јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M. Ч Signal Transduction
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Signal Transductionјвторы: Gomperts B.D., Tatham P.E.R., Kramer I.M.јннотаци€: Signal Transduction is a text reference on cellular signalling processes. Starting with the basics, it explains how cells respond to external cues (hormones, cytokines, neurotransmitters, adhesion molecules, extracellular matrix, etc), and shows how these inputs are integrated and co-ordinated. The first half of the book provides the conceptual framework, explaining the formation and action of second messengers, particulary cyclic nucleotides and calcium, and the mediation of signal pathways by GTP-binding proteins. The remaining chapters deal with the formation of complex signalling cascades employed by cytokines and adhesion molecules, starting at the membrane and ending in the nucleus, there to regulate gene transcription. In this context, growth is an important potential outcome and this has relevance to the cellular transformations that underlie cancer. The book ends with a description at the molecular level of how signalling proteins interact with their environment and with each other through their structural domains. Each main topic is introduced with a historical essay, detailing the sources key observations and experiments that set the scence for recent and current work.
язык: –убрика: “ехнологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2002 оличество страниц: 424ƒобавлена в каталог: 21.12.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Hormones, receptor binding 25Ч26 HsEg5 238 Human immunodeficiency virus see УHIVФ Hyaluronan 324 ICAD (inhibitor of capsase activated DNAase) 336 ICAM (intercellular adhesion molecule) 285 318 319 349 351 ICAM-1 352 ICRAC 158 161 IgE-R (IgE high affinity receptor) 183 IgE-R, signalling pathways 288Ч289 289 IGF1 (insulin-like growth factor 1) see УSomatomedin 1Ф IGF2 (insulin-like growth factor 2) see УSomatomedin 2Ф IL-2 (interleukin-2) 213 285 288 IL-2 (interleukin-2) receptor 283 IL-3 (interleukin-3) 249 IL-6 (interleukin-6) 288 349 IL-8 (interleukin-8) 349 Immunoglobulin receptors 161 283 Immunoglobulin superfamily 318Ч319 378 Immunophilins 154 388 389 Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs see УITAMsФ InaC 207 208 InaD 207 208 Inflammation 23 345Ч349 346 347 Inflammation, eicosanoid actions 23 Inflammation, PKC 212Ч217 Inflammatory mediators 345 347 348 Inhibitor of capsase activated DNAase see УICADФ INK4 (inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase-4) 240 241 242 Inositol lipid cycle 179 180 Inositol-1, 4, 5-triphosphate see УIP3Ф Insulin 3 19 20 22 299 310 Insulin receptor 4 Insulin receptor substrates see УIRSФ Insulin receptor, activation 259 262 Insulin receptor, PI 3-kinase activation 306 306 Insulin receptor, signalling 299Ч300 Insulin stimulated protein kinase see УISPKФ Insulin, adenylyl cyclase activation 61 Insulin, glucose transport activation 307Ч308 Insulin, glycogen synthase activation 306Ч307 308 Insulin, insulin receptor interaction 28 306 Insulin, PKB activation 307 Insulin-derived growth factor see УIGFФ Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGFl) see УSomatomedin 1Ф Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) see УSomatomedin 2Ф Insulin-stimulated protein kinase see УISPKФ Integrins 249 317 318 319Ч320 319 320 325 328 329 Integrins, leukocyte trafficking 351 352Ч353 Intercellular adhesion molecule see УICAMФ Interferon see У Interferons 23 290Ч291 Interleukin-2 see УIL-2Ф Interleukin-3 see УIL-3Ф Interleukin-6 see УIL-6Ф Interleukin-8 see УIL-8Ф Interleukins 23 Intermediate filaments 331 Interphase 233 Intracellular (second) messengers 25 Inverse agonists 59 60 60 61 76 77 Ion channel-linked receptors 42Ч51 Ion channels, cyclic AMP regulation 197 Ion channels, cytosolic 153 Ion channels, patch clamp studies 44Ч46 45 Ion channels, site-specific blocking 48 Ionomycin 150 IP3 (inositol-1, 4, 5-triphosphate) 25 120 122 