јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Ridley A., Clark P., Peckham M. Ч Cell motility: from molecules to organisms
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Cell motility: from molecules to organismsјвторы: Ridley A., Clark P., Peckham M.јннотаци€: Recent advances in molecular and biophysical techniques, particularly fluorescence and live cell imaging, are revolutionizing the study of cell motility. New bioprobes not only reveal simple intracellular localization, but also contain details of post-translational modifications, conformational state and protein-protein interactions. Coupling these insights with complementary advances in genetic and biochemical methods is enabling scientists to understand the processes involved in cell motility - from molecular motors to cell movements in vivo in a range of organisms and cell types.
язык: –убрика: Ѕиологи€ /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 2004 оличество страниц: 342ƒобавлена в каталог: 10.12.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
9 170 122 125 322 194Ч195 25 9Ч10 30 111 157 171 183 194Ч195 225 238 249Ч250 30 180 182 185 122 305 308 306Ч307 304 307 3 301 303Ч304 192 104 104 82 104 112 104 9 22 222Ч223 A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) 249 Aardvark 21 Abi2 141 AbLIM 238 Abp1 193 255 Acan125 51 Acanthamoeba 44 48 52 Acanthamoeba castellanii 137 ActA 143 Actin 1Ч2 4 УG-actinФ) Actin cytoskeleton 71 75Ч99 Actin disassembly 241 Actin dynamics 39Ч59 130 Actin dynamics and class I myosins 49Ч52 Actin dynamics in Dictyostelium 252Ч253 Actin dynamics, actors 240Ч241 Actin dynamics, background on 240Ч241 Actin dynamics, controlled by actin-binding proteins 243 Actin dynamics, summary of process 40 Actin dynamics, villin as regulator of 240Ч242 Actin dynamics, villin enhancement during cell motility 241Ч242 Actin filament network, branched 10 actin filaments 5Ч6 8 184 236 300 Actin filaments in lamella 11 Actin filaments, ageing, remodelling and disassembly 10Ч12 Actin filaments, assembly 135Ч151 Actin filaments, polymerization 204 Actin microfilaments 76 Actin microfilaments, role of villin in dynamics of 235Ч245 Actin molecule 131 Actin monomers 136Ч138 241 Actin nucleation 51 Actin nucleation and elongation model 41 Actin nucleation, Arp2/3 complex-independent 143Ч144 Actin organization 243 Actin polymerization 140 247 251 Actin polymerization and actin structures 256Ч257 Actin polymerization and depolymerization 248 Actin polymerization as initial asymmetry generating event 180Ч182 Actin polymerization transients, early and late mechanisms 182Ч184 Actin polymerization, coupling signalling pathways to Arp2/3 dependent 255 Actin polymerization, de novo 137 Actin polymerization, EGF receptor-associated 181Ч182 Actin polymerization, WASp/WAVE-Arp2/3 complex-mediated 153 Actin remodelling 239 Actin reorganization in fibroblasts 66 Actin stress fibres 66Ч67 Actin structures and actin polymerization 256Ч257 Actin structures, disassembly of 64 Actin, assembly of filamentous structures in fibroblast cells 65 Actin, control by Rho GTPases in migrating cells 204Ч205 Actin, filament dynamics 1Ч17 Actin, X-rhodamine-labelled 126 Actin-associated proteins 82 Actin-based membrane dynamics, participation of dynamin in 193Ч194 Actin-bundling proteins 236 Actin-related protein 1 (Arp1) 89 Adenomatous polyposis coli protein (APC) 212 Adenylyl cyclase 20 ADF/cofilin 1 3Ч4 9 11Ч12 240Ч242 Adherent cells 81 Adhesion components, trafficking in complexes 309 Adhesion disassembly 301 304Ч306 Adhesion dynamics 301Ч304 Adhesion formation 227 301Ч303 Adhesion formation, disassembly and turnover, working model of 306 Adhesion molecules, intracellular trafficking of 306Ч309 Adhesion receptors for vegetative cells 23 Adhesion receptors in Dictyostelium 22Ч24 