|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Katz E. (ed.) Ч Handbook of HPLC |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 -olefin sulfonates 793 -olefin sulfonates 793
 -olefin sulfonates other anionic sulfonates 793Ч795 -olefin sulfonates other anionic sulfonates 793Ч795
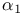 -Acidglycoprotein (ACP) chiral stationary phase 673Ч675 -Acidglycoprotein (ACP) chiral stationary phase 673Ч675
6-Methylen-androsta-l,4-diene-3,7-dione 654
Acid-base equilibria 37Ч47
Acrylic polymer-based phase for ion-exchange chromatography 386Ч387
Actinides 820Ч821
Activity coefficients in mixed liquid phases 7Ч14
Acyclovir 630
Adsorption chromatography 325Ч348
Adsorption chromatography retention mechanisms 327Ч348
Adsorption chromatography retention mechanisms, applications 344Ч348
Adsorption chromatography retention mechanisms, localized and delocalized interactions 329
Adsorption chromatography retention mechanisms, main parameters goveming solutes 329Ч340
Adsorption chromatography retention mechanisms, mobile phase choice and optimization 340Ч344
Adsorption chromatography retention mechanisms, Snyder Ч Soczewkinski model 327Ч329
Adsorption chromatography stationary phases 325Ч327
Adsorption chromatography stationary phases, bare silica 325Ч327
Adsorption chromatography stationary phases, miscellaneous adsorbents 327
Adsorption isotherms determination by displacement chromatography 883Ч885
Advanced data analysis, computer-assisted 259Ч267
Affinity chromatography (AFC) 483Ч498
Affinity chromatography (AFC) principles 483Ч491
Affinity chromatography (AFC) principles, application conditions 489Ч491
Affinity chromatography (AFC) principles, elution conditions 491
Affinity chromatography (AFC) principles, immobilization methods 489 490
Affinity chromatography (AFC) principles, support materials 487Ч489
Affinity chromatography (AFC) principles, theoretical basis 484Ч486
Affinity chromatography (AFC) principles, types of affinity ligands 486Ч487
Affinity chromatography (AFC) stationary phases 32Ч33
Affinity chromatography (AFC) types of AFC 492Ч496
Affinity chromatography (AFC) types of AFC analytical affinity chromatography 495Ч496
Affinity chromatography (AFC) types of AFC bioaffinity chromatography 492
Affinity chromatography (AFC) types of AFC dye-ligand affinity chromatography 494
Affinity chromatography (AFC) types of AFC immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography 494Ч495
Affinity chromatography (AFC) types of AFC immunoaffinity chromatography 492Ч494
Affinity chromatography (AFC) types of AFC miscellaneous ligands and methods 496
Agricultural applications of biotechnology 696
Alclofenac 630Ч631
Alcohol ethoxylates 801
Alcohols, dervatization of 684Ч685
Alkali metals 818
Alkaline earth metals 818
Alkanesulfonates 790Ч791
Alkyl sulfates 790Ч791
Alkylarylsulfonates 791Ч792
Alkylphenol ethoxylates 800Ч801
Alumina 22 24
Alumina, adsorption chromatography and 327
Alumina, chemically bonded alumina-based phases 315
Alumina, polymer-coated alumina-based phases 316
Amfenac 631
Amine oxides 802
Amines, denvatization of 685Ч686
Amino acids 707Ч716
Amino acids classic analysis of 707
Amino acids detection of underivatized ammo acids 709
Amino acids hydrolysis of polypeptides 707Ч709
Amino acids postcolumn reaction detection methods 709Ч710
Amino acids precolumn denvatization techniques 710Ч716
Ammonium 821
Amoxicillin 631Ч632
Amphoteric surfactants 796Ч798
Analytical affinity chromatography 495Ч496
Analytical affinity chromatography, ion-exchange process for low molecular weight ions in 366Ч371
Anion self-regenerating suppressor 428 429
Anion separation in nonsuppressed ion chromatography 441
Anionic surfactants 790Ч795
Anionic surfactants alkyl sulfates and alkanesulfonates 790Ч791
Anionic surfactants alkylarylsulfonates 791Ч792
Anionic surfactants ether sulfates 792Ч793
Anions see УIons and inorganic speciesФ
Arsenic anions 815Ч816
Art conservation 903Ч927
Art conservation, background 903Ч904
Art conservation, future applications 919Ч920
Art conservation, future applications fatty acid analysis and hybrid techniques 919Ч920
Art conservation, future applications LC-mass spectrometry 920
Art conservation, future applications, carbohydrate analysis of gums and celluloses 919
Art conservation, general areas of investigation 904Ч905
Art conservation, primary HPLC applications 905Ч919
Art conservation, primary HPLC applications, identification of natural and early synthetic dyestuffs 905Ч909
Art conservation, primary HPLC applications, ion chromatography for monitoring inorganic contaminants 918
Art conservation, primary HPLC applications, monitoring organic pollutants in museum environment 918Ч919
