|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Bransden B., Joachain C. Ч Physics of Atoms and Molecules |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
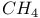 molecule see Methane molecule molecule see Methane molecule
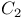 molecule 414 molecule 414
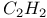 molecule 424Ч5 molecule 424Ч5
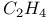 molecule 424 molecule 424
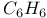 molecule see Benzene molecule molecule see Benzene molecule
 factor see Land factor see Land factor factor
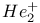 molecule 414 molecule 414
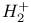 see Hydrogen molecular ion see Hydrogen molecular ion
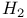 see Hydrogen molecule see Hydrogen molecule
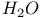 molecule see Water molecule molecule see Water molecule
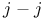 coupling 341 349Ч52 coupling 341 349Ч52
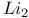 molecule 414 molecule 414
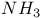 molecule see Ammonia molecule molecule see Ammonia molecule
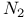 molecule 396 452 molecule 396 452
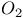 molecule see Oxygen molecule molecule see Oxygen molecule
 quantum number 449 quantum number 449
 bonds 425Ч6 bonds 425Ч6
 lines 211 213Ч14 lines 211 213Ч14
 bonds 424Ч5 bonds 424Ч5
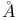 ngstrom unit 28 ngstrom unit 28
A10 molecule 439
Absorption cross section 495
Absorption in scattering 494Ч6 513
Absorption of radiation 155 161Ч3
Absorption of radiation, absorption spectra 27 362 434Ч5 584
Absorption of radiation, by many electron atoms 355Ч8
Absorption of radiation, cross-section for 162
Absorption of radiation, in the dipole approximation 167Ч8
Absorption of radiation, transition rate for 161Ч3
Alkali metals, alkali halides 420
Alkali metals, and bonding 418Ч20
Alkali metals, energy levels and spectra 359Ч64
Alkali metals, fine structure 363Ч4
Alkaline earths-energy levels and spectra 368
Allowed transitions 167
Alpha particles 24Ч6
Ammonia maser 567Ч71
Ammonia molecule NH 3 421
Anaxagoras 1
And selection rules 170Ч3 355-8
Angular momentum operators, general 95Ч6 612Ч20
Angular momentum operators, orbital 82Ч4 87Ч8 614
Angular momentum operators, spin 44Ч5 91-6
Angular momentum, addition of 95Ч6 104 615Ч17
Angular momentum, and magnetic dipole moments 41Ч2 209
Angular momentum, and the Stern Ч Gerlach experiment 44
Angular momentum, general properties of 612Ч20
Angular momentum, in the Bohr model 31 34
Angular momentum, total 42 46 95Ч6 104
Angular momentum, vector model of 45 88 spin total
Anharmonicity constant 392
Anti Ч Stokes line 437Ч8
Antibonding orbital 402 413
Antisymmetrisation operator 322
Antisymmetry see Pauli exclusion principle
Associated Laguerre polynomials 137Ч8 144 610Ч11
Associated Legendre functions 85Ч6
Astrophysics, topics in 583Ч9
Asymmetric top 421
Atomic mass unit 27
Atomic nucleus see Nucleus
Atomic number 23
Atomic number, and X-ray spectra 39 40
Atomic sizes 23
Atomic units 32Ч3 669 671
Auger effect 151 286 520 548
Autoionisation 286Ч8 366 444 519Ч20
Average value see Expectation value
Avogadro, A. 2
AvogadroТs number 2 3 23 670
Back Ч Goudsmit effect 376
Balmer series 28Ч9 205
Balmer, J. 28
BalmerТs formula 28
Band, degradation 442
Band, head 442
Band, progression 440
Band, sequence 440
Band, spectra 434 438Ч44 585
Barkla, C.G. 18 19
Baryon 151
Basis set 69
Basis set, change of basis 69Ч71
Benzene molecule 425Ч6
Bernoulli, D. 1
Beryllium ground state 333Ч4
Beth, R.A. 176
Bethe integral 508
Bethe, H.A. 231
BethТs experiment 176Ч8
Biaxial theorem 615
Black body 9
Black body radiation 9Ч15
Black body radiation, universal 583
Bless, A.A. 22
Bohr frequency relation 30
Bohr magneton 41 209 670
Bohr model and magnetic moments 40Ч1
Bohr model for atomic hydrogen 29Ч35
Bohr model for one-electron atoms 36
Bohr radius of hydrogen 32 133
Bohr, N. 15 29
BohrТs angular frequency 112
BohrТs correspondence principle 82
Boltzmann, L. 1 9
Bonding, and pairing 414Ч15
Bonding, covalent 407
Bonding, directional nature 423
Bonding, ionic 408
Bonding, orbitals 402
