|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Dewdney A.K. Ч Beyond reason. 8 great problems that reveal the limits of science |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
"Big O" notation 184 190 199 204
"Logic and the Understanding of Nature" (Hilbert) 159Ч160
"Naturkennen und Logik" (Hilbert) 159Ч160
"On Certain Difficulties of Proof..." (Goedel) 160
"On Comparable Numbers..." (Turing) 173
"On the Constitution of Atoms and Molecules" (Bohr) 66
"paradigm shift" 7
"Period Three Implies Chaos" (Yorke and Li) 89
"social constructions" 7
"Ueber Formal Unentscheldbare Saetze Principia Mathematica..." (Goedel) 160
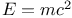 (mass-energy equation) 31 (mass-energy equation) 31
Absolute space and time 41
Abstract systems 6
Accretion of knowledge 6
Ackermann's function 180Ч181
Ackermann, Willheim 149
Aleph zero 140
Algebra 164
Algorithms 174 177Ч179 203 204
Algorithms as computer programs 185Ч190
Algorithms, big-O bottleneck and 198Ч199
Algorithms, binary search 188Ч189 191
Algorithms, complexities of 189Ч190 199
Algorithms, definitions of 165 185 198Ч199
Algorithms, deterministic 199Ч200
Algorithms, exponential 189 204
algorithms, generic 192Ч193 198 201Ч203
Algorithms, nondeterministic 198Ч202
Algorithms, solution 191Ч192
Algorithms, to find largest number in a list 185Ч188
Algorithms, verification stage of 200 202
Algorithms, worst-case instances of 199
Analog computer 205Ч206
Angstroem, Anders 60 65
Annalen der Physik (journal) 45
Archimedes 19 135
Aristotle 36 117 150
Arithmetic 139 146 149 164 170
Arithmetic, consistency 143Ч148
Arithmetic, Goedel's consistency proof 140 150 153Ч158
Arithmetic, transfinite 140Ч142
Aspect, Alain 79
Astronomy 7Ч8
Atom, excited state 70
Atomic theory of Bohr 65Ч66
Atomic theory of Dalton 6 41
Atomic theory of Rutherford 65
Attractors 97Ч104
Bacon, Francis 36
Balfour, William 17
Balmer, Jacob 60 65
Barriers to knowledge 3Ч8
Bell's theorem 75Ч79
Bell, John 75
Bernays, Paul 160
Bessler, Johann Ernst Elias (Orffyreus) 19Ч21
Beukers Ч Bezevin Ч Robba proof 134Ч135
Beukers, Frits 134
Beweisstheorie (Hilbert's theory of proofs) 147Ч148
Bezevin, Jean-Paul 134
Big-O bottleneck 183Ч204
Binary search 188 191
binary search algorithm 188Ч189
biology 7
Black body problem 63Ч64
Bohm's theory 82
Bohm, David 82
Bohr, Niels 64Ч66
Bohr, Niels, atomic structure and 65Ч66
Bohr, Niels, Copenhagen interpretation of 71
Bohr, Niels, EPR thought experiment and 74
Bohr, Niels, quantum mechanics and 62 64Ч66 72
Born, Max 68
Brahe, Tycho 7
Butterfly effect 87
Butterfly metaphor 106Ч107
Calculus 119
Cantor's theorem 142
Cantor, Georg 133 140Ч143
Carnap, Rudolph 149 159
Carnot cycle 30
Carnot, Sadi 28Ч30
Celestial mechanics 7 8 37
Chaos theory 3 6 85Ч112
Chaos theory, attractors and 97Ч104
Chaos theory, butterfly metaphor and 106Ч107
Chaos theory, double pendulum and 98Ч100
Chaos theory, example of 86Ч88
Chaos theory, fractals and 90 97 100
Chaos theory, logistic equation and 90Ч97 101
Chaos theory, researchers in 88Ч90 103Ч108
Chaos theory, sensitivity to initial conditions and 89 95 101
Chaos theory, stretching, folding and 88
Chaos theory, Verhulst equation and 91Ч92
Chaotic systems See "Dynamical systems"
Charles I, King of England 17
Church's thesis 164 165 177Ч178
Church, Alonzo 69 173
circle See "Squaring the circle"
Classical physics 24 65 80
Classical physics, conservation of energy and 34
Classical physics, perpetual motion machines and 27Ч28
Classical physics, relativity theory and 59Ч60