Art conservation, primary HPLC applications, proteinaceous materials in conservation 910Ч914
Art conservation, primary HPLC applications, study of degradation and polymerization reactions 914Ч918
Ascorbic acid 632
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) process 591Ч593 960Ч964
Atomic absorption (AA) 404Ч406
Atomic absorption (AA), LC-atomic absorption spectroscopy (LC-AA) tandem systems 596Ч600
Autosamplers 569 570Ч571
BAYy3118 632
Benorylate, quantitation of impurities in 356Ч357 358
Bioaffinity chromatography 492
Biological ion exchangers 390Ч391
Biologically active compounds see УDrugs in biological samplesФ
Biomedical science, role of hydrophobicity in 860Ч861
biotechnology 695Ч751
Biotechnology amino acids 707Ч716
Biotechnology amino acids, classic analysis 707
Biotechnology amino acids, detection of underivatized amino acids 709
Biotechnology amino acids, hydrolysis of polypeptides 707Ч709
Biotechnology amino acids, postcolunm reaction detection methods 709Ч710
Biotechnology amino acids, precolumn derivatization techniques 710Ч716
Biotechnology carbohydrates 734Ч742
Biotechnology carbohydrates complex carbohydrates 736Ч739
Biotechnology carbohydrates microheterogeneity of glycoproteins 739Ч742
Biotechnology carbohydrates simple carbohydrates and related compounds 735Ч736
Biotechnology downstream processing 742Ч745
Biotechnology general chromatographic developments 700Ч707
Biotechnology general chromatographic developments, bioprocess control 700Ч702
Biotechnology general chromatographic developments, column technology 702Ч707
Biotechnology methodology 697Ч700
Biotechnology nucleic acid and related compounds 729Ч734
Biotechnology nucleic acid and related compounds, large deoxyribonucleotides 732Ч733
Biotechnology nucleic acid and related compounds, large ribonucleotides 733Ч734
Block copolymers of ethylene oxide and propylene oxide 802
Bromazepam 633
Bulk properly detectors 536Ч539
Bulk properly detectors electrical conductivity detector 537Ч539
Bulk properly detectors refractive index detectors 536Ч537
Buprenorphine 634
Calibration for an SEC system 277Ч281
Calibration for an SEC system broad-molecular weight calibration 279
Calibration for an SEC system primary calibration 278
Calibration for an SEC system secondary calibration 279
Calibration for an SEC system universal calibration 279Ч281
Canrenone 635
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) 44Ч46 169Ч191 822Ч824
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), emergence of commercial instruments 170Ч172
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), HPLC and 170
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), modes 184Ч189
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), modes capillary gel electrophoresis 188Ч189
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), modes capillary isolectic focusing 187Ч188
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), modes capillary isotachophoresis 186Ч187
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), modes capillary zone electrophoresis 185Ч186
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), modes micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography 186
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), principles 172Ч184
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), principles, electro osmotic flow 174Ч177
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), principles, electrophoresis mobility 172Ч173
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), principles, experimental considerations 182Ч184
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), principles, factors influencing performance 180Ч182
Capillary electrophoresis (CE), principles, separation efficiency and resolution 177Ч180
Capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE) 170 188Ч189
Capillary isolectric focusing (CIEF) 170 187Ч188
Capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) 170 185Ч186
Carbamazepine 635
Carbohydrate analysis of gums and cellulose 919
Carbohydrates 734Ч742 753Ч757
Carbohydrates, complex carbohydrates 736Ч739
| Carbohydrates, microheterogeneity of glycoproteins 739Ч742
Carbohydrates, simple carbohydrates and related compounds 735Ч736
Carbon-based phases for RPLC 314
Carbon-clad zirconia 316
Carboxylic acids 817
Carboxylic acids derivatization of 686Ч687
Catecholamines 636Ч638
Cation self-regenerating suppressor 428 429
Cationic surfactants 795
Cations see УIons and inorganic speciesФ
Celiprolol 638
Cellulose-based phases 387Ч391
Check valves 505Ч508
Chelation equilibria 49Ч51
Chemically bonded alumina-based phases 315
