Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Gelman A., Carlin J.B., Stern H.S. — Bayesian data analysis
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Bayesian data analysisАвторы: Gelman A., Carlin J.B., Stern H.S.Аннотация: Incorporating new and updated information, this second edition of THE bestselling text in Bayesian data analysis continues to emphasize practice over theory, describing how to conceptualize, perform, and critiques statistical analysis from a Bayesian perspective. Changes in the new edition include: added material on how Bayesian methods are connected to other approaches, stronger focus on MCMC, added chapter on further computation topics, more examples, and additional chapters on current models for Bayesian data analysis such as equation models, generalized linear mixed models, and more. The book is an introductory text and a reference for working scientists throughout their professional life.
Язык: Рубрика: Математика /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Издание: 2nd editionГод издания: 2004Количество страниц: 668Добавлена в каталог: 11.02.2006Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
Prior distribution, conjugate, exponential model 55 Prior distribution, conjugate, generalized linear models 421 Prior distribution, conjugate, linear regression 382—385 Prior distribution, conjugate, multinomial model 83 434 533 Prior distribution, conjugate, multivariate normal model 85 87 Prior distribution, conjugate, normal model 46 50 78 Prior distribution, conjugate, Poisson model 52 Prior distribution, estimation from past data 118 Prior distribution, hierarchical see "Hierarchical models" "Hyperprior Prior distribution, improper 61 100 Prior distribution, improper, and Bayes factors 194 Prior distribution, informative 39—55 260 Prior distribution, nonconjugate 41 45 90 Prior distribution, noninformative 61—66 247 252 Prior distribution, noninformative, binomial model 43 63 Prior distribution, noninformative, Bugs software 593 596 597 Prior distribution, noninformative, difficulties 64 Prior distribution, noninformative, for hyperparameters 125 127—129 134 136 137 470 Prior distribution, noninformative, for many parameters 253 Prior distribution, noninformative, generalized linear models 420 Prior distribution, noninformative, Jeffreys' rule 62—63 66 69 Prior distribution, noninformative, linear regression 355 Prior distribution, noninformative, multinomial model 536 Prior distribution, noninformative, multivariate normal model 88 Prior distribution, noninformative, normal model 74 Prior distribution, noninformative, pivotal quantities 64 66 Prior distribution, noninformative, Student-t model 454 Prior distribution, noninformative, warnings see "Posterior distribution improper" Prior distribution, predictive 8 Prior distribution, proper 61 Prior distribution, semi-conjugate 81 134 Prior predictive checks 190 193 Prior predictive distribution 8 Prior predictive distribution, normal model 47 probability 22—25 29 Probability model 3 Probability, assignment 14—21 29 30 Probability, foundations 11—14 28 Probability, notation 7 Probit regression 417 Probit regression for multinomial data 430 440 Probit regression, Gibbs sampler 419 Probit regression, latent-data interpretation 419 Probit transformation 25 Propensity scores 206—207 227 228 238 Proper prior distribution see "Prior distribution" Proportion of female births 33 43—46 Propp, J. 348 Psychological data 165—170 468—479 PX-EM algorithm 324 331 see QR decomposition 357 385 Quality-adjusted life expectancy 553 Quinn, K. 440 609 R see "Software" Racine, A. 28 89 95 192 309 514 515 Radon decision problem 195 385 555—567 Raftery, A. 97 191 192 412 458 Raghunathan, T. 151 190 457 539 568 Raiffa, H. 66 568 Random-effects model 