Clauser, John 79
Closed-form expressions 2
Color of light 63 64
complex numbers 101 102 131
Complexities algorithms of 189Ч190 199 201Ч202
Complexities reduced to essential size 199
Computers 163Ч180 183Ч206
Computers, algorithms and 185Ч190
Computers, analog 205Ч206
Computers, big-O bottleneck and 183 184 190 198 199 203 204 206
Computers, binary search by 188Ч189 191
Computers, chaos theory simulations by 88
Computers, conceptual birth and development of 165Ч174 178
Computers, fully programmable 164
Computers, future developments in 178Ч179
Computers, intractable problems and 183Ч206
Computers, limitations of 163Ч180
Computers, weather prediction and 103Ч104 108 111Ч112
Conjectures 138 161 164
Conjectures, hypothesis and 140
Consciousness 62 81
Conservation of energy 5 14 27Ч34
Conservation of energy, Helmholtz's law of 30
Constructable 126Ч135 137 138
Continuum Hypothesis 140Ч143
Cook's theorem 193Ч196 199 203
Cook, Stephen 190Ч196 198 199
Cook, Stephen, generic transformation discovery by 192Ч193 198 201Ч203
Copenhagen interpretation 71 72
Copernican theory 7 8 37
Copernicus, Nicolaus 7
Crick, Francis 7
Cromwell, Oliver 117
Dalton, John 6 41
Darwin, Charles 7 91
Data scaling phenomena 89Ч90
Davisson, Clinton 65
de Broglie, Louis 62 64
De Corpore (Hobbes) 118
de Fermat, Pierre 130
Decision problems 165 173Ч177
Decision problems, yes-or-no answers for 191
Deductive science 2 6 7 30
Desaguliers, Jean 19Ч20
Descartes, Rene 36 41Ч42 119
Deterministic algorithms 199Ч200
Dirac transformations 69
| Dirac, Paul 69
DNA computers 163 178 179 203Ч204
DNA structure, discovery of 7
Double pendulum 98Ч100
Due Correction for Mr. Hobbes... (Wallis) 118
Dynamical systems 3 6 85Ч90 112 See
Dynamical systems, attractors 97Ч104
Dynamical systems, behavior of 85Ч89
Dynamical systems, boundary between chaotic and nonchaotic behavior in 89
Dynamical systems, double pendulum 99
Dynamical systems, sensitivity to initial conditions of 89 95 101
Dynamical systems, waterwheel example 107Ч108
EDVAC computer 178
Eigenvectors 70
Einstein, Albert, "God does not play dice" quote of 46 60
Einstein, Albert, background of 40Ч41
Einstein, Albert, basic assumptions of 6
Einstein, Albert, energy-mass formulas of 31 55Ч56
Einstein, Albert, gedanken (thought) experiments of 30 40 72Ч74
Einstein, Albert, photoelectric effect paper of 45Ч46 60 64
Einstein, Albert, quantum mechanics and 46 60
Einstein, Albert, relativity theories of 6 45 52 53 57 59
Einstein, Albert, speed of light and 5 6 31 36 42 45Ч46
Electrons 53 59
Electrons, energy level of 63 65 66
Electrons, Lorentz effect and 15
Electrons, measurement/position of 3 60 70 71
Electrons, perpetual motion and 14Ч16
Elements (Euclid) 120
Elenchus Geometriae Hobbianae (Wallis) 118
Empedocles 36
Energy 11Ч34 See
Energy, conservation of 5 14 27Ч34
Energy, Einstein's 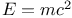 equation 31 52 equation 31 52
Energy, exchange of information and 33
Energy, heat as form of 28Ч31
Energy, joules of 32
Energy, kinetic and potential components 5 31 45 55Ч56
Energy, light and 62Ч64
Energy, mechanical 30
Energy, perpetual motion machines and 11Ч34
Energy, quanta of 34 46 63Ч65
Entscheidungsproblem 170 173
EPR (Einstein Ч Podolsky Ч Rosen) thought experiment 72Ч74 76Ч77
Equivalence, problem 191
Ether 41Ч42 44 45 48 49 52
Euclid 117Ч121 127Ч128 149
Euler, Leonhard 149
Everett, Hugh, III 81
Evolution theory 7
Examinatio et Emendatio Mathematicae Hodiernae (Hobbes) 118
