|
|
 |
| Àâòîðèçàöèÿ |
|
|
 |
| Ïîèñê ïî óêàçàòåëÿì |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Taketani M. — The formation and logic of quantum mechanics |
|
|
 |
| Ïðåäìåòíûé óêàçàòåëü |
Quantum condition, analogy to Frenel’s band theory of III89
Quantum condition, and adiabatic hypothesis II165
Quantum condition, and Balmer’s formula II118
Quantum condition, and reflection and diffraction of 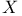 -rays II241 243 -rays II241 243
Quantum condition, and the WKB approximation III92
Quantum condition, Brillouin’s interpretation by inneratomic elastic wave of II244
Quantum condition, de Broglie’s interpretation by virtual (phase) wave of II249
Quantum condition, Debye and Sommerfeld’s application to Zeeman effect of II141 142
Quantum condition, difficulty for aperiodic motions of II195
Quantum condition, doubt’s by Poincare on II145
Quantum condition, equality of Sommerfeld’s and Planck’s II140
Quantum condition, intensified (Born — Jordan) III23
Quantum condition, Ishiwara’s III11
Quantum condition, limitation of II128
Quantum condition, Planck’s II136
Quantum condition, quantum-theoretical (Heisenberg) III11 14
Quantum condition, Rubinowicz’s application to cavity radiation of II160
Quantum condition, Schr dinger’s replacement with a variation principle of III74 77 dinger’s replacement with a variation principle of III74 77
Quantum condition, Sommerfeld, Epstein, Schwarzschild’s application to the Stark effect of II121 132 136
Quantum condition, Sommerfeld’s II116
Quantum condition, viewpoints from energetics and atomism of II146
Quantum condition, Wilson’s II108
Quantum number, as premise of the quantum condition II116
Quantum number, Bohr’s assumption of constancy of II218
Quantum number, Schr dinger’ derivation from wave equation of III76 dinger’ derivation from wave equation of III76
Quantum-theoretical multiplication formula, Heisenberg’s III10
Quantum-theoretical quantum condition 314
Quantum-theoretical quantum condition, Heisenberg’s III10 14
Radiation density and average energy of 030 37 II6 10
Ramusaner II260
Rayleigh difficulty in classical theory of spectra 073
Rayleigh dynamical model of spectral series 066
Rechenberg see Mehr-
Reciprocal theorem of balck body radiation (Kirchhoff) 6
Reciprocal theorem of the conjugate electron configuration (Pauli) II217
Reiche see Ladenberg-
Relativistic fine structure II127 III202 232
Relativistic matrix mechanics III203
Relativistic wave equation III150 154 203 231
Resonator, entropy of 019 25 31 II15
Reyleigh — Jeans distribution formula of black body radiation 023 II12
Reyleigh — Jeans’s distribution formula and the equipartition principle of energy 037 II12
Reyleigh — Jeans’s distribution formula as limit of Planck’s formula 038
Richardson II190
Ritz atomic magnet model of spectral series II60
Ritz atomic magnet model of spectral series, combination rule of spectral terms 64
Ritz atomic magnet model of spectral series, plate vibration model of spectral series II56
Ritz — Paschen spectral series 064
Robertson commutation relation and the uncertainty relation III241
Rosen II101; see Einstein — Rosenfeld
Rubens — Kurlbaum 024 312
Rubinowicz II101
Rubinowicz application of quantum condition to cavity radiation II160
Rubinowicz conservation of angular momenta and selection rule II159
Runge final determination of model of atom with or without nucleus 205 221
Runge rule for anomalous Zeeman effect II181; see Sommerfeld- Rutherford
Rutherford scattering formula, Gordon’s derivation by wave mechanics of III2II
Rutherford scattering formula, Wentzel’s Born approximation calculations of III199
Rutherford — Anderade II156
Rydberg electron configuration in rare gas atoms II198
Rydberg spectral series 064 65
Schott instability of Nagaoka model 0180
Schott intensity of radiation from electron rings 0197
Schott oscillation of electron rings II70
Schr dinger assumption of dinger assumption of 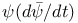 as charge density III110 120 as charge density III110 120
Schr dinger assumption of dinger assumption of 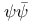 as charge density III120 as charge density III120
Schr dinger assumption of dinger assumption of 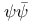 as weight function III121 as weight function III121
Schr dinger attempt to interprete wave function as catalog of expectation III269 dinger attempt to interprete wave function as catalog of expectation III269
Schr dinger critique of Machismic viewpoint III101 dinger critique of Machismic viewpoint III101
Schr dinger derivation of Balmer’s formula III76 dinger derivation of Balmer’s formula III76
Schr dinger dispersion formula in wave mechanics III118 dinger dispersion formula in wave mechanics III118