390—392 Random-effects model and superpopulation model in ANOVA 409 Random-effects model, analysis of variance (ANOVA) 406 Random-effects model, election forecasting example 396 Random-effects model, non-nested example 428—430 Random-effects model, several batches 391 Random-effects models see also "Hierarchical models" "Analysis Randomization 223—226 Randomization and ignorability 226 239 Randomization, complete 223 Randomization, given covariates 224 Randomized blocks 240 Rank test 252 Rao, J. 150 Rat tumors 118—120 127—131 151 Ratio estimation 260 272 Raudenbush, S. 411 Record linkage 17—21 Record-breaking data 238 Reeves, R. 349 Reference prior distributions see "Noninformative prior distribution" Reference set for predictive checking 165 Regeneration for MCMC 340 348 Regression models 353—387 see Regression models, Bayesian justification 354 Regression models, explanatory variables 6 201 353 369—371 Regression models, explanatory variables, exchangeability 6 Regression models, explanatory variables, exclude when irrelevant 371 Regression models, explanatory variables, ignorable models 205 Regression models, explanatory variables, include even when nonidentified 261—263 Regression models, goals of 367—369 Regression models, hierarchical 389—414 Regression models, variable selection 371 Regression models, variable selection, why we prefer hierarchical models 405—406 Regression to the mean 249 Regression trees 515 Rejection sampling 284 310 Rejection sampling, picture of 285 Replications 161 Residual plots 192 359 Residual plots, binned 170—171 Residual plots, dilution example 503 Residual plots, incumbency example 365 Residual plots, nonlinear models 503 513 Residual plots, pain relief example 170 Residual plots, toxicology example 513 Residuals 170 Response surface 148 Response variable 353 Restarting for MCMC 340 348 Reversible jump sampling for MCMC 338—339 348 Richardson, S. 151 308 348 480 Ridge regression 412 Riggan, W. 66 151 Ripley, B. 29 190 308 349 494 584 608 Robbins, H. 150 Robert, C. 308 309 Roberts, G. 309 348 Roberts, I. 238 Robins, J. 237 Robinson, G. 411 Robit regression (robust alternative to logit and probit) 447 Robust inference 177 191 270 443—459 Robust inference for regression 455—457 Robust inference, SAT coaching 451—455 Robust inference, various estimands 269 Rombola, F. 29 Rosenbaum, P. 238 Rosenberg, B. 515 Rosenbluth, A. 308 Rosenbluth, M. 308 Rosenkranz, S. 191 Rosenthal, J. 308 309 Rosner, G. 480 Ross, S. 29 Rotnitzky, A. 237 Rounded data 96 244 Roweth, D. 348 Roy all, R. 272 Rubin, D. 28 29 113 151 152 190 192 237 238 245 272 309 331 348 385 411 440 457 458 479 480 494 539 540 Runger, G. 195 Ruppert, D. 514 S, S-Plus, and R 591 Sahu, S. 309 412 440 Sampling 207—218 see Sampling, capture-recapture 242 Sampling, cluster 214—216 241 Sampling, poststratification 228 428—430 Sampling, ratio estimation 260 272 Sampling, stratified 209—214 Sampling, unequal selection probabilities 216—218 242—244 Sampson, R. 411 Samuhel, M. 237 539 Sargent, D. 191 413 SAT coaching experiments 138—145 SAT coaching experiments, difficulties with natural non-Bayesian methods 139 SAT coaching experiments, model checking for 186—190 SAT coaching experiments, robust inference for 451—455 Satterthwaite, F. 539 Savage, I. 193 Savage, L. 113 237 568 Scalar Gibbs sampler for hierarchical regression 402 Scale parameter 50 Scaled inverse- 50 574 580 Schafer, J. 440 539 Scharfstein, D. 237 Schenker, N. 113 539 Schildkraut, J. 569 Schilling, S. 348 Schizophrenia reaction times, example of mixture modeling 468—479 Schlaifer, R. 66 Schmidt-Nielsen, K. 387 Schultz, B. 113 539 Scott, A. 237 238 Searle, S. 411 Seber, G. 242 332 Sedransk, J. 151 192 238 Seidenfeld, T. 238 Selection of predictors 254 Sellke, T. 255 Selvin, S. 31 