric constant of polar, photoelectric effect for 740 Ч 741
Solids, dielectric constant of polar, rotations of molecules in 810 Ч 815
Solutions, a-regular 533 Ч 536
Solutions, ideal 527 Ч 533
Solutions, ideal, extreme dilution of 532 Ч 533
Solutions, ideal, freezing point lowering in 529
Solutions, ideal, HenryТs law for 527
Solutions, ideal, osmotic pressure of 531
Solutions, ideal, RaoultТs law for 527
Solutions, ideal, zero heat of dilution for 531 Ч 532
Solutions, of strong electrolytes (q.v.) 536 Ч 560
Solutions, perfect 532
Sommerfeld 72 338 404 416 467;
Sommerfeld and Bethe 338 397 404 406 409 416 496 526
Space charge effects 364 Ч 378
Space charge effects, with positive and negative ions 373 Ч 378
Spangenberg 322
Specific heat (of hydrogen at high temperatures 91 Ч 92
Specific heat at high temperatures 92 Ч 106
Specific heat of ferromagnetics near the curie point 492- 494
Specific heat of gadolinium sulphate 841 Ч 842
Specific heat of lithium (metallic) 131
Specific heat of methane 96 Ч 97
Specific heat of nitrous oxide 98 Ч 99
Specific heat of oxygen at high temperatures 94
Specific heat of perfect gases 77 Ч 107
Specific heat, excitational, of nitric oxide 102 Ч 103
Specific heat, excitational, of nitric oxide, of oxygen 104 Ч 106
Specific heat, of acetylene 99
Specific heat, of acetylene, configurational 805 Ч 809
Specific heat, of acetylene, electronic, of metals 343 Ч 344
Specific heat, of acetylene, electronic, of metals, of nickel (metallic) 391 Ч 397
Specific heat, of acetylene, excitational, of oases 101 Ч 106
Specific heat, of acetylene, of air, high temperatures 94
Specific heat, of acetylene, of ammonia, gaseous 95 Ч 96
Specific heat, of acetylene, of carbon dioxide 97 Ч 98
Specific heat, of acetylene, of crystals, BlackmanТs theory of 130 Ч 138
Specific heat, of acetylene, of crystals, BlackmanТs theory of, 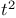 -law for 125 -law for 125
Specific heat, of acetylene, of crystals, BlackmanТs theory of, ForsterlingТs formulae for 128 Ч 129
Specific heat, of acetylene, of crystals, BlackmanТs theory of, from elastic constants 127 Ч 128
Specific heat, of acetylene, of crystals, BlackmanТs theory of, law of corresponding states for 125 Ч 126
Specific heat, of acetylene, of ethylene 99 Ч 101
Specific heat, of rotations, rigid 81 Ч 82
Specific heat, of vibrations, for diatomic gases 90
Specific heat, of water vapour 97
Specific heat, rotational, of hydrogen 82 Ч 89
Spectra, stellar absorption 593 Ч 619
Sponer 95 97 99
Stark see УBltih and S.Ф
States, non-combining groups of 26
Statistics, classical 43
Statistics, classical, classical, approximated to 55
Statistics, classical, Einstein Ч Bose 43
Statistics, classical, Fermi Ч Dirac 42
Steepest descents, method of 36
Stefan Ч Boltzmann law 116 200
StefanТs constant 116
Steiner see УSalow and S.Ф
Stellar absorption lines, decay of, part maxima 618 Ч 619
Stellar absorption lines, decay of, part maxima, formation of 610 Ч 617
Stellar absorption lines, decay of, part maxima, marginal appearance of 617 Ч 618
Stellar absorption lines, decay of, part maxima, maxima of 595 Ч 597
Stellar absorption lines, decay of, part maxima, statistical theory of 597 Ч 610
Stellar interiors, RosselandТs theorem on 638- 639
Stellar material, great densities of 647 Ч 648
Stellar material, great densities of, mean molecular weight of 643
Stellar material, great densities of, mean molecular weight of, StromgrenТs calculation of 644 646
Stellar material, great densities of, nature of 639 Ч 646
Stellar temperature scale, RussellТs 615
Sterne 26 225 655; УFowler G.
