јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M. Ч Signal Transduction
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Signal Transductionјвторы: Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M.јннотаци€: Signal Transduction is a text reference on cellular signalling processes. Starting with the basics, it explains how cells respond to external cues (hormones, cytokines, neurotransmitters, adhesion molecules, extracellular matrix, etc), and shows how these inputs are integrated and co-ordinated. The first half of the book provides the conceptual framework, explaining the formation and action of second messengers, particulary cyclic nucleotides and calcium, and the mediation of signal pathways by GTP-binding proteins. The remaining chapters deal with the formation of complex signalling cascades employed by cytokines and adhesion molecules, starting at the membrane and ending in the nucleus, there to regulate gene transcription. In this context, growth is an important potential outcome and this has relevance to the cellular transformations that underlie cancer. The book ends with a description at the molecular level of how signalling proteins interact with their environment and with each other through their structural domains. Each main topic is introduced with a historical essay, detailing the sources key observations and experiments that set the scence for recent and current work.
язык: –убрика: “ехнологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2002 оличество страниц: 424ƒобавлена в каталог: 21.12.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Cell cycle, adhesion molecules in regulation 328Ч330 330 331 Cell cycle, checkpoints 233 234 240 244 Cell cycle, cyclins expression 234Ч240 234 Cell cycle, phases 233 233 234Ч240 Cell cycle, transition points 234 Cell transformation see УTransformationФ Ceramide 162 205 CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator) 112 CGD (chronic granulomatous disease) 214 217 Checkpoint protein-kinase-1 see УChk-1Ф Checkpoint protein-kinase-2 see УChk-2Ф Chelating agents 148 Chemokine receptors 352 353 Chemokines 23 320 347 349 351Ч354 351 Chemotaxis 347 Chk-1 (checkpoint protein-kinase-1) 243 Chk-2 (checkpoint protein-kinase-2) 243 Chlorpromazine 48 Cholecystokinin 19 20 Cholera toxin 116Ч119 Cholinergic receptors 38Ч42 Chromatid segregation 238 239 240 244Ч245 Chronic granulomatous disease see УCGDФ CICR ( 155 167 182 Clonidine 36 37 62 Cohesin 244 245 Conductin 333 cones 130 Contact inhibition 334 CRE (cyclic AMP response element) 194 CREB (cyclic AMP response element binding protein) 194Ч195 194 CREB binding protein see УCBPФ CrkL 263 Csk (C-terminal Src kinase) 295 409 CTP (cytidine triphosphate) 71 Cullin see УCdc53Ф Curare 15 16 CXC chemokines 351 357 352 Cyclic ADP-ribose see УcADPrФ Cyclic AMP 25 62 107Ч109 Cyclic AMP response element see УCREФ Cyclic AMP response element binding protein see УCRBФ Cyclic AMP, 176 Cyclic AMP, 7TM receptor signalling 54 55 Cyclic AMP, cellular response estimation 27 29 Cyclic AMP, formation from ATP 109 109 110 Cyclic AMP, historical aspects 31Ч32 107 Cyclic AMP, ion channel regulation 197 Cyclic AMP, phosphorylation-related signal amplification 191Ч192 Cyclic AMP, PKA activation 192Ч193 193 Cyclic AMP, suppression by 36 Cyclic AMP, theophylline actions 30 31 Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase see УPKAФ Cyclic GMP visual transduction 127 133Ч135 Cyclic GMP-dependent kinase see УG kinaseФ Cyclin A 235 236 237 Cyclin B 237 238 240 243 Cyclin D 211 235 236 236 240 241 330 Cyclin E 211 235 236 241 246 330 Cyclin H 235 Cyclin-dependent protein kinases see УCDKsФ Cyclins 234 234 Cyclins, cell cycle expression 234Ч240 234 Cyclins, cell cycle expression, G1 phase 235Ч236 235 236 