јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M. Ч Signal Transduction
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Signal Transductionјвторы: Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M.јннотаци€: Signal Transduction is a text reference on cellular signalling processes. Starting with the basics, it explains how cells respond to external cues (hormones, cytokines, neurotransmitters, adhesion molecules, extracellular matrix, etc), and shows how these inputs are integrated and co-ordinated. The first half of the book provides the conceptual framework, explaining the formation and action of second messengers, particulary cyclic nucleotides and calcium, and the mediation of signal pathways by GTP-binding proteins. The remaining chapters deal with the formation of complex signalling cascades employed by cytokines and adhesion molecules, starting at the membrane and ending in the nucleus, there to regulate gene transcription. In this context, growth is an important potential outcome and this has relevance to the cellular transformations that underlie cancer. The book ends with a description at the molecular level of how signalling proteins interact with their environment and with each other through their structural domains. Each main topic is introduced with a historical essay, detailing the sources key observations and experiments that set the scence for recent and current work.
язык: –убрика: “ехнологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2002 оличество страниц: 424ƒобавлена в каталог: 21.12.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
145Ч168 171Ч185 150 109 112 115 148Ч149 147Ч148 149Ч166 150Ч153 152 261 172Ч173 153Ч162 162Ч166 163 164 165 165Ч166 148Ч149 148 149 166Ч168 146Ч147 165 166 182Ч185 181Ч182 199 200 25 145Ч147 275 148 127 130 135-137 149 136 149 171Ч172 772 401Ч403 see "CaM-kinase II" 176Ч177 320 172 178Ч180 see "CICR" 56Ч57 150Ч151 215 316Ч317 291 292 147Ч148 148 149 see УRas-GAPФ 241 249 370 241 249 241 241 211 241 242 246 330 370 241 242 246 262Ч263 263 215 241 246 215 216 215Ч217 271 271 75 121 122 123 124 80 123Ч124 121Ч122 123 124 121 122 123 124 124Ч125 261 285 287 294 231 19 20 231 232 359Ч364 360 359Ч362 362 364 364 362 363 368Ч369 366 367 359 360Ч361 360 361 369 359 360 361 369 362 363 359 362 363 362 364 364 23 348Ч349 349 350 349Ч351 349 359 360Ч361 360 361 369 359 360 361 361 369 180 34 34 107 194 35 35 43Ч44 3 96 34 34 52 107 185 196 63 75 191 35 36 55 60 61 62 60 60 35 35 98Ч99 99 249 333 334 334 334 4 84 85 197 276Ч277 278 see УGABAФ 11-cis-retinal 130 132 733 11-cis-retinal, light-induced isomerization 137 738 11-cis-retinal, rhodopsin interaction 54 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1 see УPDK1Ф 5-hydroxytryptamine see УSerotoninФ 7TM receptors 38 40 51Ч58 see 7TM receptors, binding to low molecular mass ligands 55 7TM receptors, calcium sensors 56Ч57 7TM receptors, categories 52 54Ч55 54 7TM receptors, ERK activation 276Ч279 7TM receptors, G-protein linkage 72 73 99 7TM receptors, intracellular domains 65Ч66 7TM receptors, ligand binding sites 57 7TM receptors, metabotropic 42 56Ч57 7TM receptors, signal transmission 65Ч66 a-type mating factor 3 96 A2387 150 Abelson murine leukaemia virus see "v-Abl" Acetylcholine 11 14 38Ч39 Acetylcholine (cholinergic) receptors 38Ч42 Acetylcholine, cholinergic receptor interactions 40 42 Acetylcholine, cholinergic