Авторизация
Поиск по указателям
Ridley A., Clark P., Peckham M. — Cell motility: from molecules to organisms
Обсудите книгу на научном форуме Нашли опечатку?
Название: Cell motility: from molecules to organismsАвторы: Ridley A., Clark P., Peckham M.Аннотация: Recent advances in molecular and biophysical techniques, particularly fluorescence and live cell imaging, are revolutionizing the study of cell motility. New bioprobes not only reveal simple intracellular localization, but also contain details of post-translational modifications, conformational state and protein-protein interactions. Coupling these insights with complementary advances in genetic and biochemical methods is enabling scientists to understand the processes involved in cell motility - from molecular motors to cell movements in vivo in a range of organisms and cell types.
Язык: Рубрика: Биология /Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats Год издания: 2004Количество страниц: 342Добавлена в каталог: 10.12.2005Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
Предметный указатель
LIS1 88 90 Listeria 146 156 Listeria monocytogenes 137—138 143 145 Local cell intercalation rates and tissue-level displacement 288 m-calpain (calpain II) 223 M10 26 M10, relationship to DdM7 31—32 M7 26 M7, link with talin 28—30 M7a 27 MAP 87 MAP kinase cascades 269 Matrix adhesions 78 Matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) 160—161 MDCK cells 54 101 104 108 160 239—240 242 MDCK cells in cell-cell adhesion 105 MDCK cells, cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion in 107 MDCK cells, Racl complexes in, during cell-cell adhesion 109 MDCK cells, Racl-containing lamellipodia drive cell-cell contact formation between 107 MDCK cells, RacT17NGFP in 109 mDia, activation by active RhoA 84 mDial 75 78 83 85 144 mDial activity 90 mDial as coordinator of actin, focal adhesions and microtubule assembly 84—91 mDial, cytoskeletal alterations produced by 86 mDial, effects on microtubule dynamics 87 mDial, role in organization of microtubule system 91 mDial-induced changes in microtubule dynamics 92 mDial-mediated microtubule regulation 87 Mediolateral cell intercalation 277 Mediolateral intercalation 279—280 284 MEK kinase signalling, chemotaxis regulated by 269—271 MEK1 261 Melanoma B16 cells 79 Melb-a melanoblasts 79 Membrane domains 102 Membrane dynamics 165—171 Membrane dynamics in cell-cell adhesion 106—107 Membrane protrusion 170 Membrane recycling 169 Membrane translocation 167 Mesodermal cells 293 Mesodermal tissues 289 Metastatic cells, chemotaxis 175 Metazoan cell types 203 Metazoans, morphogenesis of 277 Microtubule cytoskeleton 203 Microtubule cytoskeleton, organization and dynamics of 208 Microtubule dynamics 206 Microtubule dynamics in migrating cells 203—217 Microtubule dynamics, instability downstream of Rac1 210—213 Microtubule dynamics, mDial-induced changes in 92 Microtubule organization 203 206 Microtubule plus ends 206 Microtubule stabilization, downstream of RhoA 209—210 Microtubule stabilization, mDia-mediated 209 Microtubule-disrupting drugs 78 Microtubule-end-tracking proteins 90 Microtubule-mediated suppression of contractility 81 microtubules 75—99 Microtubules, disruption of 81 Microtubules, role in migrating cells 80 205—207 Microvilli 236 Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) 226 ML-7 81 Morphogenesis 277 Morphogenic processes 277 Mouse development, cell migration during 317—330 MTC cells, EGF receptor in 177 MTLn3 