|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Shore S.N. — The Tapestry of Modern Astrophysics |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
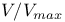 test 807—808 test 807—808
21 cm line see “Hydrogen 21
Abel equation 731—732
Absorption see “Opacity”
Absorption coefficient, H I 21 cm line 484
Absorption coefficient, synchrotron 536
Absorption coefficient, thermal bremsstrahlung 193—194 243
Absorption coefficient, total for absorption line 197—198
Abundances see “Element abundances”
Accretion disks,  -model 438—439 -model 438—439
Accretion disks, boundary layers 445—447
Accretion disks, formation of, by stream impact 435
Accretion disks, magnetic fields 442—445
Accretion disks, spectral energy distribution 440—441
Accretion disks, vertical structure 436—437 439—440
Accretion disks, viscous 437—440
Accretion from a stream inner Lagrangian point 434—435
Accretion from a wind (Bondi — Hoyle accretion) 432—434
Accretion, black holes 447 707—708
Accretion, cooling flows 723—730
Accretion-induced collapse 387
action 76
Adiabatic temperature gradient 235 302
Advection-dominated accretion flow (ADAF) 447
Agglomeration equation 68—69 519
Alfven radius 430
Alfven speed 50
Alfven waves 50—51
Algol paradox 417—418
Algorithms, CLEAN 149—150
Algorithms, maximum entropy method (MEM) 151—154 159—160
Algorithms, Richardson — Lucy 163—165
Algorithms, shift-and-add 145
Algorithms, stochastic time series 148—149
Ambipolar diffusion 51 542—543 586—588
Antenna temperature, definition of 484
Aperture synthesis 140—142
Aperture synthesis, phase closure 141
Apsidal motion 10—11 94 orbital”)
Apsidal motion and internal stellar structure 421—422
Asteration 679
Asteroseismology see “Helioseismology”
Astronomical Unit, Roemer’s determination of 106
Asymptotic Giant Branch (AGB) 373—377
Atmospheric eclipses 414—417
Autoionization 197
Baade’s window 633
Backwarming 229—230
Balbus — Hawley instability see “Instabilities magnetorotational”
Balmer limit 194
Baroclinicity 308—309 420
Barred spiral galaxies see “Galaxies spiral”
Bayes’ Theorem 150—151
Bernoulli equation 43
Biachi identities 88
Biases 161—162
Biases, Lutz — Keller 108—109 (see also “Parallax”)
Biases, Malmquist 807—808 (see also “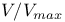 test”) test”)
Biasing (cosmological density fluctuations) 827—830
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis 680—682 798—805
Binary stars, classification relative to Roche radius 419—420
Binary stars, common envelope 423—425
Binary stars, eclipsing 119—120 414—417
Binary stars, effects of angular momentum loss 426—430
Binary stars, effects of mass transfer 426—428
Binary stars, emission of gravitational waves 428—430
Binary stars, evolutionary stages of (Cases A, B, C) 422—423 427
Binary stars, formation of 453—457
Binary stars, light curves 119—120 239—241 414—417
Binary stars, magnetic braking 430
Binary stars, mass determinations 118—119
Binary stars, mass function 119 361
Binary stars, masses 360—361
Binary stars, neutron stars in 400—401
Binary stars, pre-main sequence 453—455
Binary stars, reflection effect in 239—241
Birthline 366 (see also “Star formation”)
BL Lac objects (blazars) see “Galaxies active
Black holes 92 96—97
Black holes in active galactic nuclei 703—708
Black holes in binary systems 452—453
Blackbody radiation see “Planck Radiation Law”
Blackbody radiation, cosmic background radiation 770—771
Blackbody radiation, Rayleigh — Jeans approximation 28 129
Blackbody radiation, Wien approximation 28
Blast wave, adiabatic 574—575
Blast wave, free expansion phase 577
Blast wave, snowplow phase 579
Blue compact dwarf galaxies see “Galaxies irregular”
Blue stragglers 456—457
Bolometric correction 112 401—402
Boltzmann collision integral 55 66
Boltzmann distribution see “Distribution function Boltzmann”
Boltzmann equation 54—55 66
Boltzmann equation and H theorem 67—68
Boltzmann equation for photon scattering 210—211
Bondi — Hoyle accretion 432—434
Bonner — Ebert mass 590
Born approximation 262
Bose — Einstein distribution see “Distribution function Bose
Bose — Einstein integral, defined 35
