јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Chaikin P., Lubensky T. Ч Principles of condensed matter physics
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Principles of condensed matter physicsјвторы: Chaikin P., Lubensky T. јннотаци€: Now in paperback, this book provides an overview of the physics of condensed matter systems. Assuming a familiarity with the basics of quantum mechanics and statistical mechanics, the book establishes a general framework for describing condensed phases of matter based on symmetries and conservation laws. After surveying the structure and properties of materials with different symmetries, it explores the role of spatial dimensionality and microscopic interactions in determining the nature of phase transitions. Particular attention is given to critical phenomena and renormalization group methods. The properties of liquids, liquid crystals, quasicrystals, crystalline solids, magnetically ordered systems and amorphous solids are investigated in terms of their symmetry, generalized rigidity, hydrodynamics and topological defect structure. In addition to serving as a course text, this book is an essential reference for students and researchers in physics, applied physics, chemistry, materials science and engineering, who are interested in modern condensed matter physics.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats »здание: 1√од издани€: 1995 оличество страниц: 699ƒобавлена в каталог: 06.12.2013ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
"Problems" 103Ч7 209Ч12 283Ч7 347Ч52 411Ч6 492Ч4 585Ч9 656Ч61 372 670 175Ч82 346 183 228 298 140 152Ч4 228Ч30 267 298 79 see models 137 289 288 503; 501 138 202; see models 140 235 298 343 344 682 298Ч306 289; see 288 289 495 502 506 524 544Ч5 684 289Ч90 575Ч7 555 526Ч30 555 137 137 289 684 263Ч276 286 94 96 682 Abelian group 505 Abrikosov vortex lattice 561 571 662 Absolute solid-on solid (ASOS) model 644 662 Acoustic phonons, harmonic lattice 367Ч8; see sound modes Adatoms 78 601 662 Airy stress function 535 589 Amphiphilic molecule 68 71 662 Amplitude ratios 236Ч7 Angstrom 17 Anharmonicities see nonlinearities Anharmonicities, nonlinear 341 Anisotropic Ч Next Ч Nearest Ч Neighbor Ising (ANNNI) model 186Ч8 662 Anisotropy, anisotropic lattice 54 Anisotropy, anisotropic molecules 58 62 Anisotropy, cubic 267 Anisotropy, energy 177 Anisotropy, field 177 662 Anisotropy, quadratic 269 ANNNI see Anisotropic Ч Next Ч Nearest Ч Neighbor Ising model Antibonding orbital 22 Antiferromagnet, antiferromagnetic phase 87 176 346 Antiferromagnet, conjugate field 136 Antiferromagnet, Heisenberg model 435 Antiferromagnet, hydrodynamics 438Ч9 Antiferromagnet, model G 437 Antiferromagnet, order parameter (staggered magnetization) 136 177 435 Antiferromagnet, phase transitions 135 Antiferromagnet, spin waves 438 Argon 3 7Ч8 178 ASOS see absolute solid-on solid model Atomic form factor 31 662 Bands in metals 25 Basin of attraction 245 253Ч4 662 Basis, crystalline solids 43 48 662 BCC see body-centered cubic lattice Bend 299 301 662 Bend, expulsion from smectic phase 312 Bernal model 40 662 Biaxial nematic 16 135Ч7 662 Binding energy 18 Bipartite lattice 135Ч7 662 Block-spin variable 238Ч40 662 Blume Ч Emergy Ч Griffiths model 179 Body-centered cubic (BCC) lattice 53Ч6 87 135 189Ч94 515Ч17 662 Body-centered cubic (BCC) lattice, defects 515Ч17 Bohr magneton 25 Boltzmann constant 11 216 376 Bond-angle (bond orientational) order 58 66 328Ч9 534 556 663 Bonding orbital 22 663 Bose particles 123 Bragg scattering 47Ч9 663 Bragg scattering, and Debye Ч Waller factor 49 322 Bragg scattering, and long-range order 61 136 Bragg scattering, and quasi-long-range order 61 313 325 Bragg scattering, cylinder, TGB phase 568 Bragg scattering, law 29Ч33 663 Bragg scattering, peaks 48 75Ч6 663 Bragg scattering, peaks, and adsorbed monolayers 325 Bragg scattering, peaks, and antiferromagnetic order 88 136 Bragg scattering, peaks, and incommensurate systems 80Ч1 Bragg scattering, peaks, and quasicrystals 82 Bragg scattering, peaks, satellite 31 Bragg scattering, sheets 75 Bragg scattering, spot 10 77 Bragg Ч Williams theory 146Ч151 663 Bravais lattice 43 50Ч5 663 Breakdown of mean-field theory 208 214Ч17 225 Brillouin scattering 452 458 663 Brillouin zone 46 47 100 136 256 258Ч9 663 Broken symmetry 2 10 14 132Ч4 433 663 Broken symmetry, and defects in systems with discrete symmetry 590 Broken symmetry, and elasticity 288 Broken symmetry, and Goldstone mode 432 434 Broken symmetry, and topological defects 495 Broken symmetry, broken continuous symmetry 10 12 14 137Ч8 Broken symmetry, broken discrete symmetry 135Ч137 Broken symmetry, helium 460Ч4 