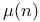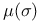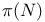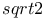|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Derbyshire J. Ч Prime Obsession: Bernhard Riemann and the greatest unsolved problem in mathematics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
"Clariton" 356
"Derbyshire function" 242Ч243
"Elementary" methods 124Ч125 198
"Foundations" 18 185 225
"Sweet Betsy from Pike" (tune) 394 395
"Taiye" 82Ч83 pl.
"Villikens and his Dinah" (song) 395
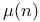 see "Moebius mu function" see "Moebius mu function"
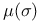 see "Lindeloef mu function" see "Lindeloef mu function"
 185 185
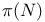 see "Prime counting function" see "Prime counting function"
 74 371 74 371
Abelian function 31 366
Abramowitz, Milton 373
Absolute error 234Ч235
Academies/societies, universities distinguished from 30 57
Adele 320Ч321
Adelic quantum mechanics 320
Airy, George 225
Alan Turing: The Enigma 262
Alexander I, Emperor of Russia 121Ч122
Alexanderson, Gerald 352Ч353
Algebra 119 194 209 225
Algebra, contrasted with geometry 385
Algebra, defined 17Ч18 86Ч87
Algebra, game theory 18
Algebraic field theory 269Ч271
Algebraic invariants, theory of 184 225
Algebraic number theory 87 184 185 194 318Ч321
Algebraic numbers 173Ч174 269
American Institute of Mathematics xi 351Ч352
American Mathematical Society 290
Amplitude of a complex number 180Ч182 333Ч334
Analysis 119 130
Analysis in complex plane 182Ч183
Analysis, arithmetic and 18 86Ч87 89Ч90 91 96
Analysis, calculus in 87Ч88
Analysis, classic texts 15 226
Analysis, continuity concept 90Ч91
Analysis, defined 15 16 17 18 87
Analysis, functional 195
Analysis, invention 87Ч88
Analysis, limit concept 16 17 88 90Ч91
Analytic number theory 18 86Ч87 96 97Ч98 153 156 198 231Ч232 238Ч239 322
Anna, Empress of Russia 59
Anti-Semitism 163 254Ч255
Apery's number 371 399
Apery, Roger 371
Apostol, Tom 393Ч394
Argand, Jean-Robert 92
Argument of a function 36
Argument plane 210Ч216 218 219 221
Arithmetic 119
Arithmetic and analysis 18 86Ч87 89Ч90 91 96
Arithmetic of congruences 97
Arithmetic of matrices 272 273
Arithmetic, "arithmetic" vs. "number theory" 371Ч372
Arithmetic, clock 97 267
Arithmetic, defined 17 86
Artin, Emil 197 270 325 pl.
Association for Computing Machinery 261
AT&T Bell Labs 291 357
Atiyah, Sir Michael 385
Babbage, Charles 225
Bachmann, Paul 231 238 381
Backlund, Ralf Josef 258 263 384
Barnes, E.W. 223 379
Basel problem 59 62 63Ч65 75Ч76 214 332 370 399
Basel series 63Ч64
Basel University 58
Battle of Auerstaedt 49Ч50
Battle of Valmy 20 49
Bays Ч Hudson number 126 348
Bays, Carter 126 236 380
Bell, Eric Temple 55 59
Berkeley, George 88
Berlin Academy of Science 30 31 60 133 135 185
Berlin Society of Sciences 60
Berlin University 29 383
Bernoulli, Daniel 58 59
Bernoulli, Jakob 10 63 322 370
Bernoulli, Johann 10 58 63
Bernoulli, Nicholas 58
Bernstein, Felix 255 383
Berry, Sir Michael 291 312 316Ч317 342 356 386Ч387 390 pl.
Bertrand's postulate 124
Bertrand, Joseph 124
Bieberbach conjecture 383
Bierberbach, Ludwig 383
Big oh 237 238Ч245 383 396
Biron, Ernst Johann 59
Bohr Ч Landau theorem 394 396
Bohr, Harald 228 325 394
Bohr, Niels 228
Bollobas, Bela 229Ч230 378
Bolyai prize 377
Bolyai, Farkas 92
Bolzano, Bernard 92
Bombieri, Enrico xiv
Book of Numbers, The (Conway and Guy) 369
Boole, George 18 225
Borchardt 135
Borel, Emile 92
Breaking the Code (Whitemore) 262
Brent, Richard P. 258
British mathematics and mathematicians 224Ч226
Brothers Grimm 26
Brouwer, Luitzen 170
Brunswick Polytechnic 193
Brunswick, Dukes of 49Ч50 pl.
