јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M. Ч Signal Transduction
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Signal Transductionјвторы: Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M.јннотаци€: Signal Transduction is a text reference on cellular signalling processes. Starting with the basics, it explains how cells respond to external cues (hormones, cytokines, neurotransmitters, adhesion molecules, extracellular matrix, etc), and shows how these inputs are integrated and co-ordinated. The first half of the book provides the conceptual framework, explaining the formation and action of second messengers, particulary cyclic nucleotides and calcium, and the mediation of signal pathways by GTP-binding proteins. The remaining chapters deal with the formation of complex signalling cascades employed by cytokines and adhesion molecules, starting at the membrane and ending in the nucleus, there to regulate gene transcription. In this context, growth is an important potential outcome and this has relevance to the cellular transformations that underlie cancer. The book ends with a description at the molecular level of how signalling proteins interact with their environment and with each other through their structural domains. Each main topic is introduced with a historical essay, detailing the sources key observations and experiments that set the scence for recent and current work.
язык: –убрика: “ехнологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2002 оличество страниц: 424ƒобавлена в каталог: 21.12.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
PI 3-kinase (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) 92 121 262 276 300Ч305 300 PI 3-kinase family 301Ч303 302 PI 3-kinase family, class I kinases 301Ч303 PI 3-kinase family, class II kinases 303 PI 3-kinase family, class III kinases 303 PI 3-kinase, activation by insulin receptor 306 306 PI 3-kinase, activation pathways 304 304 PI 3-kinase, glucose transport activation 307 PI 3-kinase, inhibition studies 303 PI 3-kinase, lipid product measurements 303 PI 3-kinase, protein synthesis regulation 307Ч308 309 PI(4, 5)P2 (phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate) 42 119 120 120 121 123 154 262 300 303 PI-3, 4, 5-P3 121 204 205 300 301 303 PI-3, 4, 5-P3, dephosphorylation 382Ч383 PI-3, 4, 5-P3, protein kinase B activation 305 305 PI-3, 4-P2 204 PICKs 205 Pilocarpine 15 Pindolol 37 60 PIP2Чsee УPI(4, 5)P2 (phosphatidylinositol 4 5- Pirenzepine 40 PKA (protein kinase A) 31 84 85 175 192Ч193 406Ч407 406 PKA, activation by cyclic AMP 192Ч193 193 PKA, ERK activation 196Ч197 PKA, glycogen metabolism 386 PKA, phosphorylation 49 185 191 193 PKA, phosphorylation, adenylyl cyclase regulation 112 115 191 PKA, transcription regulation 194 196 PKB (protein kinase B) 300 304Ч305 310 311 326 352 PKB, insulin activation 307 PKB, PDGF activation 307 PKB, PI(3, 4, 5) P3 activation 305 305 PKB, subtypes 304 305 PKC (protein kinase C) 31 198Ч204 PKC (protein kinase C) family 199Ч201 199 200 PKC, activation 120 179 199 202Ч204 203 261 407 PKC, activation, DAG (diacylglycerol) 198 199 201 203 203 204Ч205 204 PKC, anchoring proteins 205Ч206 206 PKC, cell transformation 208Ч212 PKC, inflammation 212Ч217 PKC, inflammation, integrin activation 352 PKC, inflammation, respiratory burst regulation 215Ч217 216 PKC, isoforms 199 799 PKC, isoforms, differential localization 205 PKC, isoforms, overexpression in transformed cells 211Ч212 PKC, phosphorylation 49 198Ч199 PKC, phosphorylation, adenylyl cyclase regulation 112 115 PKC, pseudosubstrates 202 PKC, SRE activation 210 211 PKC, structural domains 201Ч202 201 PKC, tRE activation 208Ч209 209 210 PLA2 (phospholipase A2) 84 121 Plakoglobin 322 Plasma membrane 2 Plasma membrane, 149 Plasma membrane, lipid raft hypothesis (microdomains) 289Ч290 Plasma membrane, voltage-operated 157 Platelet derived growth factor see УPDGFФ Platelets 