Adhesion turnover 303Ч304 Adhesion, calcium-dependent 22 Adhesion, molecules involved 22 Adhesion, role of talin and myosin VII 19Ч37 Adhesions, 22 ADP-actin subunits, recycling 12 ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) 165Ч172 Adseverin 236 Advillin 236 238 Aequorea victoria 117 Aluminium fluoride (A1F) 169 Ambystoma maculatum 279 Ambystoma mexicanum 279 Amino acids 237Ч238 Amoeboid chemotaxis 175 262Ч263 AMPA 21 Amphiphysin 192 APC 88 Apical membrane 102 ARF1 165Ч168 ARF3 165Ч166 ARF5 165Ч166 ARF6, events downstream of activation 170Ч171 ARF6, function in polarized membrane delivery at plasma membrane 168 ARF6, intracellular localization 166 ARF6, regulation of activation 167Ч168 ARF6Q67L 169 ARF6T27N 166 168 Arg(GPR) 45 ARIA (Acetylcholine Receptor Inducing Activity) 319 ARNO 167 ARNO-GEF activity 167 Arp2 77 Arp2/3 complex 1Ч5 41 50Ч53 85 112 135 137Ч138 140Ч142 183 205 241 247Ч260 Arp2/3 complex activation 8Ч9 155Ч159 Arp2/3 complex in de novo actin nucleation 248 Arp2/3 complex regulation in Dictyostelium 253 Arp2/3 complex, nucleation-promoting factors 7 Arp2/3 complex, WASp family in activation of 255Ч256 Arp2/3 complex-dependent actin polymerization, coupling signalling pathways 255 Arp2/3 complex-independent actin nucleation 143Ч144 Arp3 77 ARPC1 5 137 ARPC2 5 ARPC3 5 ARPC4 5 ARPC5 5 Aspergillus 44 49Ч50 84 Assembly-disassembly dynamics 76 ATP hydrolysis 11 ATP-actin 12 ATP-actin, subunits 11 ATP-G actin 40Ч41 ATP-sensitive plus end cap 209 Axial protocadherin (AXPC) 292 Axon guidance, Eph receptor/ephrin regulation of 62-63 Axon pathfinding 62Ч64 Axonal retraction 71 B-FABP 322 Bacterial motility 2 Barbed ends 135Ч151 Barbed ends, uncapping 240 Basal-lateral membrane 102 BDM 82 Bi-directional signalling 62Ч63 Bioprobe techniques 117Ч134 Bipolar protrusive activity 293 Bipolar traction 286Ч287 Bipolarity, special function of 293 Bleaching 129 Body axis formation 277 Brush border architecture 236 C-cadherin 291 c-ErbB 317 c-Met 317 324Ч327 c-Ret 322Ч323 C-terminal acidic domain 52 Cadherin superfamily 103 Cadherin-6 322 Cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion in MDCK cells 107 Cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion 221 Cadherin/catenin complex 103Ч104 Cadherins molecular interactions and functions 103Ч104 Cadherins subcellular distribution 104 Caenorhabditis elegans 52 84 137 196 251 Calcium transients in adhesive release 226 Calcium-dependent adhesion 22 Caldesmon 81Ч82 Calpain activation in migrating cell 230 Calpain activity and cell migration speed 228 Calpain effect on rear detachment 227 Calpain effects of external factors 224 Calpain in adhesion formation and direction migration 227Ч230 Calpain in regulating neutrophil chemotaxis 229 Calpain inhibitors 226 Calpain isoforms 222 Calpain regulation of cell migration 219Ч233 Calpain, overview 222Ч225 Calpain, role in cell detachment and focal adhesion 225Ч227 Calpain-calpastatin system 222 225 Calpastatin 225 cAMP 263 268 Cancer cells, chemotaxis during invasion and metastasis 175Ч188 Candida albicans 50 CapG 236 Capping protein 1 3 10 Capping rate 10 CapZ family 241-242 cAR1 20 Carcinoma cells, chemotactic to EGF 179 Carcinoma cells, chemotactic to EGF in vitro 178 Carcinoma cells, interaction with blood vessels 176 Carcinoma cells, motility cycle in response to EGF 181 CARMIL 51Ч53 253Ч254 CD44 hyaluronan receptor 122 Cdc42 9 65 67 107 112 154 208Ч209 228 249 252 282 Cdc42-activated N-WASp 142 Cdc42-GTP 84 Cdc42-WASp-Arp2/3 pathway 112 Cdc42H 203 Cell detachment 225Ч227 Cell intercalation 289 Cell intercalation and extracellular matrix 292Ч293 Cell intercalation by cell-on-cell traction model 289 Cell intercalation, migration on one another 287Ч289 Cell migration during mouse development 317Ч330 Cell migration in vitro and in