Exponential algorithms 189Ч190 204
exponential complexity 190
Exponential growth 183 185 204
Fermat's last theorem 130 139
Finite numbers 155
First International Congress of Mathematics (Zurich) 41
First Men in the Moon, The (Wells) 16
Fisher, Baron 19
Fitzgerald, George 46Ч49 52 57
Fitzgerald, George, Lorentz Ч Fitzgerald transformations and 52Ч56
Fizeau, Armand 39
Fludd, Robert 18Ч19
Foucault, Jean 39
Four-day weather forecasts 108Ч111
Fractals 98
Fractals, coining of term 90
Fractals, definition of 97
Fractals, Mandelbrot set 100Ч102
Frege, Gottlob 145
Fresnel, Augustin-Jean 41 46
Friction 5 13 31 33
Fulton, Robert 22Ч23
Fundamental particles See also "Electrons" "Photons"
Fundamental particles, Heinsenberg's uncertainty principle and 66Ч68
Fundamental particles, measurement problem 3
Fundamental particles, unpredictability of 6 59 60
Galilean frames 53Ч54
Galileo Galilei 2Ч3 28 30 53
Galileo Galilei, on speed of light 37 39
Galois, Evariste 132
General relativity, theory of 8 57
Generic transformation 192Ч193 198
Geometry 117Ч124 See
Geometry,  wars and 117Ч119 wars and 117Ч119
Geometry, Euclid and 120Ч121
German Mathematical Union 160
Germer, Lester 65
Goedel number 155Ч158
Goedel's incompleteness theorem 78 153 158Ч161
Goedel's incompleteness theorem, Cantor's theorem and 142
Goedel's incompleteness theorem, language of 139
Goedel, Kurt 139 140 153Ч161 164 165
Goedel, Kurt, background of 148Ч150
Goldbach's conjecture 138Ч139
Goldbach, Christian 138
Golub, Jerry 90
Gravesande, Willem Jakob s' 20
Gravity-blocking material 16
Greece, ancient, light theories 36
Greece, ancient, mathematics 116Ч117
Grundgesetze der Arithmetik (Frege) 145 146
Grundlagen, Die (Neumann) 80
Grundzuege der Theoretischen Logik (Hilbert and Ackermann) 149Ч150
Hahn, Hans 149
Hamiltonian path problem 193
Heat energy 28Ч31
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle 66Ч69
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle, statement of 66
Heisenberg, Werner 62 68
Hilbert space 69
Hilbert, David 69 134 143 146Ч150 159Ч160 164
Hilbert, David, Beweisstheorie (theory of proofs) of 147Ч148
Hilbert, David, twenty-three problem challenge by 140
Hobbes, Thomas 117Ч119
HP (Hamiltonian path problem) 193
Huygens, Christiaan 36 41 46
Hydrogen atom 65Ч66
Hyperspace drive (science fiction) 56
Hypothesis 140
Imaginary number 101 131
Incompleteness theorem See "Goedel's incompleteness theorem"
Inductive science 6
infinity 140Ч143
Infinity, exponential complexity and 190
Infinity, finite tools and 155
Infinity, fractals and 97
Infinity, mini-Mandelbrots and 102
Integers 129 130 165
Integers, Ackermann's function and 180
Integers, Goedel numbers and 155 157 158
Integers, maximum-integer problem 188
Integers, positive 127 144Ч145
Integers, rational number correspondence 126
Integers, real numbers and 140Ч143 148
Interferometer 43Ч45 48 49
Intractable problems 3 183Ч206
Intractable problems, equivalence among 191
Intractable problems, exponential time and 185 188 204
Intractable problems, finding largest number in a list 186Ч188
Intractable problems, traveling-salesman example 184Ч185
Introduction to Mathematical Philosophy (Russell) 149
Io (Jupiter's moon) 37Ч38
Irrational numbers 116 117 124Ч126
Joules 32
Kant, Immanuel 149
Keats, John 116
Kepler, Johannes 7Ч8
kinetic energy 5 31 45 55Ч56
Kleene, Stephen 60
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



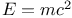 (mass-energy equation)
(mass-energy equation)  wars and
wars and