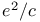|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Taketani M. Ч The formation and logic of quantum mechanics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
 -factor, anomaly in s-terms of II183 189 191 -factor, anomaly in s-terms of II183 189 191
 -factor, introduciton by Lande of II182 -factor, introduciton by Lande of II182
 -factor, of multiplet terms II188 -factor, of multiplet terms II188
 -factor, problem of the relativistic correction of II213 -factor, problem of the relativistic correction of II213
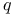 -algebraic treatment of angular momentum III53 -algebraic treatment of angular momentum III53
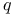 -algebraic treatment of equation of electron orbit III50 -algebraic treatment of equation of electron orbit III50
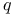 -number, DiracТs III47 -number, DiracТs III47
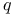 -number, matrix element and representation of III50 -number, matrix element and representation of III50
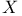 -ray doublet terms, regular and irregular II205 -ray doublet terms, regular and irregular II205
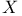 -ray doublet terms, screening and relativistic II205 -ray doublet terms, screening and relativistic II205
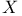 -ray doublet terms, similarity to optical doublet terms of II209 -ray doublet terms, similarity to optical doublet terms of II209
 -rays, detection of large-angle scattering of 203 -rays, detection of large-angle scattering of 203
Abraham angular momentum carried away by radiation II159
Abraham magnetic moment of rotating spherical electron II220
Adams II81
Adiabatic hypothesis, and correspondence principle II166
Adiabatic hypothesis, as generalization of WienТs displacement law II165
Adiabatic hypothesis, EhrenfestТs II165
Adiabatic invariant, indication of existence of II165
Allen II221
Andrade see Rutherford-
Andrade e Silva see de Broglie-
Angular momentum, 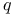 -algebraic, treatment of III53 -algebraic, treatment of III53
Angular momentum, BohrТs assumption of constancy of II93
Angular momentum, carried away by radiation II159
Angular momentum, conservation law and selection rules of II158
Angular momentum, indication of quantum nature of (Nicholson) II77
Angular momentum, of atomic body II184 187
Angular momentum, properties in matrix mechanics of III29
Angular momentum, quantum nature in Bohr model of II92
Angular momentum, relativistic limit of (Sommerfeld) II126
Anomalous Zeeman effect and half-integer quantum number II182
Anomalous Zeeman effect and RungeТs rule II181
Anomalous Zeeman effect and Stern Ч GerlachТs experiment II195
Anomalous Zeeman effect, systematization by Back of II182
Anomalous Zeeman effect, treatment by matrix mechanics of III31
Anomaly of  -factor of -factor of 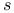 -terms and magneto-mechanical anomaly II1783 190 191 -terms and magneto-mechanical anomaly II1783 190 191
Anomaly of  -factor of -factor of 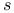 -terms and magneto-optical anomaly II189 -terms and magneto-optical anomaly II189
Anticommutation relation for de Broglie waves obeying F Ч D statistics (Jordan Ч Wigner) III225
Aperiodic motion, attempt at application of matrix mechanics to III61 125
Aperiodic motion, difficulty in applying quantum condition to II195
Aperiodic motion, generalization of matrix mechanics to III174
Arrhenius 097
Arvidsson II191
Avogadro number, ThomsonТs determination (by method of electrolysis) of 0112
Azimuthal quantum number, SommerfeldТs introduction of II123
Azimuthal quantum number, two kinds of (Bohr Ч Coster) II206
Back see Pascen-
Back systematization of anomalous Zeeman effect II182
Balmer formula, derivation using Bohr model of II88
Balmer formula, DiracТs discussion based on 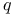 -algebra of III52 -algebra of III52
Balmer formula, IshiwaraТs derivation of a formula similar to II113
Balmer formula, PauliТs matrix mechanical derivation of III37
Balmer formula, Schr dingerТs wave mechanical derivation of III76 dingerТs wave mechanical derivation of III76
Balmer formula, SommerfeldТs derivation from the quantum condition of II118
Balmer presentation of spectral formula 063
Barkla determination of number of centers of X-ray scattering in atoms 0183
Barkla study of secondary X-rays 0180 183
Barnet II191
Bates see Sucksmith-
Beck II191
BKS theory see Bohr Ч Kramers Ч Slater
Black body radiation KirchhoffТs concept and law of 05
Bohr assumption of constancy of angular momentum II93
Bohr assumption of quantum numbers invariance II218
Bohr configuration of inner-atomic electrons II98 202
Bohr determination of number of electron in hydrogen atom 0229
Bohr doubt on energy-momentum conservation II263
Bohr doubt on half-integral quantum numbers II208