Bosons see “Distribution function Bose
Boundary layers 445—447 450—452
Boussinesq approximation 234
Breit — Wigner resonance 335
Brightness temperature 129 483
Brown dwarfs 278 369
Brunt — Vaisala frequency, defined 618
C shocks see “Magnetic fields and shocks”
Calibration, backgrounds 156—157
Calibration, Hubble constant 753—754
Calibration, infrared 127—128
Calibration, Morgan — Keenan spectral types 274
Calibration, optical 109—111
Calibration, period-luminosity relation 742—744
Carbon stars 278 349—351 375—376
Cataclysmic variables, types of 447—448
CCDs see “Detectors charge-coupled
CCDs, cD galaxies see “Galaxies elliptical”
Champagne flow 574
Chandrasekhar mass 298 382—383 387 395
Charge transfer 474—475 551—552 563—564
Chemical evolution of galaxies 669—688 (see also “Galaxies”)
Chemical evolution of galaxies, observations 349—351 647 670—672
Chemical evolution of galaxies, solar system abundances 350 669—672 802—804
Chemical evolution of galaxies, “closed-box” models 677—683
Chi-square statistic 152
Christoffel symbol 83
Classification see “Taxonomy and specific subject”
Clausius — Mossotti equation 501
clean see “Algorithms CLEAN”
Clusters of galaxies, Local Group 720—721
Clusters of galaxies, mass to light ratio 812
Clusters of galaxies, properties 719—720 723
Clusters of galaxies, Schechter luminosity function 751
Clusters of galaxies, X-ray emission from 723—730
Coagulation see “Agglomeration equation”
Colliding stellar winds see “Under Stellar wind”
Collision frequency in plasma 52
Collision rates 171—172 465—466
Collisional ionization 172
Color-magnitude diagram see “Hertzsprung — Russell diagram” “Isochrones”
Common envelope see “Binary stars”
Common envelope, U UMa stars and stellar structure 424
Compton effect see “Scattering Compton”
Compton scattering length (y) 213
Compton wavelength 209
Condensation temperature 505
Conduction see “Diffusion thermal
Conduction, thermal, effect on cooling instability 594—595
| Conductivity, thermal conduction coefficient 301
Continuity equation 41 49 54 293
Convection 232—237 302—306
Convection, Boussinesq approximation 234
Convection, effects of variable molecular weight 237
Convection, mixing length theory 234—237 305—306
Convection, overshooting 305
Convection, Rayleigh — Benard 233—236
Convection, Schwarzschild criterion 302
Convection, semiconvection 304—305
Convergence point for clusters see “Parallax convergence
Convolution 163 732—733
Cooling flows see “Clusters of galaxies X-ray
Cooling processes and fine structure transitons 466
Cooling processes and shocks 562—563
Cooling processes, molecular 548—549
Cooling processes, rate 472—474 592—593 595—597
Copernican Principle 757—758 809
CORAVEL see “Spectrographs correlation”
Coriolis acceleration 12
Correlation function 613—614 625—627 815—817 828—830
Cosmic background radiation (CBR) 769—774
Cosmic background radiation (CBR) as limitation to structure formation 822—823
Cosmic background radiation (CBR) from fine structure lines 769—770 771—772
Cosmic background radiation (CBR), decoupling epoch 773 789
Cosmic background radiation (CBR), fluctuations 834—836
Cosmic background radiation (CBR), measurement of fluctuations 830—833 836
Cosmic background radiation (CBR), temperature 770—772
Cosmic rays 527—533 547—548
Cosmic rays and heating 595
Cosmic rays and time-dependent synchrotron emission 711—712
Cosmic rays, energy distribution 529—531
Cosmic rays, ionization rate from 475 531 547
Cosmic rays, nucleosynthesis by spallation 680—682
Cosmic rays, propagation 531—533
Cosmic rays, “leaky box” model for propagation of 531—533
Cosmic scale factor 762 764—767
Cosmological constant (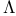 ) 774—776 793 826 ) 774—776 793 826
Cosmological density parameter ( ) 776—778 ) 776—778
Cosmological dimming 756
Cosmological distance scale and luminosity functions 750—751
Cosmological distance scale, steps in calibration 740—742
Cosmological gravitational lenses 836—841
Cosmological lookback time 783—790
Cosmological models, cosmological constant-dominated 774—775 814—815
Cosmological models, Newtonian 844—845
