|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ward S.A. — Computation Structures |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Signals, parallel 7
SIMD see architecture
Simulation 605 607
Single-sequence machine 325 335-366 612-613
Single-sequence machine, programming model 606
SISD see architecture
Skew 63 206 224
Skew, clock 192
SLT see timing disciplines
Small-scale integration (SSI) 105 107 129
Software 336
Software transparency 606
Sorters 616
Sorting network 212-223 225-226 264
Sorting network, Batcher 222-223
Sorting network, one-dimensional 216 222
Sorting network, two-dimensional 216-217 222-224
Sorting network, zero-dimensional 217 222
Sorting, bubble sort 213-222 225
Sorting, bubble sorter 222
Sorting, bubble sorter, sequential 215
Sorting, bubble sorter, serial 219-221
Sorting, by merging 222 225
Sorting, combinational sorter 213
Sorting, dimensionalities of bubble-sorter implementations 217
Sorting, merge modules 222-223
Sorting, merge networks 222-223
source file 318
Source language 276 362 513
sp 372 376 435 593;
Specification, functional 1 4
Specification, interface 473
Specification, timing 4
Speed 357 471 496
Speed, of light 238 246 605
Speed, switching 19 21
Speed, vs. power 19 21
Speed-power product 19 23
Speedup 608
Square wave 93
SRAM see random-access memory
SSI see small-scale integration
SsvcHandler 540
SSVCVEC 408-410 700
STACK 76 288 309 341-347 349 351 378 475 592
Stack architecture see architecture stack
Stack discipline 342-343 348 351 365 452 592-593
stack frame 342-347 350 364-365 398 400-407 433-434 475 492
Stack machine, pure 367
Stack pointer (SP) 309 341-343 349 367-368 393 395 399 408 434-435 458 460-461 534 592-593
Stack pointer (SP), kernel 592
Stack-machine instruction, CONST 367
Stack-machine instruction, LOAD 367
Stack-machine instruction, STORE 367
Stack-machine operators 368-371
Stanford University 530
Start bit 262-263
Start cycle 258
Start signal see control signals start
State 86-87 89 147-148 186 188 191 277
State memory 91
State registers, virtual 534
State transition 89 91 143-144
State variable 86 88 91 144-145 147 174 188
State, assignment 146
State, encoding 188
State, equations 77
State, information 534 537
State, metastable 80 96-100 147 266
State, of digital system 75-76
State, stable 77-78
State, undefined 88-89
State-transition diagram 144 146 190 218
State-transition rule 90
State-transition table 144 269
Static chain 346-347 401
Static discipline see discipline static
Static link 345-347 395 399 401 405 407
status bits 284
Stop bit 262-263
Storage allocation 347-348
Storage allocation, dynamic 348
Storage allocation, for microprogram variables 319
Storage allocation, free-storage pools 348
Storage allocation, garbage-collected heap storage 340 364
Storage allocation, heap storage 348 545
storage class 347-348
Storage class, automatic 342 348
Storage class, extent 342 347
Storage class, lifetime 347
Storage class, stack 348
Storage class, static 342 347 431
Storage levels 354-355
Storage, of temporary values 377-378 437
Store-and-forward modules 241
Struct MState 351 410 593
Structure 338 365 432 633-634
Structure, component 626
Structure, component reference 432-433
Structure, element 338
Structure, selection 338
Stub 410-411 458 538 588
Subtraction see arithmetic
Sum-of-products expressions 124
Sum-of-products expressions, canonical 51 58-61
Sum-of-products expressions, minimal 126
Sum-of-products expressions, reduced 60 145
Sum-of-products expressions, simplified 58-61
Supercomputers 271 365 477 613 615
Supercomputers, vector 615
Supervisor call 349 458 538-546 549-550 583 588
Supervisor mode 549
Supervisor-call handler 540 552
Supervisor-call handling 540-544
Sussman, G. xx
switches 240 264 292 616
Switching networks 240
Switching theory 65
symbols 2 269
Synchronization 8 93-100 171 547 606 618
Synchronization delay 176
Synchronization failure 96 174 176
Synchronization mechanisms 576
Synchronization mechanisms, eventcounts 576
Synchronization mechanisms, monitors 576
Synchronization mechanisms, sequencers 576
Synchronization problems 175 577
Synchronization problems, cigarette smokers' problem 577
Synchronization problems, firing-line problem 167
Synchronization problems, firing-mob problem 167
Synchronization problems, five dining philosophers problem 573-574 577 583
Synchronization problems, producer-consumer problem 577
Synchronization problems, readers-writers problem 577
Synchronization, of processes 547 559-585
Synchronization, probability of 100
Synchronization, producer-consumer 562-565
Synchrony 173-176 191
Synthesis 621
system call see supervisor call
System programming 365
System programs 547
System reliability 611
system software 349
systems 275-276
Systems, airline reservation 576
Systems, asynchronous 8 93 96 99 173
Systems, bistable 97
Systems, globally timed 172 190
Systems, multiple-clock 175-176