Stewart 612
Stoner 467 652
Stresses, in imperfect gases 288 Ч 291
Stresses, in imperfect gases, internal 182 Ч 184
Stromgren 644
Strong electrolytes, BjerrumТs theory of 552 Ч 557
Strong electrolytes, Debye and H ckelТs theory of 269 Ч 274 541 ckelТs theory of 269 Ч 274 541
Strong electrolytes, dissociated in solutions 536 Ч 539
Strong electrolytes, heat of dilution of 546 Ч 548
Strong electrolytes, osmotic coefficient of 541 548
Strong electrolytes, Poisson Ч Boltzmann equation solved for 549- 552
Strong electrolytes, specific ionic interactions in 557 Ч 560
Structureless particles, Schr dingerТs equation for 53 dingerТs equation for 53
Sucksmith 484
Sugiura 724 727
Superlattice order 792 Ч 801
Surfaces, adsorbed layers on 825 Ч 838
Surfaces, adsorbed layers on, gas collisions with 697 Ч 699
Susceptibilities, DarwinТs theorem on 447
Susceptibilities, DarwinТs theorem on, electromagnetic theory of 437 Ч 447
Susceptibilities, DarwinТs theorem on, LangevinТs formula for 461 Ч 463
Susceptibilities, DarwinТs theorem on, LorentzТs formula for 441
Susceptibilities, DarwinТs theorem on, of ferromagnetics above curie point 480
| Susceptibilities, DarwinТs theorem on, polarizing force for 439
Susceptibilities, DarwinТs theorem on, SellmeyerТs formula for 441
Sutherland 77 99 103
Swain see УSimon and S.Ф
Sykes 808
Symmetrical states 27 43
Symmetry number 89
Symmetry rules, derived, for complex systems 163
Symmetry rules, derived, for complex systems, for nuclei 156
systems, defined 8
Systems, degenerate 45
Systems, independence of 16
Tait 621
Tamm see УBernal and T.Ф
Tamm and Schubin 359
Tannery and Molk 54 81
Taylor 635; see УLennard-Jones and T.Ф
Teal see УUrey and T.Ф
Teller 844
Teller and Topley 101
Temperature, absolute, defined 188 Ч 189
Temperature, absolute, empirical, defined 187
Temperature, absolute, low, reached by demagnetization 838 Ч 844
Temperature, absolute, radiation, PlanckТs law for 112 116
Thermal conduction in metals, formal theory of 404 Ч 418
Thermal expansion, coefficient of, for isotropic solids 140
Thermionice see УElectrons emission
Thermodynamic, partial potentials 194
Thermodynamic, partial potentials, probability and entropy 200 Ч 206
Thermodynamics, of magnetism 481 Ч 483
Thermodynamics, of magnetism, and statistical mechanics 187 Ч 207
Thermodynamics, of magnetism, third law of 228
Thermoelectric effects in metals 411 Ч 418
Thermoelectric effects in metals, in semi-conductors 418 Ч 421
Thiele see УLaden burg and T.Ф
Third law of thermodynamics 228; see УNernstТs heat theoremФ
Thomson 690
Thomson Ч Joule effect 280 Ч 281
ThomsonТs specific heat of electricity, defined 412
ThomsonТs specific heat of electricity, defined, statistical theory of 413 Ч 418
Todes see УFrenkel T.
Toet see УTolman Y.
Tolman, Yost and Dickinson 717
Topley see УHirschfelder E. УTeller
Topping see УChapman (S.) T.
Topping and Chapman 332
Torsional oscillations of suspended mirror 779- 783
Torsional oscillations of suspended mirror, Fourier analysis of 781 Ч 783
Transferable energy in gas collisions 707 Ч 710
Transmission coefficients for electrons 349- 351
Transverse effects of magnetic fields in metals 421 Ч 425
Trkal see УEhrenfeat and T
Turner 220
Uchling and Uhlenbeck 672
Uehling 411
Uhlenbeck 107; see УUehling and U.Ф
Uhlenbeck and Goudsmit 775 781
Uhlenbeck and Ornstein 785
Unimolecular gas reactions 710 Ч 716
Unit mechanisms 660 Ч 663
Uns ld 612 633 ld 612 633
Urey 259 260 574
Urey and Teal 168
Ursell 26 241 245 294
van der WaalsТ equation of state 244 274-
van der WaalsТ interatomic energy 296 Ч 297
Van Velzer 353
Van Vleck 19 449 456 458 488 721 738;
Van Vleck, Hebb and Purcell 839 840
van Wijk see УOrnstein and v. W.Ф
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals 344- 346
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, constants, defined 209
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, constants, defined, diatomic 220 Ч 224
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, constants, defined, monatomic, from dissociation equilibria 217 Ч 218
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, constants, defined, monatomir 218 Ч 220
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, constants, defined, polyatomic 225
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, equation, statistical 210 Ч 215
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, equation, statistical, thermodynamic 208
Vapour pressure, electronic, of metals, of crystals, simple 172 Ч 173
Verechoyle 282 307
Villars and Schultce 94
Viney 82
Virial coefficient (second), for binary mixtures 306 Ч 308
Virial coefficient (second), for imperfect gases 302 Ч 305
Virial coefficient (second), for monolayers 827
Virial coefficient (second), theoretical 298 Ч 302
Virial of Clausius 286 Ч 288
Von Elbe see УLewis (G. N and
von Helmholtz 147
von Laue 366 370 375
von Neumann 7
von Smoluchoweki 766
Waibel see УSchottky and W.Ф
Walker see УJohnston (H. L.) and W.Ф
Waller 841
Wasastjema 320 Ч 322
Watson 316. 650; see УWhittaker and W.Ф
Weatherby and Wolf 459
Weber see УKamerlingh-Onnes and W.Ф
Webster 509 511 518
Weights, analysis of 16 Ч 17
Weights, analysis of, invariance of 196 Ч 197
Weights, analysis of, of atomic states 569
Weights, analysis of, of classical systems 18
Weights, analysis of, of isotropic oscillators 19
Weights, analysis of, of rotations, rigid 21
Weights, analysis of, weights, analysis of, defined 10
Weiss 479 483 493 501
Wentzel 359
Weyl 54 114
White 101
White dwarf stars 648
Whittaker and Watson 708 709
Wiebe see УGiauque and W.Ф
Wiedermann Ч FransТs law, for metals 410 Ч 411
Wigner 26 847;
Wigner and Seitz 333
Williams (E. J.) 789 793 805;
Williams (N. H.) see УHull and W.Ф
Wilson (A. H.) 398
Wilson (E. B,) 94
Wilson (H. A.) 345
Winch 359
Woitjer and Onnes 469
Wolf see УWeatherby and W.Ф
Work function, thermionic, for metals 348
Work function, thermionic, for metals, for semi-conductors 401 Ч 403
WТiersma see Уde Haas W.
Zahn 450
Zeidler 218
Zener 93 381 389;
Zero-point energy 123
Zwicky 299
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 dinger
dinger 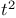 -law for
-law for  ckelТs theory of
ckelТs theory of