|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Taketani M. Ч The formation and logic of quantum mechanics |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
Field quantization, germ of (Rubinowicz, Compton) II160 243
Field quantization, of DiracТs electron field plus electro-magnetic wave (by Heisenberg Ч Pauli) III228
Field quantization, of free electromagnetic waves III227
Field quantization, of radiation as a system of light quanta (by Dirac) III210
Field quantization, of the charged de Broglie wave (by Jordan Ч Klein) III226
Field quantization, of the de Broglie waves obeying the F Ч D statistics (by Jordan) III225
Field quantization, of the de Broglie waves using anti-commutation relation (by Jordan Ч Wigner) III225
Field quantization, second quantization of de Broglie waves III208 224 225
Fine structure constant Introduction by Sommerfeld of II127
Fine structure of relativistic energy levels II127 III202 232
Fitzgerald mechanical model of spectral series 169
Floating magnets and ThomsonТs corpuscle model of atoms 1109
Floating magnets, analogous property to the periodic law 1110
Fluctuation in the ideal gas II259 III72
Fluctuation of oscillation energy of string III37
Fluctuation of radiation energy 1127
Fluctuation of radiation pressure 1130
Fock relativistic wave equation and the fine structure constant III202
Forsterling, frequency relation and theory of relativity II231
Fowler 1189
Franck Ч Hertz measurement of excitation energy of atoms II102
Frenkel derivation of spin-orbit interaction II213
Frequency condition and relativity (F rsterling) II231 rsterling) II231
Frequency condition, BohrТs 1187 151 III20
Frequency, LarmorТs 196 II142
Frequency, of de Broglie wave II248 259 III84
Frequency, of inneratomic electrons II81
Fresnel band theory, similarity to quantum condition III89
Furry support for BohrТs reply to EPRТs question III285
Geiger see Bothe Elester Rutherford Geiger
Geiger detection of large-angle scatterings of  -rays 1207 -rays 1207
Geiger measurement of scattering angle of  -rays by gold foil 1208 -rays by gold foil 1208
Ghost field, attempt to interpret wave function by III126
Giese 178
Gordon Ч Dirac electron equation and the fine structure III232
Gordon Ч Dirac electron equation, relativization of wave equation III203
Goudsmit see Uhlenbeck Ч Green
Goudsmit model of irreversible measuring apparatus III290
Group velocity of de Broglie wave II250 III71
Guiding wave in attempt to interprete wave function II252 III127
Half-integer quantum number and anomalous Zeeman effect II182 184 186 188
Half-integer quantum number, BohrТs doubts on II208
Hamilton principal function And phase of wave III84
Hamilton principle and FermatТs principle II252 III80
Hamilton Ч Jacobi partial differential equation and the wave equation at short wavelengths III83
Hass radius of an atom in Thomson model 1144
Heisenberg angular momentum of atomic body II184
Heisenberg inter-atomic resonance and permutation symmetry of wave function III143
Heisenberg negation of causality from the uncertainty relation III247
Heisenberg Qqantum-theoretical quantum condition III11 14
Heisenberg quantum-theoretical law of multiplication III10
Heisenberg state probability and matrix element of canonical transformation III172
Heisenberg symmetry of wave function and nuclear spin III221
Heisenberg symmetry of wave function and spectral terms III219
Heisenberg thought experiment on the uncertainty relation III239; see Born Kramers Sommerfeld-
Heisenberg Ч Pauli quantization of DiracТs electron field plus electromagnetic field III228
Heisenberg- Jordan matrix mechanics of anomalous Zeeman effect III31
HeisenbergТs quantum condition and dispersion relation III23
HeisenbergТs quantum condition and the commutation relation III22
Heitler Ч London quantum mechanics of covalent bond III223
Hertz energy difference in X-ray L terms II204; see Franck Hidden variables
Hertz problem on the existence of III247 273
Hilbert Ч Neumann Ч Nordheim mathematical systematization of transformation Hilbert Ч Neumann Ч Nordheim theory III190
Hori III222
Hund symmetry property of molecular wave functions III220
Hydrogen atom, BohrТs Application of the Bohr model to 1184
Hydrogen atom, BohrТs determination of number of electron in 1228
Hydrogen atom, DiracТs and GordonТs application of the Dirac electron equation to III232
Hydrogen atom, DiracТs attempt to apply 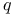 -algebra to III50 -algebra to III50
Hydrogen atom, FockТs application of the relativistic wave equation to III202
Hydrogen atom, IshiwaraТs application of the quantum condition to II113
