|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Thorne K.S., Hawking S. Ч Black holes and time warps: Einstein's outrageous legacy |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Mass-energy equivalence and conversion ("E=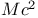 "), as consequence of principle of relativity 82 "), as consequence of principle of relativity 82
Mass-energy equivalence and conversion ("E=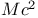 "), as implying that energy curves spacetime 488 "), as implying that energy curves spacetime 488
Mass-energy equivalence and conversion ("E=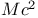 "), as power source for supernovae 173 "), as power source for supernovae 173
Mass-energy equivalence and conversion ("E=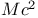 "), details of 172b 441n "), details of 172b 441n
Mathews, Thomas 334 335
Matricide paradox 56 508Ч509 508n
Matterhorn project 229
Mavalvala, Nergis 390f
Maxwell's laws of electromagnetism 62 66 67f 71 79 81 82 85 147b 433 525 565
Maxwell, James Clerk 62 147b
Mazur, Pavel 285 575
McCarthy, Joseph 226
McCrae, William 158
McIntosh, John 228f
Medvedev, Zhores A. 569Ч570 572Ч573
Melvin, Mael A. 263Ч265
Membrane paradigm for black holes 405Ч411 443 445
Mercury, perihelion shift of 94 95b 103 107 116Ч117 119b
Metaprinciple 82Ч83 94
Michaelson Ч Morley experiment 64Ч66 72Ч73 78 85 383f 565
Michell, John 122Ч124 123f 132Ч133 138Ч139 252 568
Michelson, Albert Abraham 63Ч66 72Ч73 78 85 383f 565Ч566
Michelson, Peter F. 578
Microwave radiation 251
Mie, Gustav 115
Miley, George 316
Miller, L.R. 578
Millikan, Robert Andrews 165Ч166 165f 173
Milne, Edward Arthur 152 155 161
Minkowski, Hermann 61 87Ч90 91b 92b 92Ч93 103 107Ч108 115 332f 333f 414 567
Minkowski, Rudolph 577
Misener, A.D. 187
Misner, Charles W. 246 280 295 297 369 433n 466Ч467 467f 474 516 561 572 574 580 582
Mitton, Simon 332f 333f
Mledina and Serona, tale of 88Ч90
Moffett, Alan 334
Molotov, Vyacheslav 186 571
Monroe, Marilyn 254
Moon, apparent anomaly in orbital motion 94 567
Moon, as source of tides on Earth's oceans 105 106b 111Ч126 362Ч365 362b 364f 451
Moon, search for X-rays from 311 312f
Morley, Edward Williams 64Ч66 72Ч73 78 85 383f 565 566
Morris, Michael S. 490 498 500 505 507Ч509 509n 511 583
Morse, Samuel 62
Moss, G.E. 578
Murdin, Paul 316
Murray, Margaret 228f
Murray, Stephen 316
Nadezhin, Dmitri K. 240 574
Nakamura, Takashi 379n
Naked singularity 480Ч482
NASA 321 354 390
National Science Foundation (NSF) 389Ч390
Neptune 94
Nernst, Hermann Walther 115
Nestor, James 260f
Neutron stars see also "Pulsar"
Neutron stars in binary system 38 313 379 393 571
Neutron stars, as source of gravitational waves 380 393Ч394 403
Neutron stars, formation in supernovae 171 172f 173Ч175 174f
Neutron stars, Harrison Ч Wakano Ч Wheeler computations of 198Ч206
Neutron stars, Landau's neutron cores 182 182f 184Ч186 191
Neutron stars, maximum mass 192 195b
Neutron stars, maximum mass determines fates of dying stars 176Ч178
Neutron stars, minimum mass 190Ч191
Neutron stars, observations of see "Pulsar"
Neutron stars, Oppenheimer Ч Volkoff Ч Tolman computations of 193bЧ196b
Neutron stars, Zwicky's computations of 207
Neutron stars, Zwicky's prediction of 165Ч166
Neutron, discovery of 169 171
Newman, Ezra T. 295 573
Newton, Isaac 26Ч27 61 63 93Ч94 96 111 147b 563
Newtonian laws of physics see also "Gravity" "Newton's "Maxwell's
Newtonian laws of physics, crumbling of foundations of 63Ч72
Newtonian laws of physics, domain of validity of 84Ч85
Newtonian laws of physics, foundations of 61Ч63
Newtonian laws of physics, nature of and applications of 61Ч63