Cyclins, cell cycle expression, G2 phase 237Ч238 237 Cyclins, cell cycle expression, mitosis 238Ч240 Cyclins, cell cycle expression, S phase 236Ч237 Cyclophilin 388 390 Cyclosporin 190 388 390 Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator see УCFTRФ Cytidine triphosphate see УCTPФ Cytochrome c, apoptosis regulation 339Ч340 340 Cytokines 22Ч23 232 Cytokines, inflammatory mediators 213 345 Cytokines, signalling pathways 291 Cytoskeleton 180 Cytoskeleton, adhesion molecule linkage 317 319 325 328 331 Cytoskeleton, rearrangement at mitosis 238 Cytotoxic T lymphocytes 284 285 317 D-Ras 86 daf 1 to daf 4 361 365 365 DAG (diacylglycerol) 25 115 120 179 261 265 285 DAG kinase 179 DAG, PKC activation 198 199 201 203 203 215 DAG, PKC activation, sources 204Ч205 204 Dephosphorylation 189 190 373Ч383 374 Dephosphorylation, CREB 195Ч196 Dephosphorylation, negative regulation 379Ч383 Desensitization, homologous/heterologous of phosphorylated receptors 85 Desensitization, nicotinic receptors 49Ч50 Desensitization, proteinase activated receptors (PARs) 58 Desmoplakin 331 Desmosomes 322 322 331Ч332 DFP (diisopropyl fluorophosphate) 49 DHPR 159 165 166 182 Diacylglycerol see УDAGФ Differentiation 22 Differentiation, role of adherent junctions 332 Dihydrofolate reductase 237 Dihydropyridines 157 Diisopropyl fluorophosphate see УDFPФ Dissociation constant (KD) 26 27 31 DNA helicase 237 DNA polymerase 237 DNA repair 243Ч244 DNA-PK (DNA-dependent protein kinase) 337 Dopamine 33 34 Dopamine receptors 61 Downstream of receptor kinases see УDrkФ DP-1 235 dpp 359 364 365 Drk (downstream of receptor kinases) 267Ч268 Drosophila, 361 364Ч365 Drosophila, MAP kinases 275 Drosophila, photoreceptor development 266Ч268 267 268 Drosophila, phototransduction 141 142 158 206Ч208 207 Drosophila, Ras proteins 86 Drosophila, Smad homologues 366 368 Drosophila, tyrosine phosphatases 377 378 E-selectin 323 351 354 E2F 235 236 242 E6 protein 243 EC50 27Ч28 29 30 31 EF-2 kinase (elongation factor-2 kinase) 275 EF-hand motifs 171 173 174 177 179 180 183 401Ч402 402 EGF (epidermal growth factor) 20 EGF receptor 4 229 249 EGF receptor, activation 259 261 265 271 EGF, historical aspects 227Ч230 229 EGTA 148 148 181 Eicosanoids 23 Eicosanoids, receptor binding 55 EILDV motifs 318 ELAM-1 318 Electric organs 42Ч43 eLF-4E 272 273 307Ч308 Elongation factor-2 kinase see УEF-2 kinaseФ Endocytosis 31 84 Endoglin 362 Endonexin fold 172 Endorphins 3 Endothelial cell adhesion molecules 349Ч351 Epac 197Ч198 198 Ephedrine 2 37 Epidermal growth factor see УEGFФ Epidermolysis bullosa 332 Epinephrine see УAdrenalineФ EPO (erythropoietin) 284 Epo receptor 284 380Ч381 Equilibrium constant 26 Erb-B 229 230 249 Ergot 11 12Ч14 Ergotamine 14 ERK (extracellular signal regulated protein kinase) 80 84 92 210 270 271 274 330 ERK, activation 196Ч197 196 271 407 ERK, activation, 7TM receptors 276Ч279 ERK, protein synthesis regulation 272Ч273 273 ERK, transcription activation 271Ч272 272 ERK1 274 ERK2 274 Erythropoietin see УEpoФ Eserine 14 Excitation-contraction coupling 157 182 Exocytosis 157 179 181 Exocytosis, signalling pathways 289 Extracellular matrix 315 317 319 324 Extracellular signal regulated protein kinase see УERKФ F-actin 180 F-box 246 Fab fragments 316 FADD 339 350 FAK (focal adhesion kinase) 325 326 329 337 Fas 339 Fas ligand 339 339 FGF (fibroblast growth factor) 249 Fibrinogen 319 Fibroblast growth factor see УFGFФ Fibronectin 317 325 328 FK506 154 188 FKBP 388 FKBP12 154 155 361 369 FKHRL 326 Flash 339 fMLP (formyl-Met-Leu-Phe) 354 Focal adhesion complexes 235 328Ч329 329 Focal adhesion kinase see УFAKФ Follicle stimulating hormone see УFSHФ Forskolin 117 Forskolin, adenylyl cyclase activation 109 112 116 Fos 208 209 271 272 276 FRAP/mTOR 308 FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) 20 22 195 Fura2 151 152 fyn 286 294 329 G kinase (cyclic GMP-dependent kinase) 178 G-proteins 42 72 G-proteins, 149 G-proteins, 123Ч124 G-proteins, 72 77 95Ч96 109 G-proteins, 80 84 109 G-proteins, 80 96 109 110 112 113 G-proteins, 79Ч80 79 G-proteins, 80 G-proteins, 78 80 G-proteins, 80Ч82 G-proteins, 81Ч82 81 G-proteins, 72 82Ч85 95Ч96 G-proteins, 84 G-proteins, 84Ч85 G-proteins, 83Ч84 G-proteins, 7TM receptor linkage 72 73 99 G-proteins, activation without subunit dissociation 95Ч100 G-proteins, GTPase cycle 74Ч75 74 G-proteins, heterotrimeric 73Ч74 73 G-proteins, heterotrimeric, post-translational modifications 82 82 83 G-proteins, monomeric 73 G-proteins, monomeric, oncogene products 85Ч86 G-proteins, phototransduction 130 131 G-proteins, receptor affinity modulation 76 77 G0 phase 234 G1 phase 233 233 234 235Ч236 235 236 G2 phase 233 233 237Ч238 237 G2 phase, checkpoint 243 244 GABA ( 24 GABA receptors 42 50 56 GABAA receptors 42 GABAB receptors 42 51 GABAB receptors, heterodimers 61 GABAC receptors 42 GAG 86 Gap junctions 165 GAP-43 200 Gastrin 19 20 GCAP (guanylyl cyclase activating protein) 136 GEFs (guanine nucleotide exchange factors) 95 197 Gelsolin 180 337 Geranylgeranyl groups, G-protein subunit post-translational modification 82 83 GH (growth hormone) see УSomatotropinФ Glucagon 20 62 Glucagon, receptor binding 55 Gluconeogenesis 71 Glucose transport 307 GLUT4 307 Glutamate 19 24 133 Glutamate receptors 42 56 Glutamate receptors, iGlu 4 42 Glutamate receptors, ion channel linkage 50Ч51 158 Glutamate receptors, mGlu 42 51 Glutamate receptors, mGlu, homodimers 62 Glycine 24 Glycine receptors 50 Glycogen metabolism, PP1 regulation 386Ч388 386 387 Glycogen phosphorylase 191 191 Glycogen synthase 175 307 308 386 387 Glycogen synthase kinase see УGSKФ Glycogen synthesis 107Ч108 108 306 307 Glycogenolysis 107 108 175 176 191Ч192 191 386 387 Glycogenolytic hormones 299 Glycosaminoglycans 324 GM-CSF (granulocyte-monocyte colony stimulating factor) 23 349 GM1 118 119 GnRH (gonadotrophin-releasing hormone) 3 Granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor see УGM-CSFФ Grb2 (growth factor receptor binding protein-2) 269 277 287 329 Growth factors 22 225Ч251 Growth factors, multiple effects 19 22 Growth factors, nomenclature 232 Growth hormone (GH) see УSomatotropinФ GSK (glycogen synthase kinase) 175 209 GSK- 307 333 GTP 71 72 GTP, stable analogues 76 76 GTP-binding proteins 2 71Ч100 GTP-binding proteins, 7TM receptor signalling 54 GTP-binding proteins, subunits 72 GTP-binding proteins, terminology 72Ч73 GTPase 72 90Ч91 GTPase activating G-protein see УIRAФ GTPase, activation mechanisms 93Ч95 94 GTPase, GTP/GDP cycle 74Ч75 74 GTPase, regulation 75Ч76 Guanine nucleotide exchange factors see УGEFsФ Guanylyl cyclase activating protein see УGCAPФ H-Ras, Ha-Ras 86 211 Haemopoetic growth factor receptors 381 Haloperidol 61 Helper T lymphocytes 284 285 288 Hepatocyte growth factor 328 Heterologous desensitization 85 85 Histamine 20 23 212 Histamine, receptor binding 55 Histones 237 238 HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) 352 Homologous desensitization 85 85 Hormones 2 19 20 21 Hormones, cellular response measurement (EC50) 27 29 Hormones, definition 9 Hormones, historical background 4Ч8 Hormones, lipophilic 24Ч25 Hormones, multiple effects 19
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



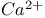 -induced
-induced 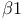 adrenergic antagonists
adrenergic antagonists  receptor homologues
receptor homologues  activation
activation  -subunits
-subunits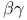 -subunit interactions
-subunit interactions  -aminobutyric acid)
-aminobutyric acid)