23 Platelets, thrombin activation 58 PLC (phospholipase C) 42 84 119Ч125 PLC, domain organization 121 123 124 PLC, intracellular 153 154 PLC, IP3 formation 121 PLC, isoenzymes 121 123 PLC, phototransduction mechanisms 130 PLC, regulation 123Ч125 PLD (phospholipase D) 121 161 Pleckstrin homology domains see УPH domainsФ PLK1 (polo-like protein kinase) 243 PMA (phorbol myristate acetate; TPA) 199 199 208 212 Pocket-proteins 235 242 Polo-like protein kinase see УPLK1Ф Polyoma virus 257 POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) 4 PP1 (protein phosphatase-1) 195 196 384 384 PP1, glycogen metabolism regulation 386Ч388 PP1G (protein phosphatase-1G) 307 384 386 387 PP2A 384 387 PP2B see УCalcineurinФ PP2C 384 PPM serine-threonine phosphatases 385 385 PPP serine-threonine phosphatases 385 385 Practolol 36 Prenylation, G-protein subunit post-translational modification 82 83 Pro-opiomelanocortin see УPOMCФ Progesterone 20 24 25 61 Prolactin 4 Prolactin receptors 284 Proliferating cell nuclear antigen see УPCNAФ Propranolol 36 37 55 60 Prostaglandin E2 23 24 58 Prostaglandins 20 Prostaglandins, adenylyl cyclase activation 62 Proteasome 246 Protein domains 393Ч409 Protein domains, 401Ч403 Protein domains, functions 394Ч395 Protein domains, identification 394 Protein domains, oligopeptide motif-binding 395Ч398 Protein domains, protein kinases 403Ч409 Protein domains, protein/lipid-binding 398Ч399 400 401 Protein domains, structurally conserved 393Ч395 393 Protein kinase A see УPKAФ Protein kinase B see УPKBФ Protein kinase C see УPKCФ Protein kinases 189 Protein kinases, domain organization 403Ч409 Protein kinases, domain organization, kinase activity 404Ч407 Protein kinases, domain organization, structure 403Ч404 404 Protein kinases, regulation by phosphorylation 407 Protein phosphatase 1 see УPP1Ф Protein phosphatase 1G see УPP1GФ Protein serinefthreonine kinases 359Ч370 Protein synthesis regulation, ERK (extracellular signal regulated protein kinase) 272Ч273 273 Protein synthesis regulation, PI 3-kinase 307Ч308 309 Protein tyrosine kinases see УPTKsФ Protein tyrosine phosphatases see УPTPsФ Proteinase activated receptors see УPAR receptorsФ Protohormones 2-4 PTB/PID domains 263 306 396 397 PTEN 249 381Ч383 383 PTH (parathyroid hormone) 20 PTKs (protein tyrosine kinases) 190 PTKs, 124 263 PTKs, 265 PTKs, non-receptor 283Ч295 PTKs, receptor 257Ч279 PTPC 340 PTPs (protein tyrosine phosphatases) 373Ч383 PTPs, cytosolic 375Ч376 PTPs, domain organization 375 PTPs, role in signal transduction 376Ч378 PTPs, transmembrane receptor-like 374Ч375 Quin2 151 151 Rab 86 RAc 216 310 328 352 Rac2 215 racks 205 Raclopride 61 RAF 91 92 210 Raf-1 210 Raf-1 kinase 271 Ran 86 RAP1 80 197 198 798 Rapamycin 308 RAS 81 86 197 210 235 275 329 352 Ras proteins 85Ч92 Ras proteins, functions 90Ч91 90 Ras proteins, post-translational lipid modification 86 86 90 Ras proteins, structure 87Ч90 87 88 89 Ras proteins, subfamilies 86Ч87 Ras, cancer-promoting mutations 91 250 251 293 Ras, functions 91Ч92 92 Ras, GEFs 95 Ras, GTPase activation mechanism 93Ч95 94 Ras, regulation pathway 269Ч270 Ras, signalling pathway 266 Ras-GAP 92Ч93 270 Ras-GAP, domain organization 93 93 Ras-MAP kinase pathway 270Ч271 270 Rb protein 242Ч243 249 250 Rb110 235 236 241 Receptors 14Ч16 33Ч66 Receptors, activation, ligand binding 58Ч59 Receptors, activation, without stimulating ligand 59Ч60 Receptors, dimerization 61Ч62 Receptors, down-regulation 30Ч31 Receptors, effector enzymes 62Ч63 63 64 Receptors, effector enzymes, experimental approaches 63Ч65 65 Receptors, evolutionary aspects 4 Receptors, G-protein modulation of affinity 76 77 Receptors, ion channel-linked 42Ч51 158 Receptors, ligand interactions 58Ч62 Receptors, ligand interactions, competitive binding 36 38 Receptors, ligand interactions, modulation by G-proteins 76 77 Receptors, metabotropic 42 56Ч57 Receptors, overexpression 60Ч61 