Newtonian laws of physics, Newton's laws of motion 61 81 93 563
Nobel prize awarded to, Chandrasckhar 149
Nobel prize awarded to, Einstein 69 83 103 147b
Nobel prize awarded to, Hulse and Taylor 393
Nobel prize awarded to, Landau 187
Nobel prize awarded to, Townes, Basov and Prokhorov 366
Nonlinearity see also "Linearity"
Nonlinearity of black holes' spacetime warpage 361
Nonlinearity, concept of 361 362bЧ363b
Nordstroem, Gunnar 115 286 458 473 581 582
novae 166Ч168
Novikov, Igor Dmitrievich 267Ч269 271f 275 277Ч281 287b 288b 308 308f 309 313 315 317 319Ч320 326 427 447 479 508 526 574Ч576 580Ч582
Novikov, Nora see "Kotok" "Nora"
Nuclear burning (fusion) see "Fusion"
Nuclear force at high densities 205
Nuclear force in atomic nuclei 170b 183b
Nuclear force, compared to electromagnetic force 221b
Nuclear force, concept of 169
Nuclear force, Nuclear force, compared to gravitational force 184
Nuclear force, pressure due to 177 190Ч192 194bЧ195b 203f 202b 571
Nuclear weapons research, American A-bomb project 223Ч224
Nuclear weapons research, American H-bomb (super bomb) project 226Ч229 231Ч232
Nuclear weapons research, relation to astrophysics research 238Ч243
Nuclear weapons research, Soviet A-bomb project 224-226
Nuclear weapons research, Soviet H-bomb (super bomb) project 229Ч232 233bЧ234b
Nuclear weapons research, Teller Ч Ulam/Sakarov Ч Zel'dovich secret 241Ч243 243f
Nucleus, atomic 169 170f 171 183b 221b
Ojala, Andrey 228f
Oke, John Beverley 568
Onnes, Heike Kamerlingh 68Ч69
Oppenheimer security clearance hearings 232 234Ч235
Oppenheimer Ч Wheeler confrontation, background of 220 223Ч224 226Ч227 234Ч235
Oppenheimer Ч Wheeler confrontation, confrontation 209Ч211 223Ч224 238 240
Oppenheimer, J. Robert 178 187Ч192 189f 193bЧ196b 196Ч197 199 202b 203f 204 206Ч220 211f 217f 222Ч223 226Ч229 232 234Ч241 235n 244 253 255 270 274Ч275 286 300 326 449Ч453 452f 454f 458Ч459 473Ч474 480 526 569 571Ч573 581
Orbit around gravitating body in science fiction scenario 24
Orbit around gravitating body, explained by Newton's laws 61
Orbit around gravitating body, Paradigm 402Ч411 416
Orbit around gravitating body, used to compute body's mass 26 561 563
Ori, Amos 479 582
Ostwald, Friedrich Wilhelm 59 68Ч69 563
Ozernoy, Leonid Moiseevich 575
Paczynski, Bohdan 317 319
Page, Don Nelson 435 446Ч447 490Ч493 500 580
Pagels, Heinz 141n
Pais, Abraham 563Ч567
Palmer, Henry P. 335
Paolini, Frank R. 311 576
Papapetrou, Achilles 342
Papastamatiou, N.I. 583
Paradigm, concept of 401
Paradigm, curved-spacetime paradigm for gravity 401Ч403
Paradigm, flat-spacetime paradigm for gravity 401Ч405
Paradigm, membrane paradigm for black holes 405Ч411 443 445
Paradigm, Newtonian paradigm for gravity 403Ч405
Parker, Leonard E. 435 505 583
Pasternak, Simon 277
Pauli exclusion principle 170b
Pauli, Wolfgang 170b 180
Pavlova, Varva 429
Pawsey, J.L. 327
Peierls, Rudolph 180
Pennington, Ralph 228f
Penrose, Jonathon 459
Penrose, Oliver 459Ч461
Penrose, Roger 36 244 281 290 294 319 341 369 414 417 419 459 461Ч463 461f 465 467Ч469 471Ч472 474 480Ч481 481f 524 527 574Ч575 579Ч582
Penrose, Shirley 459
Perley, R.A. 344f
Pernet, Jean 60
Perrin, Francis 223
Perturbation methods 275 276b 296Ч298
Petrov, A.N. 579
Petrovsky, Ivan 269
Petterson, Jacobus 260f 346Ч347 577
| Phinney, E. Sterl 352f 577
photoelectric effect 147b
Photon see also "Gamma rays" "Light" "X-rays"
Photon and wave-particle duality 146 147b 322
Photon, spontaneous emission of 431b
Photon, virtual 439Ч441 440f
Physical laws see "Laws of physics"
Piezoelectric effect 368f 369 372
Pimenov, Revol't Ivanovich 471Ч472 582