Bohr frequency condition II87 151 III20
Bohr germ of correspondence principle II92
Bohr inference of frequency of inner-atomic electrons II81
Bohr interpretation of Franck Ч HertzТs experiment II102
Bohr model and quantum nature of angular momentum II93
Bohr model and radius of hydrogen atom II84
Bohr model and structures of atom and molecule II94
Bohr model and the spectral formula II88
Bohr model, basic assumptions of II86
Bohr model, confirmation by Mosely of II99
Bohr nonmechanical compulsion to lighting electrons II209 216 III103
Bohr presentation of Bohr model of atom II82
Bohr presentation of correspondence principle II163
Bohr reply to EPRТs question III282
Bohr support for negation of causality III248
Bohr treatment of Stark and Zeeman effects by a pre-correspondence-principle II143
Bohr use of the term Уcomplementarity III248 249
Bohr Ч Coster introduction of two kinds of azimuthal quantum numbers II206
Bohr Ч Kramers Ч Slater idea of virtual oscillation II267 275
Bohr Ч Kramers Ч Slater theory of statistical conservation of energy-momentum II266
Boltzmann see Stefan-
Born approximation, WentzelТs application to Rutherford scattering III198
Born dispersion formula II277
Born introduction of concept of probability into wave mechanics III129 152
Born reversibility of transition probability III165
Born transition probability (of absorption and induced emission) III164
Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan, introduction of canonical transformation III27
Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan, matrix mechanics of a string III35
Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan, matrix mechanics of a system of multi-degrees of freedom III26
Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan, matrix mechanics of angular momentum III29
Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan, perturbation method in matrix mechanics III28
Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan, relative intensity in Zeeman effect III30
Born Ч Jordan, attempt to treat the electro-magnetic equations by matrix mechanics III33
Born Ч Jordan, equation of motion in matrix mechanics III26
Born Ч Jordan, intensified quantum condition III23
Born Ч Jordan, matrix mechanics of systems of one degree of freedom III19
Born Ч Jordan, matrixization of canonical equations of motion III21
Born Ч JordanТs quantum condition and the commutation relation III22
Born Ч K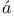 rm rm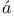 n theory of specific heats of solids 1124 n theory of specific heats of solids 1124
Born Ч Wiener attempt at applying matrix mechanics to aperiodic moeiton III61 189
Born, The Born approximation (of scattering probability) III135
Bose statistical mechanics of gas of light quanta II253
Bose Ч Einstein statistics II258 III152
Bothe Ч Geiger experiment nagating the BKS theory II269
Boundary between an object and apparatus of observation III261 274 275
Bowen see Millikan-
Brackett spectral series of 164
Breit idea of virtual orbit II275
Brillouin, L., WKB approximation of wave equation III92
Brillouin, M., inner-atomic elastic waves and quantum condition II244
Burgers II166
Busch angular momentum carried away by radiation II159
Campbell II199
Canonical transformation and wave mechanics (London) III167
Canonical transformation in matrix mechanics III27
Canonical transformation, DiracТs transformation theory based on III175
Catal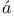 n II186 n II186
Catalog of expectation, wave function as (Schrodinger) III269
Clark Ч Duane anomalous scattering of X-rays II239
Combination rule of amplitudes (classical) III10
Combination rule of amplitudes (quantum-theoretical) III10 20
Combination rule of frequency (classical) III8
Combination rule of frequency (quantum-theoretical) III8 20
Combination rule of spectral lines (Ritz) 1163
Commutation relation and anticommutation relation III225
Commutation relation and Born Ч JordanТs intensified quantum condition III23
Commutation relation and DiracТs Poisson bracket equation III47
Commutation relation and HeisenbergТs quantum-theoretical quantum condition III23
Commutation relation and the uncertainty relation III241
Commutation relation of angular momenta III29
Complementarity in BohrТs wording III247 249
Complementarity, TaketaniТs critique of III252
Complexion number and com-bination with repetition II257
Complexion number and the derivation by Debye of the Planck formula 1118
Complexion number, PlanckТs 128 1114
Compton effect, DiracТs Aplication of matrix mechanics to III203
Compton effect, GordonТs application of wave mechanics to III203
Compton effect, interpretation according to the BKS theory of II268
Compton effect, Klein Ч NishninaТs application of DiracТs electron wave equation to III232
Compton effect, TammТs application of quantum field theory to III233
Compton Ч Simon experiment negating the BKS theory II270
| Compton, light quanta and reflection and diffraction of X-rays II242