Receptors, spare 30 Receptors, total number (Rtot) 27 28 31 Receptors, tyrosine kinase-linked see УTyrosine kinase-linked receptorsФ Recoverin 179Ч180 Regulators of G-protein signalling see УRGS proteinsФ Renin 36 Respiratory burst 213Ч215 215 317 352 Respiratory burst, PKC regulation 215Ч217 276 Restriction point 234 retina 130 131 Retinoblastoma 242 RGD motifs 318 RGS proteins (regulator of G-protein signalling) 75Ч76 RGS-12 76 Rho 86 300 352 Rho family 328 330 RhoA 328 330 337 352 Rhodopsin 51 54 61 96 127 130 180 Rhodopsin kinase 84 139 Rhodopsin, membrane-spanning sequences/topology 51Ч52 52 53 Rhodopsin, photo-excitation 134 137 738 Rhodopsin, rod cell organization 131 732 RhoGAP 94 RhoGEF 80 328 RIP 350 Rod cells 130Ч135 732 RSV (Rous sarcoma virus) 226 258 RyR (ryanodine receptor) 154Ч157 155 159 165 166 182 184 S phase 233 233 236Ч237 S49cyc lymphoma cells, 77 78 Salbutamol 36 37 SAPK (stress activated protein kinase) 274 SARA 369 Sarcolemma 182 Sarcoma 226 Sarcoplasmic reticulum see УSRФ Sarin 49 Scatter factor 328 SCF complex 246 Schizophrenia 61 Second (intracellular) messengers 25 Secretin 9 19 20 Selectins 323 323 Sem-5 268 Senescent cells 234 Serine esterase inhibitors 39 Serine esterases 58 Serine-threonine kinases 359Ч370 Serine-threonine phosphatases 383Ч390 Serine-threonine phosphatases, classification 385 385 Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) 4 20 23 Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) receptors 42 50 Serum response element see УSREФ Serum response factor ee УSRFФ Sev (sevenless) 266 267 Sf9 insect cells, adrenergic receptor/adenylyl cyclase system 59 98Ч99 99 SH2 domain 124 260 262 263 264 268 269 286 287 288 294 301 326 376 395Ч396 395 408 409 SH3 domain 124 216 262 268 269 294 301 396 398 398 408 Shc 329 SHP-1 (Src homology phosphatase-1) 376 380Ч381 SHP-2 (Src homology phosphatase-2) 376 377Ч378 379 Sialyl LewisX 323 354 SIF (Sis-inducible factor) 276 Signal transducer and activator of transcription see УSTATsФ Signal transmission 62Ч65 Signal transmission, 7TM receptors 65Ч66 Signal transmission, adenylyl cyclase activation 62Ч63 63 64 Signal transmission, adenylyl cyclase activation, experimental approaches 63Ч65 65 Simian sarcoma virus see Уv-SisФ Simian virus 40 see УSV40Ф SIS 249 Sis-inducible factor see УSIFФ Skeletal muscle, 165Ч166 Skeletal muscle, 182Ч184 Skpl 246 SLP76 287 Smad1 166 Smad2 366 367 370 Smad3 366 Smad4 366 368 370 Smad5 366 Smad6 368 Smad7 368 Smad8 366 SMADs 362 365Ч370 366 Smads, antagonistic 368 368 Smads, receptor-regulated 366 367 Smads, transcription regulation 367 369Ч370 Smads, tumour suppression 370 Smooth muscle contraction 184 SNAP25 181 SNARE complex 181 SOCs (store-operated channels) 158Ч159 759 Somatomedin 1 (IGF1; insulin-like growth factor 1) 20 242 249 Somatomedin 2 (IGF2; insulin-like growth factor 2) 20 Somatostatin 19 194 Somatostatin receptor 99 Somatotropin (GH; growth hormone) 20 119 Sos (son of sevenless) 267 268 269 277 Spare receptors 30 Sphingomyelin 161 162 Sphingosine 161 Sphingosine kinase 161 Spindle (metaphase) checkpoint 234 244Ч245 245 Spore formation (starvation response) 95 108 SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum) 154 157 166 182 SRC 84 257 294 329 Src family kinases 294Ч295 Src family kinases, activation 295 295 407 Src family kinases, suppression 295 Src homology domains 262õ265 268 Src homology phosphatases see УSHP-1У УSHP-2Ф Src, regulatory domains 408 409 408 SRE (serum response element) 92 209 210 211 271 SRF (serum response factor) 209 St Vitus dance 12 73 Starvation, cyclic AMP synthesis response 107 108 Starvation, yeast spore formation 95 STAT1 291 STAT2 291 STAT3 80 STAT5 381
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 exchangers
exchangers 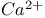 channels (VOCCs)
channels (VOCCs) 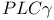 activation
activation 
 subline
subline