vivo 299Ч315 Cell migration in vivo 309-311 Cell migration to cell-cell adhesion 101Ч116 Cell migration, basic steps 220 Cell migration, calpain regulation of 219Ч233 Cell migration, classic three-step 220 Cell migration, contact-mediated inhibition 221 Cell migration, external factors regulating 220Ч221 Cell migration, molecular basis 300 Cell migration, neuronal precursors in rostral migratory stream (RMS) 310Ч311 Cell migration, overview 300Ч301 Cell migration, regulation of 203Ч217 Cell migration, speed and calpain activity 228 Cell migration-inhibiting cues 221 Cell motility regulation, general model for 76 Cell motility, leading edges 1 Cell segregation, Eph receptor/ephrin mediated control of 63Ч64 Cell spreading 227 Cell-cell adhesion 19 170 221 Cell-cell adhesion in convergent extension 291Ч292 Cell-cell adhesion junctions 103 Cell-cell adhesion, cell migration to 101Ч116 Cell-cell adhesion, E-cadherin distribution during 104Ч106 Cell-cell adhesion, epithelial complexes 102Ч103 Cell-cell adhesion, initiation 103 Cell-cell adhesion, mechanics of 102 Cell-cell adhesion, membrane dynamics in 106Ч107 Cell-cell adhesion, Racl complexes in MDCK cells during 109 Cell-cell adhesion, Rho family small GTPases in 106Ч107 Cell-cell adhesion, role of 101 Cell-cell contact 19 61 69 Cell-cell contact and Rac1 complexes 108 Cell-cell contacts, concerted formation 107 Cell-cell interactions 102 Cell-cell repulsion 64 Cell-matrix adhesions, in convergent extension 291Ч292 Cell-matrix adhesions, in crawling cell locomotion 78Ч81 Cell-surface contact 19 Centractin 89 Centrosome 87 Centrosome reorientation downstream of 207Ч209 Centrosome reorientation downstream of Cdc42 207Ч209 CFP 128Ч129 131 CFP-actin 128Ч130 Chemoattractant gradient 153Ч154 229 Chemoattractants, reaction to 12 Chemoattractants, reaction to withdrawal 12Ч13 Chemotaxis 153 262 Chemotaxis of amoeboid cells 262Ч263 Chemotaxis of carcinoma cells 175Ч188 Chemotaxis, events defining leading edge during 179 Chemotaxis, GPCR downstream effectors during 261Ч275 Chemotaxis, PI3K in 263Ч265 Chemotaxis, PTEN as negative regulator of D3-PI signalling pathway in 267Ч269 Chemotaxis, regulated by MEK kinase signalling 269Ч271 Chemotaxis, to EGF 175Ч179 Chick RGC growth cone collapse 68 CHOK1 cells 222 229 CLASPs 88 213 Clathrin-coated pits (CCPs) 193Ч191 Clathrin-dependent pathway 169 Clathrin-dsRed 123 125 CLIP-170 88 90 213 CLIP-170 associated proteins (CLASPs) 88 213 ClustalW sequence alignment 266 Cofilin 136 182 184 Complex A 109Ч111 Complex B 108Ч111 Complex C 108Ч111 Confocal microscopy 9 Contact site A (csA) 23 Convergence 277Ч297 Convergence in sandwich explants 287 Convergence, active, force-producing 285 Convergence, definition 289 Convergence, diversity and complexity of 283Ч286 Convergence, teleost germ ring 288 Convergent extension 283 Convergent extension, cell-cell adhesion in 291Ч292 Convergent extension, cell-matrix adhesion in 291Ч292 Cortactin 159Ч160 Cortactin, interaction with dynamin 192Ч193
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



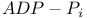
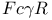 -mediated phagocytosis
-mediated phagocytosis 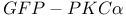 activity
activity 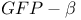 -actin
-actin 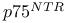
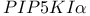
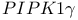
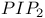
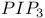
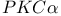
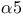 -integrin
-integrin  -actinin
-actinin 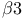 -integrin dynamics
-integrin dynamics  -Catenin
-Catenin 
 -dependent adhesion
-dependent adhesion  -calpain (calpain I)
-calpain (calpain I)