Born approximation for electron scattering 507Ч10 514Ч8 520-1
Born approximation for electron scattering, for atom-atom scattering 549Ч52
Born approximation in potential scattering for a Coulomb potential 492Ч3
Born approximation in potential scattering for a Yukawa potential 491Ч2
Born approximation in potential scattering for phase shifts 477
Born approximation in potential scattering for scattering amplitudes 489Ч92
Born series 488Ч90
Born Ч Oppenheimer separation 386Ч9 399 420 528
Born, M. 53 58
Bose Ч Kinstein statistics 106 233
Bosons 106 233 452
Bothe, W. 22
Boyle, R. 1
Brackett series 29
Bragg, W.L. 19
Breit Ч Wigner formula 483 523
Bremsstrahlung 578Ч9
Brown, R. 2
Brownian motion 2
Bunsen, R.G. 584
Byron, F.W. 275 285
Caesium atom and time standard 373Ч4
Carbon atom, fine structure of 348
Cathode rays 4
Central field approximation 263Ч4 290Ч300
Central forces 96Ч9
Centre of mass system of coordinates 463 465 600Ч7 642-4
Centre of mass, motion of 102Ч4
Centrifugal barrier 98 130
Centrifugal distortion 393Ч4
Channels in scattering 462Ч4 504
Charge exchange 540Ч7 549
Chemical bond 423
Chemical laws 2
Chemical scale 2
Chemical shifts 561
Classical mechanics of scattering 593Ч9
Classical trajectory 594
Clausius, R. 1
Clebsch Ч Gordan coefficients 615Ч17
| Cleeton, C.E. 459
Close coupling approximation 510Ч11 513 524
Closure relation 60 67
Codling, K. 287
Collision broadening 187 584
Commutators 63
Commutators, algebra of 73
Commutators, for angular momentum operators 95 612
Complete sets 66
Complete sets, of commuting observables 73
Compton effect 18Ч22
Compton equation 22
Compton shift 20
Compton wavelength 22
Compton, A.H. 18
Configuration see Electron configuration
Configuration interaction 274 339
Confocal elliptic coordinates 404 645
Conservation of probability 62 468
Controlled thermonuclear fusion 572Ч832
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, choice of reaction 574Ч5
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, diagnostics 582
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, impurity reactions 578Ч80
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, inertial confinement 576Ч7
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, magnetic confinement 576Ч7
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, neutral beam injection 580Ч2
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, reactor design 575Ч6
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, Tokamak machine 576Ч8
Controlled thermonuclear fusion, Zeta machine 578
Correlation diagrams 412Ч3 416-7
Correlation energy 338Ч9
Coulomb integral 280 409
Coulomb potential 128
Coulomb potential, scattering by 26 492Ч3 597-9
Covalent bonding 407
Critical angle 534
Crookes dark space 4
Crookes, W. 5
Cross-section, for absorption of radiation 162
Cross-section, for atomic scattering 464Ч5
Cross-section, for photoionisation 192Ч3
Cross-section, for scattering by a hard sphere 479Ч80
Cross-section, for scattering near a resonance 483
Cross-section, for scattering with absorption 494Ч6
Cross-section, for stimulated emission 163
Cross-section, in classical mechanics 595Ч7
Cross-section, total 468 596 607
Crossed-beam experiment 465 500Ч1
Dalton 2
Darwin term 196 200Ч1 641
Davisson, C.J. 47
De Broglie relations 46Ч7 53-4
de Broglie wavelength 46Ч8 54
de Broglie, L. 38 46 53
Deflection angle, classical 534 595
Deflection function see Deflection angle
Degenerate levels 64Ч5
Degenerate levels, and exchange 259 280 295
Degenerate levels, and permanent electric dipoles 222Ч3
Degenerate levels, and the Einstein 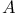 and and 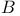 coefficients 170 coefficients 170
Degenerate levels, and the Stark effect 220Ч4
Degenerate levels, and the Zeeman effect 210 214 217 375Ч7
Degenerate levels, in diatomic molecules 396
Degenerate levels, in one-electron atoms 134
Degenerate levels, in the central field model 296 300
Degenerate perturbation theory 109Ч11
Delta function see Dirac delta function
Democritus 1
Density matrix 327
Density of states 115 165 309Ч10
Deslandres formula 440
Deslandres table 440
Detailed balancing 163 170
Deuterium 35 149
Diatomic molecules, and LCAO method 400Ч7
Diatomic molecules, and MO method 405
Diatomic molecules, and nuclear spin 452Ч5
Diatomic molecules, and spin coupling 448Ч52