Planck Ч Wheeler length, time and area 426 426n 442 446 476n 494 494n 518 520 563 582
Planck, Max 83 115 147b 388
plasma 349f 350 353 408Ч409 408f
Plutonium 199 222Ч225 222b 573 221
Podurets, Mikhail 240 301 574
Poisson, Eric 479 582
Polarization of a gravitational wave 393Ч394 406n
Polarization of light 406n
Polarization of metal or a black-hole horizon, by electric charge 405Ч407 405f
Polchinski's paradox 509Ч515 510f 512f 513bЧ514b
Polchinski, Joseph 509Ч511 510f 512f 515Ч516
Polnarev, Alexander 580
Popova, A.D. 579
Power notation for large numbers 29b
Prakash, A. 295
Prendergast, Kevin 317
Preskill, John 481Ч482 481f
Press, Margaret 297f
Press, William H. 259 260f 261 261n 295Ч296 297f 298 319 427 574Ч576
Pressure see also "Equation of state"
Pressure in rocks 145 201b
Pressure, balances gravity in star 135f 137 143Ч145 144f 151 154f 156bЧ157b 160 161f 175Ч177 190 199 202 253
Pressure, creates spacetime curvature 118bЧ119b 567
Pressure, nonthermal, degeneracy 145Ч146 148Ч152 159Ч160 169 170b 175Ч178 193b 200bЧ203b
Pressure, nuclear 177 190Ч192 194bЧ195b 203f 202b 571
Pressure, physical cause of 143Ч145
Pressure, thermal 144Ч145 159Ч160
Price, Richard H. 280Ч281 283Ч285 295Ч296 319 350 409 504Ч505 508 574Ч575 579Ч580
Pringle, James 317
Probability, quantum mechanical 147b 477 478f 493f 496 515
Prokharov, Aleksandr Michailovich 366
Pulsar see also "Neutron star"
Pulsar and teste of general relativity 58 393
Pulsar, as proof that neutron stars exist 317
Pulsar, discovery of 174 468
Pulsar, nature of 317Ч318
Pulsar, radio waves from 379
PUSTOVOIT, V.I. 383 578
Qstriker, Jeremiah P. 317
Quanta 141
Quantum electrodynamics 433
Quantum fields 284
Quantum fields in curved spacetime 436Ч439 444b 447Ч448 482 492 517 524
Quantum foam 55Ч56 477Ч478 478f 494Ч497 495f
Quantum gravity and time-machine destruction 318Ч320
Quantum gravity at endpoint of stellar implosion 210 476Ч479
Quantum gravity in singularity inside black hole 453 476Ч79
Quantum gravity, nonexistence of time in 476Ч477 518Ч519
Quantum gravity, quantum foam of space (wormholes) in 55Ч56 477Ч478 478f 494Ч497 495f
Quantum gravity, realm of validity 85Ч86
Quantum gravity, what we may learn from in future 524Ч525
Quantum gravity, Wheeler DeWill and Hartle Ч Hawking approach to 479n
Quantum gravity, Wheeler's motivation for 210 236Ч237 244 255Ч256 262 301 449
Quantum limits on measurement accuracies 372Ч375 386
quantum mechanics see also "Degeneracy" "Hawking "Probability" "Uncertainty "Vacuum "Wave-particle
Quantum mechanics and atomic nuclei 169 184 199 see "Nuclear "Nucleus atomic"
Quantum mechanics and atoms, molecules, crystals 166 169 372
Quantum mechanics and entropy 423 445Ч446
Quantum mechanics and matter at high densities 145Ч146 147b 150Ч152
Quantum mechanics and quantum hair on black holes 284
Quantum mechanics and spectral lines of light 335
Quantum mechanics and superconductivity 231 339
Quantum mechanics and superfluidity 186Ч187 186n 208
Quantum mechanics and time machines 515 517Ч523
Quantum mechanics on macroscopic scales 372Ч376
Quantum mechanics, as primary, with classical physics secondary 514Ч515
Quantum mechanics, discovery of the laws of 141 147b 162 180Ч181
Quantum mechanics, marriage with general relativity see "Quantum gravity"
Quantum mechanics, marriage with special relativity 150Ч152 160
Quantum mechanics, nature of and domain of 50 141 372 510Ч511 514Ч515
Quantum mechanics, speculations about failure of 184 207
Quantum nondemolition 375Ч376 377f 386Ч387
Quarks, search for 570Ч571
Quasars, detailed model of 351Ч353 352f
Quasars, discovery of 335Ч337
Quasars, energy of 339
Quasars, gigantic black holes as power source 346Ч354 407Ч410 408f