216 261 265 285 IP3 receptor 154 155 756 IP3 receptor, calcium channel regulation 156 159 166 167 167 184 IP3 receptor, isoforms 155 156 IP3, intracellular 154Ч157 167 IRA (GTPase activating G-protein) 108 IRS (insulin receptor substrates) 306 IRS-1 306 Isoprenaline (isoproterenol) 35Ч36 37 62 ISPK (insulin stimulated protein kinase) 385 ITAMs (immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs) 286 JAK2 (Janus-kinase-2) 293 294 380Ч381 JNK (Jun N-terminal kinase) 210 272 274 JNK, apoptosis induction 327Ч328 328 JNK-1 (Jun N-terminal kinase-1) 209 Jun 208 209 265 271 272 Keratin 331Ч332 Kinases 25 Kinetochore 238 244 245 KIP/CIP 240 241Ч242 L-selectin 323 354 L-type 157 Lambda-PKC interaction protein see УLIPФ Lamin 238 337 Large T-antigen 243 250 251 LAT (linker for activation of T-cells) 287 290 LC20 238 Lck 285 286 376 377 Let-60 268 Leucine zipper 208 Leukaemia 225Ч226 226 293 Leukocyte common antigen see УCD45Ф Leukocytes, adhesion/extravasion 345 352Ч353 354 354 355 Leukocytes, inflammatory response 212 345 Leukocytes, protection from apoptosis 326 Leukocytes, trafficking 345Ч355 Leukotriene LTB4 288 Leukotrienes 23 LFA-1 (lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1) 285 317 318 LH (luteinizing hormone) 20 LH receptors 194 Ligands, extracellular first messengers 19 20 Ligands, receptor interactions 14Ч16 Ligands, receptor interactions, binding 25Ч29 Linker for activation of T-cells see УLATФ LIP (lambda-PKC interaction protein) 205 Lipid microdomains 290 LPA (lysophosphatidic acid) 204 205 LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide) 14 Luteinizing hormone see УLHФ Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 see УLFA-1Ф Lymphotoxin 349 lyn 288 294 Lysergic acid diethylamide see УLSDФ Lysophosphatidic acid see УLPAФ M phase 233 see M phase, checkpoint 234 244Ч245 Mac-1 215 316 318 MAD 365 Mad1 244 Mad2 244 MadCAM 319 Major histocompatibility complex see УMHCФ MAP kinase (mitogen activated protein kinase) 209 210 270Ч271 270 MAP kinase phosphatase-1 see УMKP-1Ф MAP kinase, negative regulation 379Ч380 380 MAP kinase-ERK kinase see УMEKФ MAP kinase-integrating kinase-1 see УMnklФ MAP kinase-related proteins 273Ч275 274 275 MARCKS 200 Mast cells 23 158 212 288 289 Mastoparan 289 MEK (MAP kinase-ERK kinase) 271 MEK1 407 MEKK 350 Melanin 132 Metabotropic receptors 42 56Ч57 Metastasis 249 322 Metoprolol 36 37 MH1 365 370 MH2 365 370 MHC (Major histocompatibility complex) 283 285 Microfilaments 180 Middle T-antigen 257 Mitogen activated protein kinase see УMAP kinaseФ Mitosis 233 238Ч240 239 see MKP-1 (MAP kinase phosphatase-1) 379Ч380 380 MLCK (myosin light chain kinase) 184 275 Mnkl (MAP kinase-integrating kinase-1) 272 273 Monoclonal antibodies 316Ч317 Muscarine 39 40 41 Muscarinic receptors 39 40 42 Muscarinic receptors, acetylcholine interaction 40 55 Muscarinic receptors, antagonists 40 41 Muscarinic receptors, G-protein signalling 42 51 83Ч84 Muscarinic receptors, subtypes 40 41 Myc 271 myosin 182 Myosin II light chain see УLC20Ф Myosin light chain kinase see УMLCKФ Mytl kinase 237 238 N-Ras 86 NAADP (nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide Phosphate) 159 160Ч161 160 NADPH oxidase, respiratory burst 214Ч215 215 216 NCAM (neuronal cell adhesion molecule) 316 317 318 319 Nerve growth factor see УNGFФ Neurite outgrowth 315 Neurofibromatosis type 1 94 Neurofibromin 94 95 Neuromodulators 19 Neuromuscular junction, acetylcholine actions 38 40 Neuromuscular junction, nicotinic receptors 40 42Ч43 43 Neuromuscular junction, nicotinic receptors, subunits 44 45 Neuronal cell adhesion molecule see УNCAMФ Neuropeptides 24 Neurotransmitters 10Ч12 21 24 Neurotransmitters, 181Ч182 Neurotransmitters, mutiple effects 19 Neutral antagonists 60 Neutrophils, antimicrobial defences 213 214 Neutrophils, antimicrobial defences, respiratory burst 213Ч215 275 Neutrophils, inflammatory response 213 NF- 349 350 351 NF-AT 287 288 309 388 390 NFI 94 NGF (nerve growth factor) 227-230 Nicotine 15 16 39 41 Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate see УNAADPФ Nicotinic receptors 39 40 Nicotinic receptors, 43Ч44 Nicotinic receptors, acetylcholine interactions 38 49 Nicotinic receptors, antagonists 40 41 Nicotinic receptors, desensitization 49Ч50 Nicotinic receptors, electron microscopy 49 50 Nicotinic receptors, ion channel function 42Ч50 Nicotinic receptors, patch clamp studies 44Ч46 45 Nicotinic receptors, sarcolemma 182 Nicotinic receptors, subunits 44Ч45 45 51 Nicotinic receptors, subunits, membrane spanning sequences 47Ч49 48 49 Nicotinic receptors, subunits, sequence homologies 44Ч45 46 47 Nifedipine 157 NIK 350 Nitric oxide see УNOФ Nitric oxide synthase see УNOSФ NLS (nuclear localization sequence) 388 NMDA, glutamate receptor activation 158 NO (nitric oxide) 177 178 Non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase family 283-284 284 294 294 Noradrenaline (norepinephrine) 9 10 19 20 22 33 34 Noradrenaline, adenylyl cyclase activation 63 NOS (nitric oxide synthase) 177Ч178 309 Nuclear factor see УNF- Nuclear localization sequence see УNLSФ Nucleolin 238 nucleotides 71 Occludin 331 Odorant substances, receptor interactions 54 197 Oestradiol 2 Okadaic acid 190 195 384 Olfactory cell ion channels 197 Oncogenes 208 292Ч294 Oncogenes, non-viral 293Ч294 Oncogenes, tyrosine kinase signal transduction components 293 Oncogenes, viral 292Ч293 Opiate receptors 99 Opiate receptors, homodimers 62 Opsin 61 127 139 Opsonization 215 Organophosphorus compounds 39 58 Organotherapy 5Ч8 Osteopontin 317 Oxytocin 20 24 Oxytocin receptor, progesterone actions 61 76 P-glycoproteins 112 P-selectin 323 351 354 P107 235 236 P130 235 P21-activated protein kinase see УPAKФ P38/HOG pathway 274 p53 242Ч243 249 250 P70 S6-kinase 307 PAK (p21-activated protein kinase) 337 PAR receptors (proteinase activated receptors) 58 Paracrine agents 19 Parathyroid 56 Parathyroid hormone see УPTHФ Partial agonists 59 Patch clamp studies 42 44Ч46 45 PCNA (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) 241 PDGF (platelet derived growth factor) 22 249 PDGF receptor, activation 259 261 262 265 271 PDGF, historical aspects 230Ч231 PDGF, protein kinase B activation 307 PDKI (3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase-1) 305 310 Pdsl 238 245 PECAM 319 Pertussis toxin 80 116Ч119 118 197 PH (pleckstrin homology) domains 398Ч399 400 401 Phagocytosis 213 215 Phentolamine 63 Phenylephrine 36 37 Pheromone-induced mating response 96Ч100 Phorbol esters 199 201 Phorbol esters, inflammatory activity 212Ч215 213 Phorbol esters, tumour promoting activity 208 Phorbol myristate acetate see УPMAФ Phosphatases 25 175 Phosphatidylinositol see УPIФ Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase see УPI 3-kinaseФ Phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-bisphosphate see УPI(4 5)P2Ф Phosphodiesterase, 176Ч177 Phospholipase A2 see УPLA2Ф Phospholipase C see УPLCФ Phospholipase D see УPLDФ Phospholipases 120Ч121 120 Phosphorylase 189 190 191 192 387 Phosphorylase kinase 175 191 275 386 Phosphorylation reactions 25 31 189Ч217 Phosphorylation reactions, 215Ч217 Phosphorylation reactions, adenylyl cyclase regulation 115 191 Phosphorylation reactions, cyclic AMP signal amplification 191Ч192 Phosphorylation reactions, glycogenosis 175 Phosphorylation reactions, protein kinase activity regulation 407 407 Phosphorylation reactions, protein kinase activity regulation, PKC 200 202 203 Phosphorylation reactions, receptor downregulation 49 50 84 85 85 Photoreceptors, cells 130Ч135 Photoreceptors, dark current 133 134 Photoreceptors, development in Drosophila 266Ч268 267 268 Photoreceptors, function 130Ч135 Photoreceptors, function, signal amplification 133 Photoreceptors, sensitivity 127Ч128 129 Phototransduction see УVisual transductionФ PI (phosphatidylinositol) 119 120 122 301
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -receptor
-receptor  -receptorФ
-receptorФ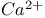 elevation
elevation  (nuclear factor
(nuclear factor  byPKC
byPKC