Selwyn, M. 151 439 SEM and SECM algorithms 322—324 331 Semi-conjugate prior distribution 81 134 Sensitivity analysis 177 189—190 443—459 Sensitivity analysis and data collection 270 Sensitivity analysis and realistic models 270 Sensitivity analysis, balanced and unbalanced data 227 Sensitivity analysis, cannot be avoided by setting up a super-model 158 Sensitivity analysis, Census recoding 261—263 Sensitivity analysis, estimating a population total 265—269 Sensitivity analysis, incumbency example 366 Sensitivity analysis, SAT coaching 451—455 Sensitivity analysis, using t models 454—455 Sensitivity analysis, various estimands 269 Separation models for covariance matrices 483—485 Sequential designs 221 244 Serial dilution assay, example of a nonlinear model 498—504 514 Sex ratio 33 43—46 Shafer, G. 28 Shao, Q. 308 Sharpies, L. 309 Shaw, J. 348 Sheiner, L. 515 Shen, W. 66 Shen, X. 589 Shnaidman, M. 514 Shoemaker, A. 439 Shrinkage 36—37 47 54 133 150 Shrinkage, graphs of 131 142 Silver, R. 238 Simoncelli, E. 494 Simple random sampling 207—209 Simple random sampling, difficulties of estimating a population total 265 Simulated tempering for MCMC 337—338 348 Simulation see "Posterior simulation" Singer, E. 568 Single-parameter models 33—72 Singpurwalla, N. 28 Sinharay, S. 190 Sinsheimer, J. 458 SIR see "Importance resampling" Skene, A. 152 348 Skilling, J. 66 Skinner, C. 238 Sleight, P. 151 Slice sampling for MCMC 336 348 Slovenia survey 534—539 Slovic, P. 28 568 Small-area estimation 151 Smith, A. 28 66 89 95 150 190—192 309 331 348 411 439 457 480 514 515 Smith, T. 152 192 237 238 Snedecor, G. 387 Snee, R. 413 414 Snell, E. 29 Snijders, T. 411 Snyder, J. 29 385 Software 591—609 Software, Bugs 27 29 151 592—600 Software, debugging 607—608 Software, extended example using Bugs and R 592—607 Software, programming tips 278—282 607—608 Software, R 27 29 600—607 Software, running Bugs from R 592 Software, setting up 591 Software, WinBugs and Bugs 592 Solenberger, P. 539 Sommer, A. 230 Souhami, R. 255 Soules, G. 331 Space-time models 494 Spatial models 493 494 Speed of light example 77 160 Speed of light example, posterior predictive checks 164 Speed, T. 237 439 Speroff, T. 238 Spiegelhalter, D. 29 151 152 191 192 194 255 308 309 608 Spitzer, E. 440 Spline models 515 Sports, football 14—17 29 Sports, golf 515 Stability 200 Stable estimation 111 Stable unit treatment value assumption 201 239 Stallard, E. 66 151 Standard errors 103 Standard normal distribution 578 State-level opinions from national polls 428—430 Statistical packages see "Software" Statistically significant but not practically significant 176 Statistically significant but not practically significant, regression example 366 Stefanski, L. 514 Stein, C. 150 Stephan, F. 440 Stephens, M. 480 Stepwise ascent 312 Stepwise regression, Bayesian interpretation of 405 Stern, A. 66 Stern, H. 29 190 191 193 440 480 540 Sterne, J. 255 Stevens, M. 568 Stevenson, M. 238 Stigler, S. 65 78 95 255 Stone, M. 66 190 Stratified sampling 209—214 Stratified sampling, hierarchical model 212—214 310 Stratified sampling, pre-election polling 210—214 Strenio, J. 411 Strong ignorability 205 Student-t approximation 315 Student-t distribution 76 576 581 Student-t model 446 451—457 Student-t model, computation using data augmentation 303—304 Student-t model, computation using parameter expansion 304—305 Student-t model, interpretation as mixture 446 Subjectivity 12 14 28 31 257 557 567 Sufficient statistics 42 247 Summary statistics 104 Superpopulation inference 202—203 205 208—209 211 212 216 218—221 241 Superpopulation inference in ANOVA 408—409 Supplemented EM (SEM) algorithm 322—324
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



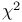 distribution
distribution