Quasars, overview of 45Ч48 47f
Quasars, role of accretion disks in 346Ч354
Quasars, speculations about power source 273 339Ч341
Quasars, variability of 337Ч338
Raab, Frederick J. 390f
Rabi, Isidore I. 208 569 572
Radio galaxies see also "Cygnus A" "Quasars" "Radio
Radio galaxies, detailed model of 351Ч353 352f
Radio galaxies, discovery of 330Ч331
Radio galaxies, discovery of double radio lobes 333
Radio galaxies, energy requirements of 339
Radio galaxies, further observations of 334
Radio galaxies, gigantic black holes as power source 346Ч354 407Ч410 408f
Radio galaxies, role of accretion disks in 346Ч354
Radio galaxies, speculations about power source 273 539Ч541
Radio jets, discovery of 343Ч345
Radio jets, gigantic black hole as source 345Ч354 407Ч410 408f
Radio jets, gyroscopic stability of source 345
Radio telescopes, as key to revolution in understanding the Universe 378Ч379
Radio telescopes, Green bank and Owens Valley 334
Radio telescopes, improvements in angular resolution 328 330 335 342 345
Radio telescopes, interferometers, principle of 328Ч330 329f
Radio telescopes, Jansky's and Reber's 323Ч324 234fЧ235f
Radio telescopes, Jodrell Bank 331Ч333 332fЧ333f
Radio telescopes, relation to radar 327
Radio telescopes, Very Large Array (VLA) 343 344f 345
Radio telescopes, VLBI 345
Radio waves, as part of electromagnetic spectrum 25f 322Ч323 379
Radio waves, cosmic see also "Cygnus A" "Radio "Radio "Radio
Radio waves, cosmic, difficulty explaining 323Ч324
Radio waves, cosmic, discovery of by Jansky 323 324fЧ325f
Radio waves, cosmic, explained as synchrotron radiation 338Ч339 338f
Radio waves, cosmic, observations by Reber 324Ч326 324fЧ325f 327Ч328
Rayleigh Ч Taylor instability 241Ч242 242f
Reber, Grote 324 324f 325f 326Ч328 344f 345 576 577
Redmount, Ian H. 409 486
Rees, Martin 272 317 319 343 348 461 574 576 577
Reference frame, accelerated, near black hole 443Ч446 444b
Reference frame, concept of 80
Reference frame, Finkelstein's, for stellar implosion 245Ч246 249 255
Reference frame, inertial (freely moving or freely falling) 80 96Ч98 99f 106 109 249
Reference frame, non-inertial 114
Regge, Tullio 275
Reissner Ч Nordstroem solution of Einstein field equation 286 458 473 581 582
Reissner, Hans 286 458 581
Relativists contrasted with other scientists 319Ч321 341Ч342
Relativity of space and time see also "Absoluteness of space and time" "Length "Time
Relativity of space and time, deduced from principle of relativity 73 77b
Relativity of space and time, Einstein's conception of 72Ч78
Relativity of space and time, explained in terms of spacetime 88Ч92 91bЧ92b
Relativity theory see "General Relativity" "Special
Relativity, principle of, as a metaprincipl 82
Relativity, principle of, consequences of 76Ч78 82
Relativity, principle of, formulated in absence of gravity 73 81
Relativity, principle of, generalized to include gravity 98 100 99f 114
Renn, Juergen 563 566
Research methods and styles, "small science" style vs. "big science" style 388Ч391
Research methods and styles, approximations 194bЧ195b 276b
Research methods and styles, arguments by analogy 429Ч430
Research methods and styles, attitudes toward mathematics 469Ч472
Research methods and styles, choice of physical laws 193b
Research methods and styles, competition 369Ч370
Research methods and styles, curiosity 207 236Ч237
Research methods and styles, different mathematical representations of same physics 402
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



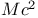 "), as consequence of principle of relativity
"), as consequence of principle of relativity