Cosmological models, relativistic see “Friedmann — Robertson — Walker equations”
Cosmological principle see “Copernican principle”
Cosmology, large scale structure 101—102 830—836
Coulomb barrier 331
Coulomb integral 52 302
Curie — Weiss law 515
Curvature scalar 88
Curvature, cosmic 777—778
Curve of growth 201—203 478—482
D-fronts see “H II regions as shocks”
Damping factor 335
Dark matter 699—700 811—815
Dark matter and cosmological density parameter 776—778
Dark matter and dark energy 814—815
Dark matter and galactic rotation curves 697—700
Dark matter in clusters of galaxies 720—723 730—731
Dark matter, galactic halos 699—700
De Sitter solution (also called Einstein-de Sitter) 598 791 Cosmological “Inflation”)
de Vaucouleurs law 693
Debye length 48 52 356
Debye temperature 518
Debye — Hueckel model for screening 356
Deceleration parameter 765
Decoupling epoch for cosmic background radiation 773 789
Degeneracy parameter, defined 292
Degenerate gas 28—29 291—292 380—385
Degenerate gas, thermonuclear runaway 372 448—450
Density waves 661—668
Departure coefficients 468
Detailed balance 35—36 54—55 68—69 169—171 176—177 344 464 536 617—618
Detailed balance and Compton scattering 210—211
Detailed balance, ionization equilibrium 196—197
Detectors 120—128
Detectors, bolometers 126—128
Detectors, charge-coupled device (CCD) 124—125
Detectors, multianode microchannel array (MAMA) 125—126
Detectors, photographic plate 120—123
Detectors, photomultiplier 123—124
Detectors, proportional counter 128
Deuterium 530—532 799—805
dielectric constant 501—502
Dielectronic recombination 468
Diffuse interstellar band (DIB) 511—514 553—554
Diffuse interstellar radiation field (DIRF) 493 (see also “Dilution factor”)
Diffusion and Fokker — Planck equation 65
Diffusion and semiconvection 305
Diffusion coefficient 65
Diffusion coefficient, radiative 190 300
Diffusion coefficient, thermal see “Diffusion thermal
Diffusion equation, time-dependent accretion 438
Diffusion in plasma 51—55 65
Diffusion, ambipolar see “Ambipolar diffusion”
Diffusion, cosmic rays 531—532
Diffusion, Fick’s law 65
Diffusion, induced by gravitational settling 53—54
Diffusion, magnetic fields 407—408
Diffusion, radiation 190 299—301 440
Diffusion, radiatively driven dynamics 248—249
Diffusion, thermal conduction 301—302
Diffusion, turbulent 376—377 410 687
Diffusion, viscous energy dissipation 457—458
Dilution factor 231 241—242 493
Dispersion measure 538 540—541
Distance scale see “Cosmological distance scale”
Distribution function, Boltzmann 23—25
Distribution function, Bose — Einstein 34—35 511
Distribution function, Fermi — Dirac 29—34
Distribution function, Maxwellian 21—23 641—642
Distribution function, Planck 26—28
Distribution function, Schwarzschild 641—642
Doppler boosting 714
Doppler imaging 223—224 417
Double diffusive convection 305
Dredge-up 375—377 (see also “Asymptotic giant branch (AGB)”)
Dreiser field 49
Dust and radiative equilibrium 242
Dust, broad extinction features 500—501 513
Dust, charge of 507—508
Dust, composition of 500—501 504—506 514—518 544—546
Dust, interstellar dust to gas ratio 506
Dust, surface reactions 544—546
Dust, wavelength dependent extinction 498—500
Dynamical friction 38—39
Dynamical instability 316
Dynamo see “Magnetic fields generation
Dynamo number 409
Eddington approximation 174 181 237
Eddington factor 178—179
Eddington luminosity 245—246 707
Eddington — Barbier relation 185 414
Einstein coefficients see “Transition probabilities”
Einstein field equation 89
Einstein radius 838
Einstein summation convention 82
Element abundances 349—351 (see also “Neutron reactions” “Radionuclides” “Thermonuclear “Chemical
Elliptical galaxies, fundamental plane 694—695 748—749
Emission lines, nebular diagnostics 462—472
Emission mechanisms, synchrotron 533—536
Emission mechanisms, thermal bremsstrahlung 192—194
Energy generation, gravitational contraction 329—330 363
Enthalpy see “Thermodynamics enthalpy”
entropy 16 20—21
Entropy, Boltzmann form of 21 67
Entropy, cosmological 773—774 800—801
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



 test
test  -model
-model  )
)  )
)