176—179 Multicellular organisms 101 Muscle precursor cells 325—328 Muscle precursor cells, development of 324 Muscle precursor cells, Eph receptor signals during migration of 328 Myo1c 54 Myo3p 49—50 Myo5p 49—51 MyoA 44 49 MYOB 44 49 51 MyoC 44 51 MyoD 44 MyoE 44 MyoF 44 Myogenic precursor cells 326 MyoK 44—48 51 MyoK GPR loop 47 MyoK, molecular functions 52 Myosin ATPase (BDM) 81 Myosin I 39—59 Myosin I and actin dynamics connection 49—52 Myosin I, phenotypes resulting from manipulation 48—49 Myosin IB 44 Myosin IC 44 Myosin IE 44—45 Myosin IF 44 Myosin II 42 81—83 136 226 262—263 Myosin II-driven cell contractility 75 Myosin II-driven contractility 80—81 92 Myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) 92 Myosin superfamily 40—42 Myosin VII, role in adhesion 19—37 Myosin X 123 Myosins, structure function analysis 44—48 Myotome (MY) 326 MyTH4/FERM module 31 N-CAM 310—311 N-WASp 9 138 141 155 161 247—260 N-WASp in podosome formation and tubulogenesis 159—160 N-WASp, mechanism of activation 157—159 N17Rac 66 Nap124 141 Nap125 159 Nck 64 Nck Associated protein 1 (NCKAP1) 251 NDF (Neu Differentiation Factor) 319 Neural cells 281 Neural cells, intercalation 282 Neural crest cells 320 Neural crest cells, development of 321—323 Neural crest cells, migration of 318 320—321 Neuronal axons 71 Neuronal precursors in rostral migratory stream (RMS) 310—312 Neurulation 277—279 Neutrophil chemotaxis, calpain in regulating 229 Nrg1 318—321 Nucleation-promoting factors 7—8 Nucleotide hydrolysis 9 Opl8/stafhmin 90 206 Opl8/stafhmin, phosphorylation of 211 P13K1/2 267 p41-Arc 137 p85-PI3 kinase 64 Pak 11 50 303 309 PAK kinase 40 PAK/LIM kinase pathway 13 PAK/Ste20 family 41 PAK1 208 PAK1-mediated phosphorylation 90 Paraxial protocadherin (PAPC) 292 Paxillin 299 301 303—304 306 309 Paxillin adhesions 303 PDGF 193 PDGF-dependent activation of tyrosine kinase 120 PDZ 27 pECFP-C1 128 pEYFP-C1 128 PH domain 111 167—168 190 198 PH domain localization, mechanisms controlling 263—265 PH domain translocation kinetics 268 PH domain translocation to leading edge 271 Phagocytosis 170 Phalloidin 9 phg1 23—24 Phosphatidic acid (PA) 170 Phosphatidylinositol (4)-phosphate 5-kinase (PIP 5K) 170 Phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bis-phosphate ( 125 136 170 Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase see “PI3K” Phosphoinositide (PI) lipids 190 Phosphoinositide 3-kinase see “PI3K” Phosphoinositide 3’-phosphatase see “PTEN” Phosphoinositides (D3-PI) 261 Phospholipase D (PLD) 170—171 Phospholipase P (PLC) 181 238 Photoactivation of fluorescence (PAF) 127 PI3K 31 111 167 179—180 182 185 261 263 PI3K in chemotaxis 263—265 PI3K, activation 168 PI3K, translocates upon stimulation with chemoattractant 265—267 PI3K, translocation kinetics 268 PI3K1, constitutive localization 266 PIP5K 171 PIP5KI 190 PIR121 141 158—159 251 PIX 303 309 pKa 225 Plasma membranes 103 183 193 300 Pleckstrin homology see “PH” Podosomes, formation of 159—160 Polymerization-depolymerization transition 207 Polyphosphoinositides 136 Polysialic acid chains (PSA) 310—311 Postsynaptic density (PSD) 197 Pre-bleach images, FLAP 130 Pro 45 Profilin 1 3—4 40 Proline-arginine-rich domain (PRD) 47 50 190 192 195 198 Protein dynamics 117-134 Protein kinase 122 Protein kinase P (PKC) 185 222—223 Protocadherins 292 Protrusion 300 Pseudopod formation 170 PTEN 180 261 264 271 PTEN as negative regulator of D3-PI signalling pathway in chemotaxis 267—269 PTEN, translocation kinetics 268 PTEN-GFP 269 PtK1 206 210—212 RAc 65—67 154 241 310 Rac GTPase 120 Rac-mediated Rho activation 67 Rac1 107 112 203 205 208—209 Rac1, localization and activity 108 Rac1, microtubule dynamic instability downstream of 210—213 Rac1, mutant expression effects on endogenous Rac1 complexes and cell behaviour 108 Rac1-containing lamellipodia drive cell-cell contact formation between MDCK cells 107 Rac1-driven process 106 Rac1:PAK effector complex 108 Rac1G12V 110 Rac1Q61L 110 Rac1T17N 110 RacGFP localization 107 RacGFP localization, changes in 108 RacGFP, accumulation of 107 Racl complexes 111 Racl complexes and cell-cell contact 108 Racl complexes in MDCK cells during cell-cell adhesion 109 Racl complexes, linking back to mechanisms of cell cell adhesion 111—112 RacT17NGFP in MDCK cells 109 Radial intercalation 284 Receptor tyrosine kinases 7 Receptor-mediated endocytic (RME) machinery 194 Restriction enzyme mediated insertion (REMI) mutagenesis 44 Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) 63 71 Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), axons 63 67 Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), ephrin-induced growth cone collapse in 67 Retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), growth cones 61 63 69—70 Retrograde-flow-induced breakage 208 Rho 65 75 83 Rho activation, Rac-mediated 67 Rho associated kinase (ROCK) 67 69 71 75 83 87 92 Rho GTPases 12 40 61 76 78 120 203—217 248 257 Rho GTPases as molecular switches 204 Rho GTPases in cell-cell adhesion 106—107 Rho GTPases, activation 106 Rho GTPases, role in ephrin induced growth cone collapse 67—71 Rho-binding domain (RBD) 84 Rho-family members 170 Rho-Rho kinase pathway 68 Rho/Rac/Cdc42 family 41 RhoA 154 203 209 RhoA, microtubule stabilization downstream of 209—210 Robo 7 Rostral migratory stream (RMS) 299 309 Rostral migratory stream (RMS), cell migration of neuronal precursors in 310—311 Rostral migratory stream (RMS), neuronal precursors in 312 Saccharomyces 250 Saccharomyces cerevisiae 40 44 50 137 167 255 SadA 24 Scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy 290 Scanning electron micrography 290 Scar 8 249—260 Scar, regulation of 250—251 Scar/WAVE 140 Scar1 139 254 Scar1, discovery of 253 Scar1/WAVE1 141 SCAR1—3 138 Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor (SF/HGF) 324 Schizosaccharomyces pombe 44 50 137 Schwann cell precursors 321 Sec7 domains 167 Semaphorin3A 67 SF/HGF 324—327 SH3 45 49 192 Shigella 156 Shigella flexneri 235 239 SHP2 325 Signalling pathways 6—8 71 185 255 267—269 Single cell imaging 121 Slice technology 313 Slit 7 Soluble ephrin 70 Soluble ephrin, Eph receptor activation by 65 Soluble ephrin-A5 71 Somitic migration 310 SOP2Hs 137 Sox10 321 Spatio-temporal signalling relationships 121 SRC 64 222—223 Src homology 3 (SH3) 190 Subcellular targeting of GPCR downstream effectors during chemotaxis 261—275 Subventricular zone (SVZ) 310 sumo 270—271 SUMOylation 270—271 Supervillin 236 238 Surface receptors 19 Swiss 3T3 cells 65 Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts 61 70 125 T cells 207 Tail homology (TH) domains 44 TalA 25 28—29 Talin, link with M7 28—30 Talin, role in adhesion 19—37 TalinA 24—26 TalinB 25—26 Taricha torosus 279 TEDS 40 42 50 52 Tfn-R 168 TH1 42 44—45 48 TH2 42 45 48
Реклама
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



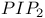 )
) 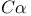 (
(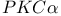 )
)