Systems, on-line banking 574 576
| Systems, synchronous 8 93 173 191
Systems, time-sharing 547
Systolic array 225
Tack, bottom of 342
Tack, directions of growth 341
Tack, kernel 592
Tack, operator 383
Tack, pop operation 309 341-342 434
Tack, push operation 309 341-342 434
Tack, top of 342
Tag 317 320 361
Tag bits 339
Tag field 482
Tagged architectures see architecture tagged
Tagged data see data tagged
Tape see memory magnetic
Tape target language 276 362
Technological progress 605
Tektronix Corporation xx
Telephone line 291
Teletypes 540
temporary location 358
Temporary results 288 359 454
Temporary values 319
Terman, C.J. xx
Terminal (TTY) 291 540
Terminal (TTY), number 540 542
Ternary logic 25
test see arithmetic
Text string 633
Tfpd see propagation delay
Then clause 628
Three-address machine, ADD instruction 359 367
Three-address machine, ADD1 instruction 360
Three-address machine, ADD2 instruction 360
Three-address machine, ADD4 instruction 360 362
Three-address machine, ASH4 instruction 360 369
Three-address machine, JUMP instruction 360
Three-state driver 20 178 240 246 283 286 288
Three-state driver, drive enable 293
Three-state driver, output enable 175 178 188 283-284 288
Three-state logic 20 246
Threshold logic 14-15 607
Threshold voltage (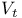 ) 5-7 ) 5-7
Throughput 205-210 212-221 224 233 241 610 614
Throughput, variations in 224
Time-sharing 613
Time-sharing systems see systems time-sharing
Timing diagram 63 78 80
Timing disciplines 171-200 260
Timing disciplines, asynchronous 172-174
Timing disciplines, asynchronous globally timed (AGT) discipline 173
Timing disciplines, asynchronous locally timed (ALT) discipline 173-174 176 182 191-196 247 260
Timing disciplines, global 172-173 182
Timing disciplines, globally timed systems, design of 188
Timing disciplines, independently clocked modules 175
Timing disciplines, local 172-173 182 190 257
Timing disciplines, self-timed 146 172 190 192
Timing disciplines, single-clock synchronous systems 93 175 197
Timing disciplines, synchronous 172-175 191 248
Timing disciplines, synchronous globally timed (SGT) discipline 173-174 182-183 187-191 260 516
Timing disciplines, synchronous locally timed (SLT) discipline 173-174 182 190-191 260
Timing granularity 192
Timing variations 187
TLB see buffer memory translation
Totem-pole output 19-20
TpC-Q see propagation delay clock-to-Q
tr see rise time
Transaction 575
transaction processing 576-577
Transfer characteristic 13 97
transistor 9 14-16 121
Transistor, active region 9-12 14 96
Transistor, base 9
Transistor, bipolar 9
Transistor, collector 9 121
Transistor, cutoff region 9-12 21
Transistor, depletion-mode FET 22
Transistor, drain 22
Transistor, emitter 9
Transistor, field-effect transistor (FET) 22
Transistor, gate see gate
Transistor, junctions 16
Transistor, linear region 9
Transistor, multiemitter 15
Transistor, n-channel FET 22
Transistor, NPN 9
Transistor, saturation charge 21
Transistor, saturation region 9-12 19 21
Transistor, source 22
Transition 8 16-18
Transition signaling 192-196
Transition signaling, bipolar 192-196
Transition time 78
Transition, unmarked 190
Transitivity 179
Transitivity, of 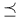 181 181
Translation 276
Transmission delay 192
transmission line 245-247 263
Transmit 587
Transparency 427
Trap 349 408-411 458-459 489-490 536-539 588
Trap handler 351-352 458 538 549
Trap return 350-352 409 458 540 543 549 552 594
Trap vector 350-351 408 411 458 491 549
TREE 203 238
Truth table 47-51 58 75 110 119 144 150 188 295-296 312
TS see setup time
TTL see logic families
TTL series 74181
tty see terminal
TTYNumber 542
TTYRead 540 542
TTYReadOK 542
TTYWrite 540 543
TTYWriteOK 542-543
Turing machine 269-275 277 347
Turing machine, alphabet 269
Turing machine, inputs 270
Turing machine, outputs 270
Turing machine, read/write head 269
Turing machine, representation of data 270
Turing machine, tape 269 271
Turing machine, universal 272-273 286 325 607 613
Turing machine, unrealizability 271
Turing universality 272-273 298 325 335
Turing, Alan 269
TypeCh 540 542-543 552
Types see data types
TypeSt 552 555-556
UART see universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter
Uncomputability 335
Uncountability 42
Unification 607
Uniprocessor 616
Universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) 262-263 291-293
Universal machines, simplest 272
Universality see Turing universality
user mode 549
Variable 277 319 323 626
Variable definition 319
Variable reference, free 344-347 401 403
Variable reference, nonlocal 404
Variable, binary 5 33
Variable, free 344-345 347 401-407
Variable, local (of a procedure) 340 342-345 347 397 401 454 475
Variable, private (of a procedure) 340
Variable, shared 606 618
Variable, SP-relative access to local variables 454
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



 )
)