receptor interactions, muscarinic receptors 55 Acetylcholine, cholinergic receptor interactions, nicotinic receptors 44 49 Acetylcholine, neuromuscular junction actions 24 Acetylcholinesterase 38 Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors 39 39 ACTH (adrenocorticotrophic hormone) 4 20 ACTH, adenylyl cyclase activation 62 64Ч65 65 ACTH, receptor binding 55 Actin 182 325 329 332 Activator protein complex-1 see "AP-1" Adenine 62 63 Adenosine receptor 63 Adenosine receptor, homodimers 62 Adenosis poliposis coli see "APC" Adenylyl cyclase 55 62Ч63 63 107Ч119 Adenylyl cyclase, 176Ч177 Adenylyl cyclase, activation by receptors 62Ч63 63 64 Adenylyl cyclase, activation by receptors, experimental approaches 63-65 65 Adenylyl cyclase, ATP conversion to cAMP 72 109 109 110 Adenylyl cyclase, constitutive activity 59 Adenylyl cyclase, G-protein 80 96 109 110 112 113 113 Adenylyl cyclase, G-protein 109 110 112 113Ч115 113 Adenylyl cyclase, GTP cofactor 72 Adenylyl cyclase, regulation 109Ч110 112Ч119 112 114 Adenylyl cyclase, structural organization 110Ч112 111 ADH (antidiuretic hormone) see "Vasopressin" Adherens junctions 321Ч322 322 331Ч332 Adherens junctions, cell polarity maintenance 332 332 Adhesion molecules 212 249 315Ч325 316 Adhesion molecules, cell cycle regulation 328Ч330 330 331 Adhesion molecules, cell survival promotion 325Ч328 327 Adhesion molecules, leukocyte trafficking 345Ч355 Adhesion molecules, nomenclature 318 Adhesion molecules, T cell activation 285 Adhesion molecules, tumour suppression 331Ч334 ADP ribosylation 116Ч119 117 Adrenaline (epinephrine) 2 9 20 22 31 32 33 62 66 Adrenaline, actions 33Ч34 Adrenaline, adrenergic receptor interactions 29 36 38 Adrenaline, historical aspects 8 9Ч10 Adrenergic receptors 31 32 34Ч38 34 Adrenergic receptors, adrenaline interactions 29 36 38 Adrenergic receptors, agonists 35Ч36 35 Adrenergic receptors, antagonists 35 36 60 Adrenergic receptors, G-protein signalling 51 115 Adrenergic receptors, ligand structural features 36 37 38 Adrenergic receptors, membrane spanning sequences/topology 51 52 53 Adrenergic receptors, subtypes 35 35 36 Adrenocorticotrophic hormone see "ACTH" Aequorin 150Ч151 AGC protein kinases 310 311 Aggrecan 324 Agonists 59 60 76 77 AIF (apoptosis inducing factor) 340 All-trans-retinal 132 133 137 139 Aluminium fluoride, adenylyl cyclase regulation 115Ч116 Amino acid receptors 42 AMPA receptors 158 Anaphase 238 Anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome see "APC/C" Anergy 285 ANF (atrial natriuretic factor) 4 20 Angiogenesis 248Ч249 Angiogenic factors 248 249 Angiotensin 36 Annexins 171 Antagonists 59 60 Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) see "Vasopressin" AP-1 (activator protein complex-1) 208 265 272 288 Apaf (apoptotic protease activating factor) 338 339 APC (adenosis poliposis coli) 249 333 APC, mutations in cancer 334 334 APC/C (anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome) 238 240 244 245 Apoptosis 22 179 227 240 242 248 249 325 326 335Ч340 Apoptosis inducing factor see "AlF" Apoptosis, avoidance (rescue pathway) 325Ч328 Apoptosis, bcl-2 338Ч339 338 Apoptosis, caspases 335Ч338 Apoptosis, cell morphology 335 336 Apoptosis, cytochrome c 339Ч340 340 Apoptosis, Fas ligand 339 339 Apoptosis, JNK pathway 327Ч328 328 Apoptotic protease activating factor see "Apaf" Arachidonate 23 23 204 Arf 86 Arrestin 84 139 276 Aspirin 23 299 