Schr dinger example of a cat (critique of observation theories of v. Neumann-type) III268 dinger example of a cat (critique of observation theories of v. Neumann-type) III268
Schr dinger light quantum and Doppler effect II231 dinger light quantum and Doppler effect II231
Schr dinger mathematical equality of matrix and wave mechanics III96 101 dinger mathematical equality of matrix and wave mechanics III96 101
Schr dinger objective interaction as origin of statistical nature of quantum mechanics III271 dinger objective interaction as origin of statistical nature of quantum mechanics III271
Schr dinger relative intensity of Stark effect III112 dinger relative intensity of Stark effect III112
Schr dinger relativitization of wave equation III155 dinger relativitization of wave equation III155
Schr dinger replacement of quantum condition using variation principle III74 77 dinger replacement of quantum condition using variation principle III74 77
Schr dinger theory of gases by means of de Broglie waves III64 dinger theory of gases by means of de Broglie waves III64
Schr dinger time-dependent wave equation III115 155 181 dinger time-dependent wave equation III115 155 181
Schr dinger time-independent wave equation III77 dinger time-independent wave equation III77
Schuster 078
Schwartzschild quantum condition and Stark effect II136
Second quantization of Dirac electron wave equation III228 234
Second quantization, quantization of de Broglie wave field III208 225 226
Selection rule and conservation of angular momentum II159
Selection rule and internal quantum number II186
Selection rule, derivation by matrix mechanics of III30
Selection rule, derivation from correspondence principle II163
Shimizu II221
Siegbahn measurement of characteristic X-rays II130
Signal velocity see Group velocity
Simon see Compton-
Slater idea of virtual radiation II262; see Bohr-
Smekal aperiodicity of translational motion in magnetic field II195
Smekal light quanta and normal and anomalous scatterings of light II278
Sommerfeld derivaiton of formula for spectral terms II179
Sommerfeld hypothesis of action integral II48
Sommerfeld introduction of internal quantum number II181
Sommerfeld introduction of quantum condition II116
Sommerfeld magneto-optical anomaly of  -factor of -factor of 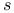 -terms II191 -terms II191
Sommerfeld permanence of multiplicity II180 186
Sommerfeld provisional selection rule II120 129
Sommerfeld quantum condition and Balmer’s formula II118
Sommerfeld quantum condition and quantization of direction II123
Sommerfeld quantum condition and Stark effect 121
Sommerfeld quantum condition and Zeeman effect II142
Sommerfeld theory of relativistic fine structure II127
Sommerfeld — Heisenberg selection rule for internal quantum number II186
Sommerfeld — Kossel displacement law of spectral series II180
Sommerfeld — Runge wave equation of light of short 316
Sommerfeld — Runge wavelengths III83
Sommerfeld’s II179
Sommerfeld’s in the Bohr model II88
Sommerfeld’s Kayser — Ringe’s 065
Sommerfeld’s provisional II120 129
Sommerfeld’s, Balmer’s 063
Sommerfeld’s, Rydberg’s 064 65
Specialty of spin angular momentum (Jordan) III218
Specialty of spin angular momentum (Jordan), Uhlenbeck — Goudsmidt’s introduction of II219
Specific charge measurement by Thomson of cathode-ray electron 01II 105
Specific charge measurement by Wien of anode-ray particle 0196
Specific charge measurement by Zeeman of electron 94
Specific heat of solids, Born — K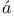 rm rm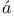 n’s theory of II24 n’s theory of II24
Specific heat of solids, Debye’s theory of II23
Specific heat of solids, Einstein’s theory of II19 21
Spectral term formula, Ritz’s II63
Spectrum theory, breakdown for oscillation of electron rings of 0206
Spectrum theory, difficulty in the classical theory of 74
Spectrum theory, Nicholson’s II67
Spectrum theory, Ritz’s II56 60
Spin and magneto-mechanical anomaly II221
Spin, Darwin’s attempt to introduce vector-type III214
Spin, Pauli’s introduction of wave function for III215
Spin-orbit interaction in Dirac electron wave equation III232
Spin-orbit interaction, Thomas — Frenkel’s II223
Stark effect, Bohr’s treatment by a pre-correspondence-principle of II143
Stark effect, Pauli’s application of matrix mechanics to III42
Stark effect, relative intensity by correspondence principle (Kramers) in II171
Stark effect, relative intensity by wave mechanics (Schr dinger) in III112 dinger) in III112
Stark effect, Sommerfeld, Epstein and Schwartzschild’s application of quantum condition to II121 132 136
Stark effect, Wentzel’s and Schr dinger’s application of wave mechanics to III92 108 dinger’s application of wave mechanics to III92 108
State as an essentialistic concept III273
State probability and matrix element of canonical transformation III172
State probability, introduction by Born of III129 162