Hydrogen atom, PauliТs application of matrix mechanism to III38
Hydrogen atom, Schr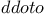 dingerТs application of wave mechanism to III74 dingerТs application of wave mechanism to III74
Hydrogen atom, SommerfeldТs application of the quantum condition to II117 125
Hypothesis of action integral SommefeldТs 1148
Hypothesis of elementary action and anharmonic oscillation III 15
Hypothesis of elementary action and rotational motion II115
Hypothesis of elementary action, PlanckТs 1147
In-radiation and absorption and induced emission of light II149
Inneratomic elastic wave And the quantum condition (Brillouin) II245
Intensified quantum condition Born Ч JordanТs (commutation relation) III24
Intensity of radiation from ring of electrons (Schott) 1197 206
Intensity of radiation of Stark effect by correspondence principle II171
Intensity of radiation of Stark effect in wave mechanics III112
Internal quantum number, introduction by Sommerfeld of II181
Internal quantum number, of half-integer (Land ) II182 ) II182
Internal quantum number, selection rule for II186
Irreversible measuring apparatus GreenТs model of III290
Irreversible process in measuring apparatus III275 289
Ishino II235
Ishiwara derivation of Balmer-like formula II113
Ishiwara quantum condition of II111
Jammer II88 101 157
Jeans attempt to defend classical radiation theory II14; see Rayleigh
Jordan irreversible process and observation apparatus III289
Jordan quantization of de Broglie waves obeying FD statistics III225
Jordan speciality of spin angular momentum III218
Jordan transformation theory by means of probability amplitudes III184; see Born Heisenberg-
Jordan Ч Klein quantization of charged de Broglie waves III226
Jordan Ч Pauli quantization of free magnetic waves III227
Jordan Ч Wigner quantization of de Brogie waves using anticommutation relation III225
K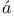 rm rm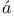 n see Born- n see Born-
Kamerlingh Onnes see Ehrenfest Kelvin
Kamerlingh Onnes, Ether vortex model of atoms 175 76
Kamerlingh Onnes, mechanical model of spectral series 169
Kamerlingh Onnes, model of atoms without nucleus interms of electrions 1117
Kelvin model and property of matter 1124
Kelvin model, characteristics of 1127
Kelvin model, stability of 1122
Kennard commutation relation and uncertainty relation III241
Kirchhoff law of black body radiation 15
Kiuti III91
Klein relativitization of wave equation III202; see Jordan-
Klein Ч Nishina calculation of compton effect by DiracТs electron wave equation III232
Kopenhagen spirit see Copenhagen spirit
Kossel analysis of characteristic X-rays II130
Kossel electron configuration of atoms II196; see Sommerfeld-
Kramers calculation of intensity of Start effect using correspondence principle II171
Kramers dispersion formula and induced radiation II273
Kramers WKB approximation of wave equation III92; see Bohr-
Kramers Ч Heisenberg generalization of dispersion formula II282
Kuhn sum rule III13
Kunsman see Davisson-
Kurlbaum see Rubens-
Ladenberg Ч Reiche dispersion formula and transition probability II272
Lamor discussion on stability of atoms 199
Lamor general theory of Zeeman effect based on electron theory 195
Lamor precession and antimagnetism 1137
Lamor precession in the Zeeman effect 195
Lamor radiation theory in terms of electron motion 198
Lanczos attempt to formulate matrix mechanics by integral equation III57 174 189
LanczosТs integral equation and the wave equation III61
LanczosТs unit integration kernel and  -function III60 174 -function III60 174
Land anomalous anomalous  -factor of s terms and the magneto-mechanical anomaly II183 -factor of s terms and the magneto-mechanical anomaly II183
Land anomalous anomalous  -factor of s terms, -factor of s terms,  -factor of multiplet terms II187 -factor of multiplet terms II187
Land anomalous anomalous  -factor of s terms, half-integer quantum number and Land -factor of s terms, half-integer quantum number and Land anomalous anomalous  -factor of s terms, -factor of s terms,  -factor II182 -factor II182
Land anomalous anomalous  -factor of s terms, similarity of X-ray and optical doublet terms II209 -factor of s terms, similarity of X-ray and optical doublet terms II209
Langevin Lamor precession and antimagnetism 1137
Langmuir improvement of LewisТs octet theory II198
Langmuir value of chemical combination heat of hydrogen molecule 1199
Larmor frequency of Zeeman effect 195 II142
Laser beams, NagasakiТs analysis of interference of III298
Lenard cathode rays and Larmor ray 11II
Lenard measurement of absorptive power for cathode rays 1164