Compton, scattering of X-rays and size of electron II235
Compton, spin and the magneto-mechanical anomaly II221
Compton, theory and experiment of Compton effect II236
Condon, commutation relation and the uncertainty relation III241
Conflict between field and matter Indication by Taketani of II225 III235
Conjugate configuration about a closed shell II217
Conservation law of energy-momentum, doubts by Bohr of II263
Conservation law of energy-momentum, statistical II256
Continuity equation of charge density (Schrodinger) III123
Continuity equation of four-current density (Klein, Gordon) III203
Contradiction in radiation theory Indication by Einstein of 149 117
Copenhagen spirit, cause of vagueness of III274
Copenhagen spirit, in interpretation of quantum mechanics III252
Corpuscle, name of electron (Thomson) 1115
Corpuscle, ThomsonТs model of atoms without nucleus by means of 1106 128 140
Correspondence principle and intensity of radiation II169
Correspondence principle and selection rule II163
Correspondence principle and the adiabatic hypothesis II166
Correspondence principle, germ of 1192
Correspondence principle, presentation by Bohr of II163
Coster screening doublet terms and Coster relativsitic doublet terms II205
Covalent bond, Heitler and LongonТs Quantum mechanical elucidation of III223
Covalent bond, Lewis and LangmuirТs phenomenological introduciton of II198
Crowther  -function DiracТs III175 -function DiracТs III175
Crowther single and multiple scatterings of  -rays 1207 219 -rays 1207 219
Darwin attempt to introduce spin of vector type III214
Darwin on Dirac electron equation and fine structure constant III232
Darwin theory of scattering and absorption of  -particles 1222 -particles 1222
Davisson Ч Kunsman II261
de Broglie prediction of diffraction of electrons II251
de Broglie supposition of small mass for light quantum II248
de Broglie virtual wave (phase wave) and the quantum condition II249
de Broglie waves theory of gases and flactuation in gases in terms of II259 III72
de Broglie Ч Andrade e Silva 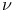 -wave and light III297 -wave and light III297
de Hass II190
Debye derivation of PlankТs distribution formula 1118 261
Debye hypothesis of elementary action and unharmonic oscillators II114
Debye theory of Compton effect II239
Debye theory of specific heats of solids 1123
Debye Ч Zeeman effect and the quantum condition II141
Dennison, determination of nuclear spin of hydrogen atom III223
Difficulty of frequency in classical oscillation models of spectral series 173
Difficulty of frequency in wave equation III78
Dirac commutation relation and Poisson bracket equation III46
Dirac difficulty in matrix mechanics for many-body systems III147
Dirac equation of motion in 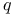 -numbers III47 -numbers III47
Dirac introduction of  -function III 175 -function III 175
Dirac introduction of transformation functions III176
Dirac matrices with continuous row and/or column III174
Dirac number representation of wave equation III209
Dirac permutation symmetry of 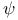 for a many-body system III148 for a many-body system III148
Dirac quantization of radiation as a system of light quanta III210
Dirac relativitization of matrix mechanics III204
Dirac relativitization of wave equation III150 154
Dirac spin-orbit interaction based on DiracТs electron equation III232
Dirac theory of positive electron III234
Dirac transformation function and BornТs scattering probability III182
Dirac transition probability of absorption and induced emission of radiation III158
Dirac treatment of Balmer formula by Dirac 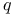 -numbers III42 -numbers III42
Dirac treatment of equation of electron orbit by 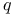 -numbers III51 -numbers III51
Dirac wave equation (time-dependent) III154 181
Dirac Ч Compton effect by matrix mechanics III204
Discussion of number of inneratoic electrons 0182 186 190 193
Dispersion formula and HeisenbergТs quantum ondition III11 14
Dispersion formula by wave mechanics (Schr dinger) III118 dinger) III118
Dispersion formula, BornТs II277
Dispersion formula, Kramers II273
Dispersion formula, Kramers Ч HeisenbergТs II282 III6
Dispersion formula, Ladenberg Ч ReicheТs II272
Displacement law of spectral series II180
Displacement law, WienТs 18 118
Distribution law of black body radiation, MichelsonТs 113 117
Distribution law, PlanckТs 125 1111
Distribution law, Rayleigh Ч JeanТs 122 1112
Distribution law, WienТs 116 118
Doubleness of the electron Indication of (Pauli) II215
Drude determination of inneratomic electrons (by method of light dispersion) 1191 1120
Dual nature of radiation, indication by Einstein of 1132
Dual nature of radiation, intermediary viewpoint of II160 241
Dual nature of radiation, solution of conflict in III206
Duane see Clark Ч Dynamiden
Duane light quantum and Bragg reflection II241
Duane number in a hydrogen atom of 0165
Duane their true radius and specific absorption power of cathode rays 1166
Duane Ч LenardТs model of atom by 0163
Ehrenfest see Epstein-
Ehrenfest adiabatic hypothesis II164
Ehrenfest adiabatic hypothesis and the quantum condition II165
Ehrenfest hypothesis of elementary action and rotational motion II115
Ehrenfest Ч Kamerlingh Onnes analysis of number of complexion II257
Einstein demand for a quantum-theoretical theory of radiation II156
Einstein derivation of PlanckТs distribution formula II150 258
Einstein fluctuation in a gas and de Broglie waves II259
Einstein fluctuation of radiation energy 1127
Einstein fluctuation of radiation pressure 1131
Einstein hypothesis of light quantum 143
Einstein indication of contradictions in theory of radiation 117
Einstein indication of dual nature of radiation II32
Einstein indication of existence of adiabatic invariants II165
Einstein introduction of transition probability II149
Einstein out-radiation, positive and negative in-radiation II149
Einstein quantum-statistical mechanics of ideal gases II255
Einstein recoil of molecule in the theory of light quantum II151
Einstein relation between the elementary action and 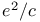 II42 II42
Einstein theory of specific heats of solids II19 22
Einstein Ч Ehrenfest difficulty in interpretation of Stern Ч GerlachТs experiment II193
Einstein Ч Podolsky Ч Rosen see EPR Electrion
Einstein Ч Podolsky Ч Rosen, KelvinТs model of atoms without nucleus using 0115
Einstein Ч Podolsky Ч Rosen, KelvinТs name for electron 1116
Electromagnetic field equations Attempt to matrixize III33
Electron configuration by Bohr II98 202
Electron configuration by Kossel II196
Electron configuration by Stoner II211
Electron configuration of rare gas atoms (Rydberg) II198
Electron configuration, conjugate II217
Electron diffraction, ElsasserТs Indication of experimental evidence for II260
Electron diffraction, prediction by de Broglie of II251
Electron specific charge, magnetomechanical anomaly of II190 213
Electron specific charge, ThomsonТs Measurement on free electrons of 01II
Electron specific charge, ZeemanТs measurement using the Zeeman effect 092
Elementary action and radius of atom of Nagaoka type 72 73
Elementary action and radius of atom of Thomson type 144
Elementary action, relation to 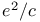 (Einstein) II42 (Einstein) II42
Elementary electric charge, equality of positive and negative elementary charges 1114
Elementary electric charge, measurement by Thomson of (by gas ionization method) 1111
Elementary electric charge, measurement by Townsend of (by ion diffusion method) 1113
Elementary electric charge, measurement by Wilson of (by falling drop method) 1113
Elester Ч Geiter 178
Elsasser indication of experimental evidence of wave nature of electron II260
Energy quantum (element) of resonator 131
Entropy of PlanckТs resonator 119 25 30 15
Entropy of the radiation obeying Wien distribution law 041
EPR see Einstein Ч Podolsky Ч Rosen EPRТs question
EPR on interpretation of quantum EPR, Einstein Ч Podolsky Ч Rosen EPRТs question, mechanics III279 282 299
EPR, BohrТs and FurryТs replies to III282 285
EPR, problem of III280 282
Epstein equality of SommerfeldТs and PlanckТs quantum conditions II140
Epstein wuantum condition and Stark effect II132
Epstein Ч Ehrenfest light quantum and X-ray diffraction II244
Equation of motion in 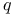 -number (Dirac) III47 -number (Dirac) III47
Equation of motion in matrix mechanics (Born Ч Jordan) III25
Equipartition law of energy and Rayleigh Ч JeanТs distribution formula 137 1112
Eucken II115
Example of cat, Schr dinger critique of v. NeumannТs theory of observation III268 dinger critique of v. NeumannТs theory of observation III268
Exclusion principle, presentation by the name of general rule II207 218
Fermat principle and Hamilton principle II240 III80
Fermi quantization of ideal gas III153
Fermi Ч Dirac statistics II260 III153
Field quantization, beginning of (Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan) III37
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 -factor, anomaly in s-terms of
-factor, anomaly in s-terms of  -algebraic treatment of angular momentum
-algebraic treatment of angular momentum 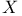 -ray doublet terms, regular and irregular
-ray doublet terms, regular and irregular  -rays, detection of large-angle scattering of
-rays, detection of large-angle scattering of 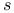 -terms and magneto-mechanical anomaly
-terms and magneto-mechanical anomaly  dingerТs wave mechanical derivation of
dingerТs wave mechanical derivation of 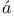 rm
rm -function DiracТs
-function DiracТs  -rays
-rays 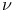 -wave and light
-wave and light 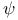 for a many-body system
for a many-body system