Chemically bonded silica-based phases for RPLC 298Ч310
Chemically bonded silica-based phases for RPLC, characterization techniques 308Ч310
Chemically bonded silica-based phases for RPLC, monomeric stationary phases 299Ч302
Chemically bonded silica-based phases for RPLC, polymeric stationary phases 302
Chemically bonded silica-based phases for RPLC, selectivities of phases 303Ч308
Chemicals, application of biotechnology for 696
Chemisorption chromatography 496
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis 669Ч693
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral mobile-phase additives (CMPAs) 677Ч682
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral mobile-phase additives (CMPAs), chiral counterions 678Ч680
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral mobile-phase additives (CMPAs), cyclodextrins 680Ч682
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral mobile-phase additives (CMPAs), ligand- exchange chromatography 678
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral stationary phases (CSPs) 670Ч677
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral stationary phases (CSPs), 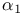 -acidglycoprotein 673Ч675 -acidglycoprotein 673Ч675
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral stationary phases (CSPs), cyclodextrin stationary phases 675Ч676
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral stationary phases (CSPs), ovomucoid-bonded stationary phase 675
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral stationary phases (CSPs), Pirkle phases 677
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral stationary phases (CSPs), polysaccharides 670Ч673
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, chiral stationary phases (CSPs), serum albumin phases 675
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, enantioselectivity in biological systems 669
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, indirection separation of enantiomers 682Ч687
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, indirection separation of enantiomers derivatization of alcohol 684Ч685
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, indirection separation of enantiomers derivatization of amines 685Ч686
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, indirection separation of enantiomers derivatization of carboxylic acids 686Ч687
Chiral pharmaceutical analysis, separation of enantiomers by HPLC 670
Chiral stationary phases (CSPs) 33Ч35 670Ч677
Chloroguanide 638
Chloroqume 638
Chlortetracycline 666
Chlorzoxazone 638Ч639
Chromate 816
Chromatographic hydrophobicily index 867Ч873
Chromatographic profiles and retention, prediction of 238Ч246
Chromatographic profiles and retention, prediction of quantitative structure-retention relations 241Ч243
Chromatographic profiles and retention, prediction of simulation of profiles 240Ч241
Chromatographic profiles and retention, prediction of Уfirst-guessФ expert systems 243Ч246
Clobazam 639
Clozapine 639
Cocaine 639Ч641
Collection devices 617Ч627
Collection devices applications 622
Collection devices fraction collectors 617Ч618
Collection devices operational considerations of fraction collection 618Ч622
Collection devices operational considerations of fraction collection low-resolution techniques 618
Collection devices operational considerations of fraction collection separation of complex mixtures 618Ч622
Collection devices other types of fraction collection devices 622Ч625
Collection devices troubleshooting 625Ч627
Column efficiency, effects of temperature on 608
Column-switching methods 198Ч205
Column-switching methods, effects of the column in LC 198Ч200
Column-switching methods, relative advantages and disadvantages of gradient-elution LC methods and 230
Column-switching methods, relative advantages and disadvantages of isocratic LC separations and 229
Column-switching methods, valve-switching options and requirements 200Ч205
Column-switching valves 569Ч573
Complex carbohydrates 736Ч739
Complex stability constants, determination of 875Ч878
Complexation equilbna 47Ч51
Compressibility effects onflow and plate weight 118Ч120
Computers 233Ч271
Computers, advanced data analysis 259Ч267
Computers, advanced data analysis, multivariate data analysis 263Ч267
Computers, advanced data analysis,univariate data analysis 260Ч263
Computers, automation and instrument control 234Ч238
Computers, automation and instrument control, column coupling and hyphenated separation techniques 237Ч238
Computers, automation and instrument control, on-line monitoring and control 238
Computers, automation and instrument control, sample preparation 235Ч237
Computers, computer-assisted method development 246Ч257
Computers, computer-assisted method development for gradient separations 253Ч255
Computers, computer-assisted method development for isocratic separations 255Ч257
Computers, computer-assisted method development, general considerations 247Ч251
Computers, computer-assisted method development, optimization criteria 251Ч252
Computers, interlaboratory tests using on-line LC 964Ч970
Computers, method validation 257Ч259
Computers, prediction of chromatographic profiles and retention 238Ч246
Computers, prediction of chromatographic profiles and retention, quantitative structure-retention relations 241Ч243
Computers, prediction of chromatographic profiles and retention, simulation of profiles 240Ч241
Computers, prediction of chromatographic profiles and retention, Уfirst-guessФ expert systems 243Ч246
Conductimetric detection 395Ч396
Conductivity detection 160Ч162
Conductivity detection in ion chromatography 417Ч419
Conductivity detection principles of operation 160Ч161
Conductivity detection suppression systems 161Ч162
Constant flow rate pumps 500Ч501
Constant-pressure pumps 500
Cosmetics, applications of biotechnology for 696
Coumann 641Ч642
Cyclamates 754
Cyclodextrins (CDs) 680Ч682
Danazol 642
Debrisoquine 642
Deoxyribonucleotides, large 732Ч733
Detectors (detection) 143Ч168 531Ч558
Detectors (detection) as operating variable in ion-exchange chromatography 395Ч406
Detectors (detection) in ion interaction chromatography 457Ч459
Detectors (detection) to identify lipid components 758Ч761 764 765 766
Detectors (detection), bulk properly detectors 536Ч539
Detectors (detection), bulk properly detectors, electrical conductivity detector 537Ч538
Detectors (detection), bulk properly detectors, refractive index detectors 536Ч537
Detectors (detection), choice of detectors 555Ч556
Detectors (detection), comparison of detector performances 167Ч168
Detectors (detection), conductivity detection 160Ч162
Detectors (detection), conductivity detection principles of operation 160Ч161
Detectors (detection), conductivity detection suppression systems 161Ч162
Detectors (detection), derivatization 554Ч555
Detectors (detection), detectors for polymer analysis 162Ч165
Detectors (detection), detectors for polymer analysis, evaporative detectors 163Ч164
Detectors (detection), detectors for polymer analysis, light-scattering detection 164Ч165
Detectors (detection), detectors for polymer analysis, viscosity detectors 165
Detectors (detection), effects of temperature on 609Ч610
Detectors (detection), electrochemical detection 156Ч160
Detectors (detection), electrochemical detection, electrode materials, flow-cells, and instrumentation 158
Detectors (detection), electrochemical detection, principles of operation 156Ч158
Detectors (detection), electrochemical detection, pulsed-amperometric detection 159Ч160
Detectors (detection), electrochemical detection, selectivity enhancement 159
Detectors (detection), fluorescence detection 150Ч154
Detectors (detection), fluorescence detection, fluorescence yields 152
Detectors (detection), fluorescence detection, instrumentation 152Ч153
Detectors (detection), fluorescence detection, postcolunm denvatization 154
Detectors (detection), fluorescence detection, precolunm fluorescence labeling 153
Detectors (detection), for the SEC system 284Ч289
Detectors (detection), for the SEC system, composition detectors 285Ч287
Detectors (detection), for the SEC system, concentration detectors 284Ч285
Detectors (detection), for the SEC system, molecular-weight-sensitive detectors 287Ч289
Detectors (detection), operation of LC detectors 556
Detectors (detection), other detectors 165Ч167
Detectors (detection), other detectors, gas-phase detectors 167
Detectors (detection), other detectors, infrared detection 165Ч166
Detectors (detection), other detectors, optical activity detection 166
Detectors (detection), other detectors, radiochemical detection 166
Detectors (detection), refractive index detection 154Ч156
Detectors (detection), refractive index detection, optical principles 155
Detectors (detection), refractive index detection, performance and application 156
Detectors (detection), requirements for and characterization of detectors 143Ч147
Detectors (detection), requirements for and characterization of detectors, linearity 146
Detectors (detection), requirements for and characterization of detectors, peak broadening 144
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -olefin sulfonates
-olefin sulfonates 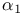 -Acidglycoprotein (ACP) chiral stationary phase
-Acidglycoprotein (ACP) chiral stationary phase