Diatomic molecules, and the Heitler Ч London method 408Ч10
Diatomic molecules, and valency 414Ч15
Diatomic molecules, Born Ч Oppenheimer separation for 386Ч9
Diatomic molecules, electronic spectra of 438Ч48
Diatomic molecules, heteronuclear 415Ч20
Diatomic molecules, homonuclear 412Ч14 452-5
Diatomic molecules, rotational motion 389Ч90 393Ч4 428-30
Diatomic molecules, rotational spectrum 431Ч2
Diatomic molecules, symmetry properties of 395Ч7
Diatomic molecules, tables of constants for 392Ч3
Diatomic molecules, vibrational motion 389Ч94
Diatomic molecules, vibrational-rotational spectrum 432Ч6 (see Hydrogen molecular ion hydrogen
Differential cross-section 25 465 467
Differential cross-section, for charge exchange 546
Differential cross-section, for Coulomb scattering 26 493 599
Differential cross-section, for elastic atom-atom scattering 532Ч8 546
Differential cross-section, for electron scattering by H 504Ч5 516Ч7 521
Differential cross-section, for scattering near a resonance 483
Differential cross-section, in classical mechanics 595Ч7
Differential cross-section, in laboratory and centre of mass coordinates 600Ч7
Differential cross-section, in the Born approximation 490
Differential cross-section, partial wave expansion of 473
Diffuse series 362
Dipole polarisability 227 512 529
Dirac delta function 59Ч60
Dirac equation 195Ч6 201 633-7
Dirac equation,  and and  matrices 633Ч5 matrices 633Ч5
Dirac notation 67 87 617
Dirac, P.A.M. 53
DiracТs method of variation of constants 111Ч16
Direct integral 280 324 415
Direct potential 327 506 511
Displaced terms 371
Dissociation energy 392Ч3
Dissociation energy, for 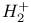 , , 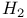 411 411
Dissociative state 444
Doppler broadening 187Ч9 229 572 587-8
Doppler shift 187Ч8 587
Doubly excited states 286 371 519Ч20 522-5
Dyson, F.J. 231
E/m, measurement of 4Ч6
Eckart, C. 284 285
Effective charge 40 263Ч4 284Ч5 403-4
Effective potential 98 130 144 292Ч3 359 474 528
EhrenfestТs theorem 63
Eigenfunction 64
Eigenfunction, of parity 98Ч9
Eigenfunction, of spin 91Ч2
Eigenfunction, of total angular momentum 96 (see also Wave function)
Eigenvalues of operators 64
Eigenvalues of operators, degenerate 64
Einstein 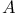 and and 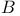 coefficients 168Ч70 coefficients 168Ч70
Einstein, A. 15 16 17 29 155 168 572
Elastic scattering 462 596 603Ч7
Elastic scattering, and absorption 494Ч6
Elastic scattering, by a hard sphere 479Ч80
Elastic scattering, by a potential 465Ч93
Elastic scattering, by a square well 477Ч9
Elastic scattering, of atoms by atoms 532Ч8 546
Elastic scattering, of electrons by atomic hydrogen 505Ч13
Elastic scattering, resonances in 480Ч4
electric dipole moment 167 222Ч3 356-7 431Ч3
Electric dipole moment, of alkali halides 420
Electric dipole moment, of diatomic molecules 393
Electric dipole moment, permanent 222Ч3 431
Electric dipole transitions 135 166Ч8
Electric quadrupole moment 233 244Ч5 374
Electric quadrupole transitions 167 178Ч9
Electrolysis 2
Electromagnetic field equations 156
Electromagnetic potentials 156
Electromagnetic radiation, and plane waves 156Ч7
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



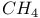 molecule
molecule 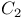 molecule
molecule 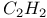 molecule
molecule 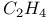 molecule
molecule 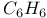 molecule
molecule  factor
factor  factor
factor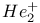 molecule
molecule 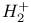
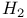
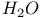 molecule
molecule  coupling
coupling 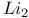 molecule
molecule 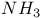 molecule
molecule 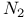 molecule
molecule 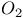 molecule
molecule  quantum number
quantum number  bonds
bonds  bonds
bonds 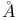 ngstrom unit
ngstrom unit 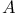 and
and 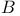 coefficients
coefficients  and
and  matrices
matrices