State vector and unified formulation of matrix and wave mechanics III193 197
| Stationary state, assumption in the Bohr model of 86
Statistical aggregation, introduction by v. Neumann of III257
Statistical nature (in quantum mechanics), making much in the Copenhagen spirit of III252
Statistical nature (in quantum mechanics), objective interaction as origin of III271
Statistical operator introduction by v. Neumann of III258
Stefan — Boltzman law of the black body radiation 07
Stereo-structural logic of quantum mechanics (Taketani) 317 III272 275
Stern — Gerlach’s experiment and the anomalous Zeeman effect II195
Stern — Gerlach’s experiment, difficulty of interpretation of II192
Stewart II190
Stieltijes’s integral-in v. Neumann’s formulation III195
Stokes — Law of photoelectric effect 044
Stoner Rrvision of Bohr’s electron configuration II211
Sucksmith — Bates II191
Sugiura-calculation of covalent bonds III223
Sum rule, Kuhn’s and Thomas’s III13
Sutherland II21
Taketani conflict between field and matter 225 III235
Taketani critique of Bohr’s complementarity III253
Taketani irreversible process and the objective boundary in observation III275
Taketani stereo-structural logic in quantum mechanics III271 275
Tamm calculation of Compton effect by quantum field theory III233
Theory of electron Lorentz’s 077
Theory of magnetic body 0128 136
Theory of multiple scattering 0207 218
Thomas, L. H. derivation of spin-orbit interaction II222
Thomas, W. sum rule III14
Thomson analogy of floating magnets and periodic law 0108
Thomson determination of Avogadro’s number (by method of electrolysis) 0112
Thomson equality of positive and negative elementary charges 0114
Thomson measurement of elementary electric charge (by method of gas ionization) 0111
Thomson measurement of specific charge of free chathode ray electron 01II 104
Thomson model and construction of periodic system 150
Thomson model and electron mass as origin of atomic mass 0158
Thomson model and electron temperature 0159
Thomson model and intensity of radiation 0135
Thomson model and intensity of spectral lines 0198 206
Thomson model and oscillation of inneratomic electrons 0154
Thomson model and radioactivity 0161
Thomson model and valence 0156
Thomson model of atoms without nucleus by corpuscles 0106 129 141
Thomson model, stability condition and oscillation modes of 0141 150
Thomson specific charge of anode ray particle and mass of positively charged particle 0196
Townsend equality of positive and negative elementary charges 0114
Townsend measurement of elementary charge (by method of ion diffusion) 0113
Transformation function and Born’s scattering probability (Dirac) III182
Transformation function, introduciton by Dirac of III176
Transformation function, wave function as III179 318
Transformation theory, Dirac’s, Jordan’s III179 189
Transition probability and correspondence principle III70
Transition probability and dispersion formula II272 274
Transition probability and quantum theoretical amplitude III7
Transition probability of absorption and induced emission of light in wave mechanics III158 164
Transition probability of spontaneous emission of light in quantum mechanics III212
Transition probability, introduction by Einstein of II149
Transition probability, reversibility of (Born) III165
Uhlenbek- Goudsmit introduction of electron spin II219
Uncertainty principle, arbitrary interpretation in philosophical discussions of III244
Uncertainty principle, name of the uncertainty relation III244
Uncertainty relation, derivation from commutation relation of III242
Uncertainty relation, Heisenberg’s derivation by means of thought experiments III240
Uncertainty relation, negation of causality on the basis of (Heisenberg) III247
Unification, framework of III164
Unification, moment of III180
Unified formulation of matrix and wave mechanics III193 197
Uniform aggregation as a statistical aggregation (v. Neumann) III259
Uniformising variable for multi-periodic system III49
Unit operator, splitting in v. Neumann’s theory of III195
v. Neumann mixed aggregation as a statistical aggregate III260
v. Neumann statistical aggregation III257
v. Neumann statistical operator III259
v. Neumann theory of observation based on principle of psycho-physical parallelism III261
v. Neumann unified formulation of matrix and wave mechanics III193 197
v. Neumann uniform aggregation as a statistical aggregate III259; see Hilbert-
v. Neumann’s type of measurement apparatus, conditions for III263 287 292
Viewpoint of atomism about the quantum condition II146
Viewpoint of atomism about thermal phenomena 06 17
Viewpoint of energetics about quantum condition II146
Viewpoint of energetics about thermal phenomena 06 17
Villard II156
Virtual orbit Bleit’s II275
Virtual oscillator, Bohr — Kramers — Slator’s II267 275
Virtual radiation field Slator’s II265