Broken symmetry, magnetic order 85Ч90 Broken symmetry, phase 10Ч15 419 Broken symmetry, variables 417Ч419 Broken symmetry, variables, hydrodynamic variable 427 Brownian motion 375 663 Buckling instability 315 bulk modulus 320 663; Burgers vector 663 Burgers vector, dislocation 508Ч9 513 534 Burgers vector, lattice 514 c-director 64 506 Cahn Ч Hilliard model (model B) 448 468 664 Callen Ч Welton theorem 387 664; canonical ensemble 119 Canted spin order 87 Cantor set 604 664 Causal 355 664 Charge-density response function 205 chemical potential 110 117 Chiral liquid crystal 561; see cholesteric liquid crystal Chiral molecule 60Ч1 664 Cholesteric (chiral) liquid crystal 58Ч61 87 299 561 569 665 Cholesterol nonanoate 64 CI see commensurate-incommensurate Classical fluid 452Ч53; see response functions Classical fluid, and cross-sections 405Ч6 Classical fluid, and fluctuation-dissipation theorem 387 397 Classical fluid, and inelastic scattering 404Ч8 Classical fluid, Brownian particle 383Ч4 Classical fluid, density-density correlation function 354 372 374 405 Classical fluid, dynamic scaling 469 Classical fluid, rigid rotor 430 Classical fluid, self-diffusion (problem) 416 Classical plasma 205 Climb 521 664 Clock model 139 664 Close-packing 9 52 56Ч7 664; HCP and Closure 44 Coarse graining process 217Ч19 239 664 Coarsening 483 490 Codimension 499 664 coexistence 117 159 161 170 178 180 664 Coherence length 231; see correlation length Coherent and incoherent scattering 404Ч5 664 Coherent cross-section 404Ч6 Columnar discotic phase 68 664 Columnar discotic phase, homework problem 103 Columnar discotic phase, lyotropic systems 71 Commensurate see incommensurate Commensurate, ANNNI model 187 Commensurate, Frenkel Ч Kontorowa model 602 604 Commensurate, lattice 78 665 Commensurate, magnetic wave vector 77Ч82 89 Commensurate, overlayer 254 Commensurate-incommensurate transition 77Ч82 89 603Ч7 640Ч3 Commensurate-incommensurate transition, and the Frenkel Ч Kontorowa model 601Ч20 Commensurate-incommensurate transition, dislocations 640Ч3 Commutation relation 120 218 434 461 Completeness relation 98 Compressibility 5 114 116 162 328 451 488 664 Compressibility, in adsorbed overlayers 639 Compton scattering 88 665 Conjugate field 134 139 Conjugate variables 111 665 Conservation laws 2 418 Conservation laws, and hydroydnamic modes 418 Conservation laws, and model B 468 Conservation laws, and model C 469 Conservation laws, angular momentum 420 Conservation laws, density 369 418 Conservation laws, density, and diffusion 369 Conservation laws, energy 420 438 440Ч41 Conservation laws, mass 441 445 453 Conservation laws, momentum 441 Conservation laws, momentum, and model H 476 Conservation laws, spin and models E & F 476 Conservation laws, spin and models G & J 477 Conservative dislocation motion 520 665 Constitutive relation 418 425 665 Continuous symmetries, groups 135 137Ч9 157 288 495 665 Continuous symmetries, groups, hydrodynamics and broken 418 Continuous transition 13 15 665; Conventional unit cell 51 53 665 Cooperative diffusion 376Ч8 Core energy of a topological defect 526 665 Corrections to scaling 241 665 Correlation functions, dynamic, chapter 7 353Ч83 Correlation functions, static 123Ч132 226 231 243 260 383 Correlation functions, static, and compressibility 126 Correlation functions, static, and long-range order, QLRO, and disorder 295 Correlation functions, static, and susceptibility 131 Correlation functions, static, density-density 34Ч36 Correlation functions, static, direct pair correlation function 126 Correlation functions, static, displacements in a smectic liquid crystal 313 Correlation functions, static, displacements in an isotropic solid 322 324 533 Correlation functions, static, mean-field order parameter 157 Correlation functions, static, nematic director 306 Correlation functions, static, pair correlation function 36 40 Correlation functions, static, pair distribution function 36 Correlation functions, static, spin-spin 130 Correlation functions, static, spin-spin, in KT transition 577 Correlation functions, static, static scaling of 252 Correlation functions, static, static structure factor 36 42 Correlation functions, static, static structure factor, of a crystal 48 Correlation functions, static, structure function 32 62 66 Correlation functions, static, structure function, 1D crystal 323 Correlation functions, static, structure function, 2D crystal 325 Correlation functions, static, structure function, Smectic- 313 Correlation functions, static, transverse in systems with broken continuous symmetry 292 correlation length 154Ч5 213 214 228 231 244 262 341 665 Correlation length exponent 