Buckley, William F., Jr. 85
Bump, Daniel 352 391
Bump-Ng Theorem 352
Burkill, J.C. 376
Calcul des Residus (Lindeloef) 379
Calculus 119
Calculus and PNT 107Ч113
Calculus in analysis 87Ч88
Calculus, invention 87Ч88 313
Calculus, limit concept 16 175
Cambridge spy ring 226 380
Canonical form 40Ч41
Cantor, Georg 18 92 179
Caratheodory, Constantin 92 372
Card trick exercise 3Ч8
Carl Wilhelm Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick 49Ч50 pl.
Caroline of Brunswick 368
Carroll, Lewis 395
Casti, John L. 377
Catherine the Great, Empress of Russia 60Ч61 121
Catherine, Empress of Russia (wife of Peter the Great) 58
Cauchy Ч Riemann equations 121
Cauchy, Augustin-Louis 92 119
Cayley, Arthur 225 226 277
Chaos theory 312Ч317 387Ч388
Characteristic of a field 268 395 402
Characteristic polynomial of a matrix 272Ч273 274 276
Charles of Sweden 56Ч57
Chebyshev bias 125Ч126 380
Chebyshev limits 154
Chebyshev, Pafnuty Lvovich 122Ч124 125 154 pl.
Chiliads 54
Chinese culture and language 82Ч84
Chowla, Sarvadaman 288 386
Chrystal, George 364
Church, Alonzo 195
Class number problem 386
Clay Mathematics Institute xi 353Ч354
Clay, Landon T. xi 353Ч354
Clebsch, Alfred 364
| Clock arithmetic 97 267
Closed forms 63 64Ч65 75 171 176 314
College de France 159 317 354
Columbia University 164
Complete number system 173 320
Complex function theory 30Ч31 121 124 159 198 206Ч208 379
complex numbers 169Ч170 171 172 173 175Ч177 180 190
Complex Numbers and Functions (Estermann) 206
Complex numbers, amplitude 180Ч182 215
Complex numbers, conjugate 181 191 274 336
Complex numbers, functions of 201Ч204 206Ч208 216Ч217
Complex numbers, modulus 180Ч182
Complex numbers, to complex powers 204Ч205
Complex plane 180Ч181
Complex plane, analysis in 182Ч183
Complex plane, non-trivial zeros on 190Ч192
Complex plane, squaring function on 209Ч210
Congress of Vienna 20Ч21 61 92
Congruences, arithmetic of 97
Conjugate of a complex number 181
Connes, Alain 317Ч321 384 388 pl.
Conrey, Brian 353
Continuity 88 90Ч91 119
Continuum Hypothesis 170 188Ч189
Contour integration 402
Convergence and completeness of a number system 173
Convergence as illustrated by rulers 10Ч15 173
Convergence in Riemann's formula for J(x) 338Ч339 342
Convergence of a complex series 182Ч183
Convergence of a sequence for 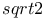 16 67 179 16 67 179
Convergence of a series for e 202Ч203
Convergence of Basel series 64
Convergence of sequences for  and e 16 173 and e 16 173
Convergence of series for 1/(1-x) 138
Convergence of series via sequences 16Ч17
Convergence of the eta series 145
Convergence of the zeta series for complex arguments 205
Convergence of the zeta series for real arguments 79
Convergence, absolute 150
Convergence, conditional 149Ч150 339
Conway, John 369
Counting logic vs. measuring logic 82Ч86
Courant Institute conference 245 351Ч352 355 359
Courant, Richard 187 255
Cours d'Analyse (Jordan) 226
Course of Pure Mathematics, A, (Hardy) 226
Coxeter, H.S.M. "Donald" 196 378
Cramer model 323Ч324
Cramer, Harald 323 388 394 pl.