Lenard model of atoms in terms of Dynamiden 1163
Lenard quantitative study of photoelectric effect 134 46
Lewis octet theory of electron configuration II197
Light quantum and anomalous and normal scatterings of light (Smekal) II279
Light quantum and Compton effect II236
Light quantum and Doppler effect (Schr dinger) II233 dinger) II233
| Light quantum and photoelectric effect (Einstein) 144
Light quantum and recoil of atom (Einstein) II151
Light quantum and reflection and diffraction of X-rays (Duane, Compton) II223 241 2442
Light quantum and Stokes law (Einstein) 143
Light quantum de BroglieТs assumption of a minute least mass for light quantum II248
Limit of observation, difference with the limit of cognition of III272 274
Lindemarn Ч Nernst 1122
Lodge confirmation of Zeeman effect 194
Lodge Eether montistic theory of atoms 176
London indication of wave function as state quantity in Hilbert space III169
London wave equation and canonical transformation III166; see Heitler-
LorentzТs paradoxes of 1134
LorentzТs paradoxes of Bose statistical mechanics for II255 258
LorentzТs paradoxes of EinsteinТs presentation of the hypothesis of 143
LorentzТs paradoxes of quantization of radiation as aggregate of III206
Lummer Ч Pringsheim 123 32
Lyman spectral series 164
Machismic viewpoint, critique by Schr dinger of III1II dinger of III1II
Magneto-mechanical anomaly and electron spin II222
Magneto-mechanical anomaly of electron specific charge II190 214
Magneto-optical anomaly of  -factor of -factor of 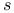 -terms II191 -terms II191
Magyar Ч Mandel III296
Mandel see Magyar- Pfleegor-
Mardenberg 1121
Margenau, necessary condition of measurement III289
Marsden see Geiger Ч Matrix element
Marsden and representation of  -number III50 -number III50
Marsden representation by wave function of III95 119
Matrix mechanics and angular momenta III29
Matrix mechanics and anomalous Zeeman effect III31
Matrix mechanics and Stark and Zeeman effects III42
Matrix mechanics, application to vibration of string III35
Matrix mechanics, Born Ч WienerТs attempt at application to aperiodic motion of III61 129
Matrix mechanics, difficulty in the case of many body of III140 147
Matrix mechanics, diracТs generalization to aperiodic motion of III 173
Matrix mechanics, Lanczos attempt at treatment in terms of integral equation of III57
Matrix mechanics, mathematical equivalence to wave mechanics of (Schr dinger) III97 101 dinger) III97 101
Matrix mechanics, of many-body systems (Born Ч Heisenberg Ч Jordan) III26
Matrix mechanics, of systems of one degree of freedom (Born Ч Jordan) III19
Matrix mechanics, PauliТs application to hydrogen atoms of III38
Matrix mechanics, relativization of (Dirac) III203
Mayer floating magnets 1108
Mehra Ч Rechenberg 1188 206
Michelson confirmation of Zeeman effect 094
MichesonТs distribution formula, improvement by Wien of 014 II8
Millikan Ч Bowen critique of Bohr Ч CosterТs theory II210
Millikan Ч Bowen critique of Bohr Ч CosterТs theory, similarity of X-ray and optical doublet terms II209
Mixture as statistical agggregate (v. Neumann) III260
Model of atom BohrТs II82
Model of atom BohrТs, final determination of the models of atom with and without nucleus 0207 221
Model of atom BohrТs, KelvinТs ether voltex 075 76
Model of atom BohrТs, with nucleus by Nagaoka 0169
Model of atom BohrТs, without nucleus by Thomson 0106 129 140
Model of atom BohrТs, without nucleus in terms of electrions by Kelvin 0117
Molecular-theoretical derivation of 013 II7
Moseley verification of the Bohr model II99
Multiple scattering and  -ray scattering (Crowther) 0207 218 -ray scattering (Crowther) 0207 218
Multiple scattering, ThomsonТs theory of 0207 218
Multiplet lines SommerfeldТs displacement law of II180
Nagaoka model and ideal atoms 0181
Nagaoka model and intensity of spectral lines 0197 206
Nagaoka model and line- and band-spectra 0169 177
Nagaoka model and radioactivity 0165 175
Nagaoka model, problem of stability of 0180
Nagaoka model, quantity of central charge in 0171
Nagaoka model, quantity of central mass in 0181
Nagaoka presentation of model of atom with nucleus 0169
Nagaoka reply to SchottТs scritique 0180
Nagasaki analysis of interference of two laser beams III298
Natural radiation PlanckТs II10
Negation by Pauli of II216
Negation of causality, BohrТs support for III249
Negation of causality, on the basis of uncertainty relation (Heisenberg) III247
Nernst see Lindemann Nicholson
Nernst indication of quantum nature of angular momentum II77
Nernst radius of an atom of the Nagaoka type II72 73
Nernst theory of corona spectra II67
Nishina see Klein-
Nonmechanical compulsion to lighting electrons (Bohr) II209 216 III103
Nordheim see Hilbert Ч Nuclear spin
Nordheim and symmetry of wave function (Heisenberg) III221
Nordheim, DennisonТs experimental value for hydrogen atom of III222
Number of electrons DrudeТs determination about atoms of 1191
Number of electrons, determination about hydrogen atom of (Bohr) 0229 II80
Number of electrons, investigation about atoms of (Thomson) 0182 193
Number representation of the wave equation (Dirac) III209
Objective interaction as origin of statistical nature of quantum mechanics III271
Observation apparatus, boundary between object of observation and III261 274 275 312
Observation apparatus, conditions for v. Neumann type of III263 287 292
Observation apparatus, GreenТs model of III290
Observation apparatus, of the so-called negative experiment type III293
Observation apparatus, PauliТs model of III277
Observation in quantum mechanics Necessary condition for III276 288
Observation theory on the basis of principle of psycho-physical parallelism (v. Neumann) III261
Octet theory about electron configurations by Lewis II197
Octet theory, improvement by Langmuir of II198
Ortho-helium II201
Out-radiation similarity to radioactivity II149
Par-helium II201
Paschen II183 218 222;
Pauli conjugate configuration of electrons and reciprocal theorem II217
Pauli indication of the doubleness of electron II215
Pauli introduction of spin wave function III216
Pauli matrix mechanics of hydrogen atom III38
Pauli matrix mechanics of Stark and Zeeman effects III42
Pauli model of measuring apparatus III277
Pauli negation of BohrТs idea of nonmechanical compulsion II216
Perihelion of relativistic electron orbit II125
Person magnetic force between self-rotating electrons II220
Perturbational method in matrix mechanics III28
Perturbational method in wave mechanics (time-dependent) III158 163
Perturbational method in wave mechanics (time-independent) III107
Pfieegor Ч Mandel III296
Pfund spectral series 063
Phase of wave and HamiltonТs principal function III84
Phase velocity of the de Broglie wave II250 III70
Phase wave (virtual wave) de BroglieТs II250 III85
Photoelectric effect and Stokes law 043
Photoelectric effect and the hypothesis of light quantum 44
Photoelectric effect, derivation by wave mechanics (Wentzel) III2II
Photoelectric effect, quantitative study of (Lenard) 034 46
Physical mechanics, name of wave mechanics (Schr dinger) III93 dinger) III93
Pickerling 1189
Planck complexion number 028 II15
Planck constant see Elementary action
Planck distribution formula of the black body radiation 025 II11
Planck hypothesis of elementary action II47
Planck hypothesis of natural radiation II10 313
Planck quantum condition II136
Planck resonator 017 24 II9
PlanckТs distribution formula, and the entropy of resonators 025 39 II11 15
PlanckТs distribution formula, derivation by Bose of II255
PlanckТs distribution formula, derivation by Debye of II18 261
PlanckТs distribution formula, derivation by Einstein of II150 258
PlanckТs distribution formula, two limits of 037 49
Podolsky see Einstein-
Poincare doubts on quantum condition II145
Poisson bracket equation and the commutation relation III47
Positive electron, DiracТs theory of III234
Presentation of the exclusition principle (the general rule) II217 219
Presentation of the exclusition principle (the general rule), quantization of direction and magnetization of gas II192
Presentation of the exclusition principle (the general rule), relativistic correction of  -factor II213 -factor II213
Presentation of the exclusition principle (the general rule), wave function as probability amplitude III180; see Heisenberg- Jordan
Principle of psycho-physical parallelism in the Copenhagen spirit III252
Pringsheim see Lummer-
Probability amplitude as interpretation of wave function (Pauli) III183
Probability amplitude, JordanТs transformation theory by means of III184
Quantization of direction and magnetization of gas II192
Quantization of direction and Stern Ч GerlachТs experiment II192
Quantization of direction, SommerfeldТs intorduction of II123
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 rsterling)
rsterling)  -rays
-rays 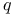 -algebra to
-algebra to 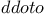 dingerТs application of wave mechanism to
dingerТs application of wave mechanism to  )
) 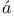 rm
rm -function
-function  -factor of s terms and the magneto-mechanical anomaly
-factor of s terms and the magneto-mechanical anomaly  -terms
-terms  -ray scattering (Crowther)
-ray scattering (Crowther)