Voigt model of Paschen — Back effect of Na — D line II183
Vortex atom, Kelvin’s 075 76
Wave equation and photoelectric effect III2II
Wave equation, Dirac, Schr dinger, Klein, Fock, Gordon’s relativization of III150 155 202 dinger, Klein, Fock, Gordon’s relativization of III150 155 202
Wave equation, Dirac’s relativistic electron III231
Wave equation, number representation of (Dirac) III209
Wave equation, Schr dinger’s and Dirac’s time-dependent III116 154 181 319 dinger’s and Dirac’s time-dependent III116 154 181 319
Wave equation, Schr dinger’s time-independent III76 dinger’s time-independent III76
Wave function as a state quantity in Hilbert space (London) III 169
Wave function as a transformation function (Dirac) III179
Wave function as expectation catalog (Schr dinger) III269 dinger) III269
Wave function as probability amplitude (Pauli) III183
Wave function as probability amplitude transformation in theory (Jordan) III184
Wave function, attempt at interpretation as ghost field of III126
Wave function, attempt at interpretation as guiding wave of II251 III126
Wave function, Born’s assumption of 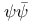 as probability of existence III129 162 as probability of existence III129 162
Wave function, of spin (Pauli) III216
Wave function, permutation property and nuclear spins III221
Wave function, permutation property and spectral terms III219
Wave function, permutation property for a many-body system III144 149
Wave function, Schr dinger’s assumption of dinger’s assumption of  \propto$ density of electric charge III110 118 \propto$ density of electric charge III110 118
Wave function, Schr dinger’s assumption of dinger’s assumption of 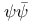  density of electric charge III118 density of electric charge III118
Wave function, Schr dinger’s assumption of dinger’s assumption of 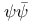 weight function III121 weight function III121
Wave function, Schr dinger’s representation of matrix element by III95 119 dinger’s representation of matrix element by III95 119
Wave mechanics, applied to diatomic molecules III88
Wave mechanics, applied to hydrogen atom III74
Wave mechanics, applied to Planck’s oscillator III88
Wave mechanics, Born’s application to scattering problem of III131
Wave mechanics, Born’s introduction of particle nature to III129 135
Wave mechanics, mathematical equality to matrix mechanics of (Schr dinger) III97 101 dinger) III97 101
Weight function as an interpretation of 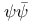 (Schr (Schr dinger) III121 dinger) III121
Weiss molecular magnetic field of gases 60
Wentzel Born approximation of Rutherford scattering formula III199
Wentzel regular and irregular doublet  -ray terms II205 -ray terms II205
Weyl commutation relation and uncertainty relation III241
Whiddington discussion of velocity loss of charged particles 0222
Whiddington energy of generating characteristic X-rays II81 98
Whole and parts in quantum mechanics III273
Whole and parts in quantum mechanics (Weyl) III273
Wien anode rays 0196
Wien displacement law of black body 08 8
Wien distribution formula of black body radiation 016 II8
Wien improvement of Michelson’s distribution formula II8
Wien measurement of specific charge of 320
Wiener see Born — Wien’s formula Jordan-Wilson H.
Wiener and hypothesis of light quanta 043
Wiener as a limit of Planck’s formula 049
Wigner development of cloud chamber 0110 111
Wigner measurement of elementary charge (by method of falling drop) 0113
Wilson, W. quantum condition II108
WKB approximation for Stark effect III91
WKB approximation for wave equation III90 92
WKB approximation, applied to Stark effect III891
WKB approximation, for wave equation III86 91
Wright II71
Zeeman effect and Larmor frequency 096 II142
Zeeman effect and verification of Lorentz electron theory 091
Zeeman effect, Bohr’s pre-correspondence-principal treatment of II143
Zeeman effect, Debye and Sommerfeld’s application of quantum condition to II141 142
Zeeman effect, Pauli’s application of matrix mechanics to III42
Zeeman effect, relative intensity by matrix mechanics of III30
Zeeman measurement of specific charge of electron 094
Zeeman, discovery of Zeeman effect 085
|
|
 |
| Ðåêëàìà |
 |
|
|
 |
|
Î ïðîåêòå
|
|
Î ïðîåêòå



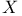 -rays
-rays  dinger’s replacement with a variation principle of
dinger’s replacement with a variation principle of 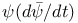 as charge density
as charge density 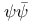 as charge density
as charge density  -factor of
-factor of 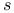 -terms
-terms 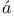 rm
rm \propto$ density of electric charge
\propto$ density of electric charge  density of electric charge
density of electric charge