Creasy, Sir Edward 20
Critical line 191 192 198Ч199 217 221Ч222 337 346Ч347
Critical line, height up 258Ч260
Critical line, number of zeros on 258 259 289Ч290
Critical strip 191 216 306Ч309
Critique of Pure Reason (Kant) 130
d'Oresme, Nicole 9 88
Data vs. datum 85Ч86
Davenport, Harold 372 383
Davis, Martin 187
Davis, Philip J. 122 123
de Bourienne, Louis 60
de Branges, Louis 383
de Fermat, Pierre 371
de la Vallee Poussin, Charles x 153 155Ч156 161 189 223 232 237 352 356 376 pl.
de Maupertuis, Pierre 370
de Morgan, Augustus 226
de Tocqueville, Alexis 118
Decembrists 122
Dedekind, Richard 19 25 27 30 92 120 131 132 133 134 193 362Ч363 366 pl.
Deleglise, Marc 380
Deligne, Pierre 270 325 355 384 pl.
Denjoy's probabilistic interpretation 325 388
Density hypothesis xiv
Derbyshire, John pl. 8
derivatives 109 110
Desargue's Theorem 196
Descartes, Rene 18 164
Diamond, Harold 287 386
Differential geometry 128
Differentiation 41Ч42 109Ч110
Dirichlet, Lejuene 91 93 94Ч95 96Ч97 119 126Ч127 133 134 194 232 372 374 pl.
Disquisitiones Arithmeticae (Gauss) 93 97
Divergence and convergence compared 11Ч15
Divergence of harmonic series 9Ч10 18 63Ч64 338 399
Divergence of series for 1/(1-x) 139
Divergence of series of reciprocals of primes 154
Divergence of the zeta series for arguments less than one 80Ч81
Doxiadis, Apostolos 90
Dreyfus Affair 162Ч163 164 165
Dreyfus, Alfred 162Ч163
Dreyfus, Mathieu 162
DuBois-Reymond, Emil 253
Dukas, Paul 156
Dynamical systems 281 315
Dyson, Freeman 282 287 288 290Ч291 pl.
e 40Ч41 55 69 185 202Ч203 365Ч366
Ebell, Charlotte (mother of Bernhard Riemann) 22
Edwards, Harold 153 217 263 298 375 377 384
Eigenfunction 318
Eigenvalues 273 274 276 283 284 285 295
Einstein, Albert 128 165 313 386
Eisenstein, Gotthold 119 129
Elizabeth, Empress of Russia (daughter of Peter the Great) 58
Encke, Johann Franz 53Ч54
Entire functions 332Ч333
Eratosthenes of Cyrene 100Ч101 372
Erdos, Paul 125 378
Ernest Augustus, King of Hanover 26 366
Error term 190 234Ч235 236Ч237 241 243Ч244 326 327Ч349
Erwin Schroedinger Institute 352
Esterhazy, Major Count Ferdinand Walsin- 162
Estermann, Theodor 206 226 379
Eta function 145Ч146
Euclid of Alexandria 18 34 232
Euler product formula 105Ч106 373
Euler Ч Maclaurin summation 263
Euler Ч Mascheroni number 55 369Ч370
Euler, Catherine (nee Gsell) 59 62
Euler, Leonhard 9 15 40 55Ч56 58 59 60 61Ч62 65 75Ч76 87 88 95 97 98 100 106 121 146Ч147 374 pl.
Euler, Salome (nee Gsell) 62
Evelyn, John 56
Exiguus, Dionysus 84
Existence proofs 184Ч185
Exponential function for complex numbers 202
Exponential function, canonical form 40Ч41
Exponential function, defined 39Ч40
Exponential function, inverse of 43Ч44
exponentiation 68Ч69
Extended Riemann hypothesis xiv
Extrapolation, card trick exercise 7Ч8
Extrapolation, defined 7
Factor, defined 32
Factor, proper 32
Factor, trivial 32 36
Factorial function 124 147
Faure, Felix 162 163
Fejer, Lipot 378
Fermat's last theorem x xi 90 161 197 271 354 371
Fermi, Enrico 280
Feynman, Richard 291
Field theory 197 265Ч271
Field, characteristic of 268
Field, defined 266
Field, finite 267
Field, infinite 266
Fields medal 261 270 384 385
Finite fields 267 321Ч322
Form factor 287 288Ч289
Four-color theorem x xi 197
Fourier, Joseph 92 93 119
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте