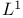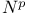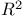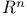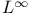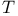|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Stein E.M. Ч Harmonic Analysis: Real-Variable Methods, Orthogonality, and Oscilattory Integrals |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
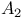 194 216Ч217 225Ч226 194 216Ч217 225Ч226
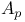 weights 193Ч227 weights 193Ч227
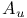 56 197 214Ч216 56 197 214Ч216
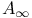 196 201Ч203 212Ч214 218 219 225 196 201Ч203 212Ч214 218 219 225
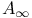 and BMO 141 177 197 218 219 225 and BMO 141 177 197 218 219 225
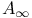 and maximal functions 195 198Ч203 and maximal functions 195 198Ч203
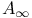 and real-variable structures 223 and real-variable structures 223
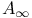 and singular integrals 204Ч211 221 and singular integrals 204Ч211 221
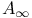 , , 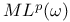 210 222 210 222
 , duality 194 , duality 194
 , extrapolation theorem 223 , extrapolation theorem 223
 , factorization 216Ч217 , factorization 216Ч217
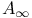 , functions in 218 , functions in 218
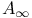 , interpolation 218 , interpolation 218
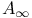 , overspill 202 212Ч214 218 , overspill 202 212Ч214 218
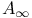 , relative 219 (see also УSeverse Holder inequalitiesФ) , relative 219 (see also УSeverse Holder inequalitiesФ)
 (Triebel Ч Lizorkin spaces) 264 319 (Triebel Ч Lizorkin spaces) 264 319
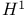 88 91Ч92 128 88 91Ч92 128
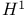 and BMO 142Ч144 163Ч165 178 183 and BMO 142Ч144 163Ч165 178 183
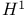 and Fourier integral operators 402Ч405 410Ч411 428 and Fourier integral operators 402Ч405 410Ч411 428
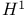 and VMO 180 and VMO 180
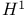 , atomic decomposition 77 142 147 , atomic decomposition 77 142 147
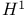 , atoms 91 129 , atoms 91 129
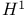 , dense subspace , dense subspace  142 142
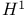 , functions in 137 178 , functions in 137 178
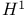 , martingale 188 (see also УSingular integralsФ) , martingale 188 (see also УSingular integralsФ)
 (Heisenberg group) 5 11 517 527Ч588 594Ч618 627Ч635 (Heisenberg group) 5 11 517 527Ч588 594Ч618 627Ч635
 (Heisenberg group) and rotational curvature 495 (Heisenberg group) and rotational curvature 495
 (Heisenberg group) as translations of (Heisenberg group) as translations of  530 530
 (Heisenberg group), approximation by 631 639Ч640 (Heisenberg group), approximation by 631 639Ч640
 (Heisenberg group), balls (Heisenberg group), balls  542 542
 (Heisenberg group), dilations 541 (Heisenberg group), dilations 541
 (Heisenberg group), Fourier transform 569Ч573 583 (Heisenberg group), Fourier transform 569Ч573 583
 (Heisenberg group), Haar measure 531 (Heisenberg group), Haar measure 531
 (Heisenberg group), heat equation 632Ч633 642Ч643 (Heisenberg group), heat equation 632Ч633 642Ч643
 (Heisenberg group), Lie algebra (Heisenberg group), Lie algebra 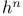 543Ч547 584 543Ч547 584
 (Heisenberg group), multiplication law 530 (Heisenberg group), multiplication law 530
 (Heisenberg group), multipliers 642 (Heisenberg group), multipliers 642
 (Heisenberg group), nonstandard dilations 620 (Heisenberg group), nonstandard dilations 620
 (Heisenberg group), norm (Heisenberg group), norm  541 638 541 638
 (Heisenberg group), polar coordinates 542 (Heisenberg group), polar coordinates 542
 (Heisenberg group), radial functions 583 (Heisenberg group), radial functions 583
 (Heisenberg group), representations 551 568Ч569 577 598 635 (Heisenberg group), representations 551 568Ч569 577 598 635
 (Heisenberg group), restriction theorems 642 (Heisenberg group), restriction theorems 642
 (Heisenberg group), Riesz transforms 605Ч608 (Heisenberg group), Riesz transforms 605Ч608
 (Heisenberg group), singular integrals 536Ч543 557Ч568 580Ч581 586 (Heisenberg group), singular integrals 536Ч543 557Ч568 580Ч581 586
 (Heisenberg group), vector fields X, Y, Z, T 544Ч547 584 597 598 (Heisenberg group), vector fields X, Y, Z, T 544Ч547 584 597 598
 (Hardy spaces) 4 87Ч138 (Hardy spaces) 4 87Ч138
 (Hardy spaces) and (Hardy spaces) and 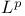 87 91 92 87 91 92
 (Hardy spaces) and (Hardy spaces) and 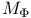 ( ( singular) 130Ч131 singular) 130Ч131
 (Hardy spaces) and Fourier transform 128 (Hardy spaces) and Fourier transform 128
 (Hardy spaces) and harmonic functions 88 118Ч127 133Ч134 (Hardy spaces) and harmonic functions 88 118Ч127 133Ч134
 (Hardy spaces) and real-variable structures 186 (see also УSingular integralsФ) (Hardy spaces) and real-variable structures 186 (see also УSingular integralsФ)
 (Hardy spaces) and weights 223 (Hardy spaces) and weights 223
 (Hardy spaces), atomic decomposition 105Ч112 137 182 (Hardy spaces), atomic decomposition 105Ч112 137 182
 (Hardy spaces), atoms 105Ч106 112 130 (Hardy spaces), atoms 105Ч106 112 130
 (Hardy spaces), boundary values 127 (Hardy spaces), boundary values 127
 (Hardy spaces), definitions 87 (Hardy spaces), definitions 87
 (Hardy spaces), dense subspaces 109Ч112 128 133 (Hardy spaces), dense subspaces 109Ч112 128 133
 (Hardy spaces), distributions in 88 129 131 (Hardy spaces), distributions in 88 129 131
 (Hardy spaces), duals for p < 1 130 (Hardy spaces), duals for p < 1 130
 (Hardy spaces), maximal characterization 90Ч101 131 (Hardy spaces), maximal characterization 90Ч101 131
 (Hardy spaces), norm (Hardy spaces), norm  100 100
 (Hardy spaces), product theory 138 (Hardy spaces), product theory 138
 (Hardy spaces), topology 100 127 (Hardy spaces), topology 100 127
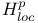 (local (local  ) 134 264 ) 134 264
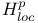 (local (local  ), distributions in 135Ч136 429 ), distributions in 135Ч136 429
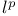 4 13 4 13
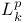 (Sobolev spaces) 251Ч252 634 (Sobolev spaces) 251Ч252 634
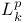 and and  264 264
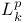 and and 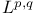 265 265
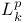 and and  264 264
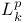 and tangential approach 79 and tangential approach 79
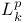 , nonisotropic , nonisotropic  606Ч610 634 606Ч610 634
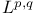 (Lorentz spaces) 36 265 418 526 (Lorentz spaces) 36 265 418 526
 see У see У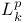 Ф Ф
 (usual symbols) 229 232Ч263 (usual symbols) 229 232Ч263
 (usual symbols) and BMO 264 (usual symbols) and BMO 264
 (usual symbols) and singular integrals 235 241Ч249 (usual symbols) and singular integrals 235 241Ч249
 (usual symbols) on (usual symbols) on 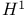 402Ч403 402Ч403
 (usual symbols) on (usual symbols) on  264 264
 (usual symbols) on (usual symbols) on 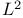 234Ч237 234Ч237
 (usual symbols) on (usual symbols) on 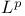 250 250
 (usual symbols) on (usual symbols) on 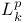 251Ч252 (see also УPseudo-differential operatorsФ) 251Ч252 (see also УPseudo-differential operatorsФ)
 (usual symbols) on (usual symbols) on 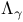 253Ч257 253Ч257
 (usual symbols) on S 232 (usual symbols) on S 232
 (usual symbols), (usual symbols), 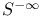 261 261
 (usual symbols), adjoints 259 554 (usual symbols), adjoints 259 554
 (usual symbols), calculus 237Ч241 579 (usual symbols), calculus 237Ч241 579
 (usual symbols), change of variables 259 (usual symbols), change of variables 259
 (usual symbols), commutators 261 308Ч312 (usual symbols), commutators 261 308Ч312
 (usual symbols), dyadic decomposition 243Ч245 253Ч257 (usual symbols), dyadic decomposition 243Ч245 253Ч257
 (usual symbols), homogeneity 262 (usual symbols), homogeneity 262
 (usual symbols), kernels 235 241Ч245 262 (usual symbols), kernels 235 241Ч245 262
 (usual symbols), symmetric (usual symbols), symmetric  579 579
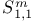 (forbidden symbols) 270Ч275 (forbidden symbols) 270Ч275
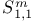 (forbidden symbols) and singular integrals 269 302 324 (forbidden symbols) and singular integrals 269 302 324
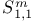 (forbidden symbols) on (forbidden symbols) on 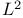 272Ч273 272Ч273
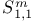 (forbidden symbols) on (forbidden symbols) on 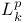 319 319
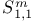 (forbidden symbols) on (forbidden symbols) on 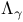 274Ч275 274Ч275
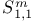 (forbidden symbols), dyadic decomposition 271Ч275 (forbidden symbols), dyadic decomposition 271Ч275
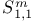 (forbidden symbols), kernels 271 (forbidden symbols), kernels 271
 (exotic symbols) 271 (exotic symbols) 271
 (exotic symbols) on (exotic symbols) on 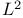 319 319
 (exotic symbols) on (exotic symbols) on 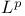 322Ч323 322Ч323
 (exotic symbols) on S 271 (exotic symbols) on S 271
 (exotic symbols), calculus 320 (exotic symbols), calculus 320
 (exotic symbols), examples 277Ч278 (exotic symbols), examples 277Ч278
 (exotic symbols), frequency decomposition 319 (exotic symbols), frequency decomposition 319
 (exotic symbols) 276 282Ч288 (exotic symbols) 276 282Ч288
 (exotic symbols) on (exotic symbols) on 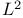 282Ч288 323 282Ч288 323
 (exotic symbols) on (exotic symbols) on 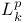 319 319
 (exotic symbols), dyadic decomposition 286Ч288 (exotic symbols), dyadic decomposition 286Ч288
 (exotic symbols), examples 276Ч277 585Ч586 (exotic symbols), examples 276Ч277 585Ч586
 (exotic symbols), frequency decomposition 282Ч285 (exotic symbols), frequency decomposition 282Ч285
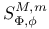 320Ч321 320Ч321
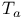 (operator w/symbol a) 231 (operator w/symbol a) 231
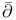 -complex 591Ч592 -complex 591Ч592
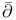 -Neumann problem 587 592 627Ч631 -Neumann problem 587 592 627Ч631
 -Neumann problem and integral formulas 631 -Neumann problem and integral formulas 631
 -Neumann problem and strong pseudoconvexity 631 -Neumann problem and strong pseudoconvexity 631
 -Neumann problem and weak pseudoconvexity 631 -Neumann problem and weak pseudoconvexity 631
 -Neumann problem, sharp estimates 631 -Neumann problem, sharp estimates 631
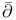 -Neumann problem, solution on -Neumann problem, solution on  630 630
 -complex 592Ч595 -complex 592Ч595
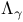 (Lipschitz spaces) 130 253Ч257 274 (Lipschitz spaces) 130 253Ч257 274
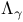 (Lipschitz spaces), (Lipschitz spaces),  264 319 264 319
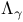 (Lipschitz spaces), nonisotropic (Lipschitz spaces), nonisotropic 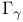 (Lipschitz spaces) 634 (Lipschitz spaces) 634
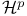 (holomorphic (holomorphic  ) 131Ч132 137 226 ) 131Ч132 137 226
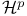 (holomorphic (holomorphic  ), ),  \mathcal{U}^n \mathcal{U}^n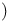 532Ч541 532Ч541
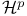 (holomorphic (holomorphic  ), boundary values 532Ч535 ), boundary values 532Ч535
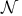 (tent spaces) 58Ч65 77Ч78 (tent spaces) 58Ч65 77Ч78
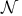 (tent spaces) and Carleson measures 59Ч61 63 77 161Ч163 (tent spaces) and Carleson measures 59Ч61 63 77 161Ч163
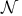 (tent spaces), (tent spaces), 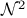 161Ч164 161Ч164
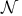 (tent spaces), (tent spaces),  180Ч184 180Ч184
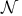 (tent spaces), atomic decomposition 63Ч65 77 181Ч182 (tent spaces), atomic decomposition 63Ч65 77 181Ч182
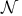 (tent spaces), atoms 63 181 (tent spaces), atoms 63 181
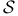 (Schwartz class) 88 (Schwartz class) 88
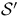 (tempered distributions) 89 (tempered distributions) 89
 90 90
 (upper half-space) 528Ч543 587 (upper half-space) 528Ч543 587
 (upper half-space), (upper half-space),  (boundary) 529 545Ч547 641Ч642 (boundary) 529 545Ч547 641Ч642
 (upper half-space), (upper half-space), 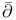 -Neumann problem 627Ч631 -Neumann problem 627Ч631
 (upper half-space), (upper half-space),  532Ч541 532Ч541
 (upper half-space), automorphism group 574Ч576 (upper half-space), automorphism group 574Ч576
 (upper half-space), coordinates (upper half-space), coordinates ![$[\zeta,t, r]$](/math_tex/13d4d09dad972ba3e8d60621e279b3ac82.gif) 531 628 531 628
 (upper half-space), defining function r(z) 530 (upper half-space), defining function r(z) 530
 (upper half-space), dilations 530 538 (upper half-space), dilations 530 538
 (upper half-space), equivalence with ball 529 (upper half-space), equivalence with ball 529
 (upper half-space), measure (upper half-space), measure 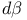 532 532
|  (upper half-space), rotations 530 (upper half-space), rotations 530
 (upper half-space), translation group (upper half-space), translation group  530 530
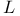 (sub-Laplacian) 39 46 636 642 (sub-Laplacian) 39 46 636 642
 588 596Ч610 628Ч630 632Ч635 588 596Ч610 628Ч630 632Ч635
 , forbidden values 598 , forbidden values 598
 , fundamental solution , fundamental solution 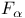 598Ч602 632 598Ч602 632
 , hypoellipticity 604 635 , hypoellipticity 604 635
 , invertibility 598 635 , invertibility 598 635
 , local solvability 602Ч604 , local solvability 602Ч604
 , relative solution 615Ч618 634 , relative solution 615Ч618 634
 , sharp regularity 609Ч610 , sharp regularity 609Ч610
 , solution operator , solution operator 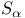 602 602
 , symmetry 596 599 633Ч634 , symmetry 596 599 633Ч634
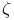 -convexity 48 -convexity 48
a(x, D) (operator w/symbol a) 231
Approximations of the identity 23Ч24 56 198 242
Approximations of the identity and singular integrals 81
Approximations of the identity, relations between 93Ч94 138
Approximations of the identity, singular 71Ч75 80Ч83 130Ч131 481
Approximations of the identityon homogeneous groups 638
Area integral 47 182Ч184
Area integral and  124Ч127 124Ч127
Atomic decomposition in 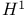 77 142 147 77 142 147
Atomic decomposition in  105Ч112 137 182 105Ч112 137 182
Atomic decomposition in 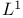 129 129
Atomic decomposition in 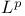 (p > 1) 112 185 (p > 1) 112 185
Atomic decomposition in 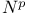 181Ч182 181Ч182
Atomic decomposition in N 63Ч65 77
Atomic decomposition, localized 137
Atoms in 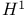 91 129 91 129
Atoms in  105Ч106 112 130 105Ч106 112 130
Atoms in 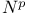 181 181
Atoms in N 63
Averages over hypersurfaces 467Ч472 493Ч511 517Ч525
Averages over hypersurfaces and 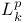 370Ч372 517 370Ч372 517
Averages over hypersurfaces and averages over submanifolds 467Ч469
Averages over hypersurfaces and Fourier integral operators 360 496 517
Averages over hypersurfaces in 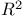 519Ч523 519Ч523
Averages over hypersurfaces on 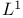 503 503
Averages over hypersurfaces, 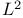 estimates 469Ч471 501Ч502 504Ч507 estimates 469Ч471 501Ч502 504Ч507
Averages over hypersurfaces, 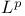 estimates 370Ч372 471Ч472 499 503 507 estimates 370Ч372 471Ч472 499 503 507
Averages over hypersurfaces, curvature has zeros 512 518
Averages over hypersurfaces, definability on 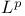 508Ч509 508Ч509
Averages over hypersurfaces, dilated 510Ч511
Averages over hypersurfaces, dimension restrictions 471Ч472 502 509Ч510
Averages over hypersurfaces, finite type 518
Averages over hypersurfaces, sharp exponents 471Ч472
Averages over hypersurfaces, smoothing 173Ч174 370Ч372 517
Averages over hypersurfaces, spheres 131 173Ч174 395 399 469Ч472 518Ч519 523
Averages over hypersurfaces, variable 493Ч499
Averages over measures on universal variety 486Ч489
Averages over measures, 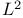 estimates 487Ч488 511 estimates 487Ч488 511
Averages over measures, 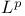 estimates 486Ч489 514 estimates 486Ч489 514
Averages over measures, cancellation conditions 513
Averages over measures, Fourier transform 486 513
Averages over measures, lifting technique 483Ч486
Averages over rectangles and averages over hypersurfaces 467Ч469
Averages over rectangles and real-variable structures 473 478
Averages over rectangles and singular Radon transforms 513Ч517
Averages over rectangles, 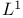 estimates 526 estimates 526
Averages over rectangles, 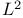 estimates 472Ч476 478Ч479 estimates 472Ч476 478Ч479
Averages over rectangles, 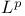 estimates 476Ч482 485Ч486 490Ч493 estimates 476Ч482 485Ч486 490Ч493
Averages over rectangles, algebraic varieties 477 485Ч486
Averages over rectangles, angles and bounds 464Ч466
Averages over rectangles, arbitrary orientations 445Ч446 449 455
Averages over rectangles, convex 525Ч526
Averages over rectangles, definability on 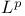 492Ч493 492Ч493
Averages over rectangles, eccentricity and bounds 419 464Ч466
Averages over rectangles, finite type 476Ч477 490Ч493
Averages over rectangles, infinitely flat 493 512Ч513 525Ч526
Averages over rectangles, lacunary orientations 459Ч464
Averages over rectangles, on 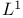 493 493
Averages over rectangles, parabola 472Ч476
Averages over rectangles, singularities 493
Averages over rectangles, universal variety 477Ч482
Averages over rectangles, unrotated 83Ч85 446Ч447 458
Averages over rectangles, variable 516Ч517
Averages over submanifolds 467Ч469 472Ч493 512Ч517
Balls 8Ч9
Balls, equivalence 10
Balls, examples 9Ч12 37Ч39 41 361 473 478 542 620
Besicovitch set 433Ч440 445 453Ч456 510
Besicovitch set, higher-dimensional analogues 455
Bessel functions 131 338 347 356Ч357 390 395 426 430
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) 139Ч180 300Ч305
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) and 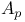 141 177 197 218 219 225 141 177 197 218 219 225
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) and 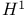 142Ч144 163Ч165 178 183 142Ч144 163Ч165 178 183
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) and Carleson measures 158Ч173 180Ч184 303
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) and Fourier integral operators 411 427
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) and harmonic functions 165
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) and homeomorphisms of 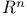 180 219 180 219
BMO (bounded mean oscillation) and square functions 158Ч173 180Ч184
BMO (bounded mean oscillation), distance to 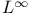 180 186 180 186
BMO (bounded mean oscillation), dyadic 154 173
BMO (bounded mean oscillation), functions in 140Ч141 177Ч179
BMO (bounded mean oscillation), local 264
BMO (bounded mean oscillation), martingale 188
BMO (bounded mean oscillation), orthogonal expansions 166Ч173 (see also УSingular integralsФ)
BMO (bounded mean oscillation), weak topology 166 186 301
Bochner Ч Riesz means 388Ч394 418Ч423
Bochner Ч Riesz means and  131 131
Bochner Ч Riesz means and restriction theorems 422
Bochner Ч Riesz means in 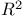 412Ч414 418Ч420 412Ч414 418Ч420
Bochner Ч Riesz means in 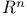 , n > 3 423 , n > 3 423
Bochner Ч Riesz means on compact manifolds 431
Bochner Ч Riesz means, analogue for cones 521
Bochner Ч Riesz means, kernel 390 430
Bochner Ч Riesz means, maximal 420Ч423
Bochner Ч Riesz means, sharp exponents 389 414 430
Bounded distribution 89
Bounds independent of dimension 523Ч525
Brownian motion 189 642Ч643
Bump functions 293
Bump functions and  262 262
Bump functions and  100 (see also УRestricted boundednessФ) 100 (see also УRestricted boundednessФ)
Bump functions and BMO 300Ч301
Bump functions and singular integrals 248Ч249 293Ч295
Calderon Ч Zygmund decomposition 16Ч18 20 51 101Ч105 110 138 150 431
Calderon Ч Zygmund kernels 289 305
Calderon Ч Zygmund operators 191 325
Calderon Ч Zygmund, symbolic calculus 268
Campbell Ч Hausdorff formula 584 635
Cancellation conditions 26 248 562 622
Cancellation conditions and averages over measures 513
Cancellation conditions for  262 262
Cancellation conditions for atoms see УMoment conditionsФ
Cancellation conditions, necessity 289Ч292 305Ч308
Cancellation conditions, special  295 299 624 295 299 624
Cancellation conditions, sufficiency 305Ч308\
Canonical coordinates 584 636
Canonical transformations 396
Carleman estimates 370
Carleson measures 58Ч59 78 314
Carleson measures and 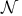 59Ч61 63 77 161Ч163 59Ч61 63 77 161Ч163
Carleson measures and BMO 158Ч173 180Ч184 303
Carleson measures and weights 225
Carleson measures, operator 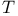 162Ч163 181Ч183 162Ч163 181Ч183
Carleson measures, space 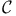 59 59
Cauchy integral 310Ч316
Cauchy Ч Riemann operators 589Ч592
Cauchy Ч Riemann operators, tangential 545Ч547 592Ч593
Cauchy Ч Szego projection 5 532Ч543
Cauchy Ч Szego projection and  601 615Ч618 601 615Ч618
Cauchy Ч Szego projection and Lewy example 611Ч618
Cauchy Ч Szego projection on 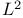 537 537
Cauchy Ч Szego projection on 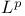 541Ч543 541Ч543
Cauchy Ч Szego projection, Fourier transform 573
Cauchy Ч Szego projection, kernel 277 536Ч541 575Ч577 580 585 601
Characteristic polynomial 231
Commutation relations 545 546 548Ч549 593
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 weights
weights 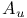
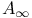
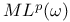
 (Triebel Ч Lizorkin spaces)
(Triebel Ч Lizorkin spaces) 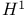

 (Heisenberg group)
(Heisenberg group) 

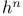

 (Hardy spaces)
(Hardy spaces) 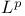
 (
( singular)
singular) 
 (local
(local 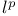
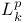 (Sobolev spaces)
(Sobolev spaces) 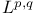


 (usual symbols)
(usual symbols) 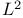
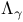

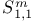 (forbidden symbols)
(forbidden symbols)  (exotic symbols)
(exotic symbols)  (exotic symbols)
(exotic symbols) 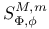
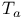 (operator w/symbol a)
(operator w/symbol a) 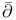 -complex
-complex  -complex
-complex 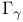 (Lipschitz spaces)
(Lipschitz spaces) 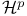 (holomorphic
(holomorphic  \mathcal{U}^n
\mathcal{U}^n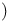
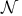 (tent spaces)
(tent spaces) 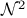

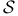 (Schwartz class)
(Schwartz class) 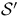 (tempered distributions)
(tempered distributions) 
 (boundary)
(boundary) 
![$[\zeta,t, r]$](/math_tex/13d4d09dad972ba3e8d60621e279b3ac82.gif)
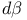
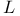 (sub-Laplacian)
(sub-Laplacian) 
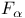
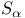
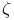 -convexity
-convexity