155 231 228 262 266 269 665 Coulomb attraction 18 19 Coulomb gas 546 584 588Ч9 Covering surface 511 665 creep 12 665 Critical density 5 159 665 Critical dimensions, dynamic 471 Critical dimensions, lower 15 227 295 313 322 Critical dimensions, upper 15 213 226 263 283 285Ч6 Critical endpoint 180 665 Critical exponents 230 665 Critical exponents, 469Ч71 Critical exponents, 231 233Ч4 237 Critical exponents, 153 167 174 231 237 Critical exponents, 154 174 Critical exponents, 324 341 Critical exponents, 231 232 237 268 286 Critical exponents, 2 Critical exponents, 558 Critical exponents, 313 640 Critical exponents, 325 Critical exponents, 431 Critical exponents, 153 174 227 231 237 285 Critical exponents, 273 Critical exponents, 324 340 Critical exponents, 240 Critical exponents, 155 174 231 237 240 251 262 266 269 286 284 Critical exponents, 238 Critical exponents, 240 Critical exponents, 235 270 Critical exponents, percolation from one-state Potts model 286 Critical exponents, tables of 231 237 Critical exponents, universality, and scaling, field theory 230Ч7 Critical exponents, Yang Ч Lee edge 286 Critical isobar 160 Critical isochore 159 162Ч5 Critical isotherm 160 Critical nucleus 480 Critical opalescence 4 5 165 665 Critical point 4 5 118 159 162Ч5 666 Critical pressure 162 Critical slowing down 4 465 666 Crossover exponent 235 269 270 Crossover functions 216 228 270Ч3 Crystal and liquid phases 78 Crystalline solids 43Ч5 Crystalline solids, Bragg scattering 47Ч9 Crystalline solids, close packed structures 56Ч7 Crystalline solids, disclinations 517Ч8 Crystalline solids, dislocations 513Ч17 Crystalline solids, growth 522 Crystalline solids, hydrodynamics 459 Crystalline solids, order parameter and transition to 187Ч98 Crystalline solids, periodic functions 46Ч7 Crystalline solids, reciprocal lattice 45Ч6 Crystalline solids, space groups 57Ч8 Crystalline solids, strength 518Ч22 Crystalline solids, three-dimensional Bravais lattices 53Ч6 Crystalline solids, topological defects 506Ч26 Crystalline solids, two-dimensional Bravais lattices 50Ч3 Crystallographic point group 51 666 Cubatic 328 666 Cubic anisotropy 267 666 Cubic fixed point 268 666 Cubic lattice 52Ч7 Curie spin susceptibility 243 666 Curvature 623Ч5 666 Curvature, and elasticity of smectic liquid crystals 311 Curvature, mean 625 676 Cutoff 221 226 256 294 666 D xy-model) 296 Dangerous irrelevant variables 273Ч5 666 de Gennes energy 566 De Gennes free energy for the smectic- 566 de Gennes Ч Taupin length 628 630 667 Debye Ч H 204 206 558 666 Debye Ч Waller factor 49 294 322 407 666 Decimation 245Ч8 667 Delocalization energy 25 Density functional theory 195Ч8 Density operator 34Ч8 Destructive interference 29 667 DevilТs staircase 603Ч5 667 dielectric constant 20 206Ч7 546 551
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -sum rule
-sum rule 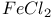 , crystal structure
, crystal structure 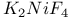
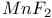
 -dimensional orthogonal group
-dimensional orthogonal group 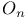
 and incommensurate crystal
and incommensurate crystal  model
model  model
model  symmetry
symmetry 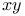 symmetry
symmetry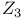 symmetry
symmetry 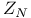 symmetry
symmetry  -expansion
-expansion  solvent
solvent  model
model 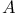 liquid crystal
liquid crystal 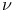
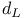
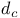
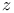 (dynamic scaling)
(dynamic scaling)  (specific heat)
(specific heat)  (order parameter)
(order parameter) 
 (gap exponent)
(gap exponent) 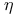 (critical point)
(critical point) 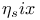 , hexatic QLRO
, hexatic QLRO 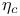 (smectic liquid crystal)
(smectic liquid crystal) 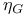 (2D crystal)
(2D crystal) 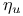 and
and 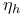 (polymerized membranes)
(polymerized membranes)  (susceptibility)
(susceptibility) 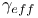
 (external field scaling)
(external field scaling) 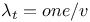 (thermal)
(thermal) 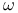 (field scaling)
(field scaling) 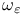 (energy density scaling)
(energy density scaling)  (crossover)
(crossover)  ckel screening length
ckel screening length