Atenolol 37 ATM 243 ATP 19 71Ч72 ATP, cyclic AMP formation 109 109 110 Atrial natriuretic factor see "ANF" Atropine 11 15 40 Avian erythroblastosis virus 229 Avian leukaemia viruses 225Ч226 B lymphocyte receptor 283 b558 215 B7 288 Bacteriorhodopsin 51 66 Bad (Bcl associated dimer) 326 339 340 Basophils 23 212 288 Bax 242 340 Bcl associated dimer see "Bad" Bcl-2 249 337 338Ч339 338 Bcl-XI 249 Betaglycan 362 Bid 340 Binding affinity 25 26 Binding affinity, measurement 26Ч27 28 Binding reactions 25Ч28 Binding site heterogeneity 26 Boss (bride-of-sevenless) 266 267 Bradykinin 23 Brevican 324 Bride-of-sevenless see "Boss" Btk (BrutonТs tyrosine kinase) 80 294 Bub2 244 Bubl 244 245 C-terminal Src kinase see "Csk" C2 domain 171 179 181 402Ч403 403 C3bi 316 CAD (caspase activated DNAase) 226 Cadherins 249 320Ч322 327 322 331 332 Cadherins, classification 322 Cadherins, contact inhibition 334 cADPr (cyclic ADP-ribose) 159 160 760 Caenorhabditis elegans, Smad homologues 366 368 Caenorhabditis elegans, TGF 361 364Ч365 Caenorhabditis elegans, vulval cell development 268Ч269 269 CAK (CDK activating kinase) 235 237 Calcineurin (PP2B) 177 177 190 384 386 387 Calcineurin, T cell proliferation regulation 388Ч390 389 Calmodulin 154 173Ч174 174 175 275 388 Calmodulin, adenylyl cyclase regulation 112 Calmodulin, glycogenolysis regulation 175 176 Calpain 179 Calreticulin 149 CaM-kinase II ( 156 175 275 CaM-kinases 174Ч175 184 Cancer 247 Cancer, definition 246Ч247 Cancer, genetic alterations 249Ч250 334 334 Cancer, malignancy-related alterations 248Ч249 Carbachol 39 Carbarmylcholine see УCarbacholФ Cardiac muscle, 166 182 185 Cartilage link proteins 324Ч325 Caspase activated DNAase see УCADФ Caspase-3 328 Caspase-8 339 Caspase-9 326 339 Caspases, apoptosis 335Ч338 Caspases, cellular targets 336Ч337 337 Caspases, effector 335 337 Caspases, initiator 335 337 Caspases, regulation 338 Catecholamines 2 32 33 34 194 Catecholamines, 7TM receptors 38 Catecholamines, receptor binding 55 56 Catenins 322 332 CBP (CREB binding protein) 194Ч195 CC chemokines 351 351 352 CD28 288 CD3 285 286 CD4 285 286 290 CD44 324Ч325 324 CD45 (leukocyte common antigen) 286 376Ч377 377 CD8 285 286 290 Cdc20 238 244 245 246 Cdc25 95 108 238 Cdc42 310 Cdc53 (Cullin) 246 Cdhl 238 240 246 CDK inhibitors 240Ч242 241 CDK-activating kinase see УCAKФ CDK1 237 238 243 CDK2 236 237 241 330 407 CDK4 235 236 240 241 330 CDK6 235 236 241 CDK7 235 407 CDKs (cyclin-dependent protein kinases) 234 CED genes 335 Cell culture, historical aspects 230Ч231 231 Cell cycle 232Ч246
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



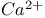
 receptor
receptor  -receptor
-receptor 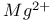




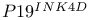
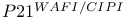

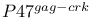

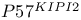
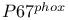



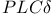
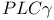

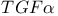

 -mediated activation
-mediated activation  )
)  (tumour necrosis factoru)
(tumour necrosis factoru) 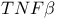 (tumour necrosis factor
(tumour necrosis factor )
) 
 -actinin
-actinin  -Aminobutyric acid
-Aminobutyric acid 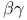 -subunit interactions
-subunit interactions