|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Ward S.A. — Computation Structures |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Input/output (I/O), memory-mapped 253 548
Input/output devices 539 542 548 600
Input/output devices, device registers 253-254 548
Input/output devices, interfacing 253 591
Input/output devices, memory-mapped 619
Instruction 281 286 315 336-337 356-357 359
instruction counter see program counter
Instruction formats 358-361
Instruction formats, flexible 459
Instruction formats, immediate-mode 520
Instruction formats, one-address 359
Instruction formats, short 354 451
Instruction formats, stack (zero-address) 359
Instruction formats, three-address 358 451
Instruction formats, two-address 358 451
Instruction formats, variable 451
Instruction handlers as microsubroutines 380
Instruction register 515
instruction sets 287 547
Instruction sets, comparison of 362
Instruction sets, extended 349
Instruction sets, virtual 539
Instruction size 514
Instruction stream 367-368 373 431 613
Instruction stream, arguments in 370
Instruction stream, constants from 370 520-522
Instruction traps 349-352 408 411 458 540 593
Instruction, address fields 358
Instruction, atomic 576-577
Instruction, branch see instruction conditional unconditional
Instruction, comparison 388 625
Instruction, conditional jump 385 388-389 449
Instruction, decoding 287 355 357 513 515
Instruction, destination operand 358
Instruction, execution 355
Instruction, execution time 337
Instruction, fetch 355 357 474 478 513 515
Instruction, fetch/dispatch loop 593
Instruction, fetch/execute loop 375-376
Instruction, generic 339-340
Instruction, high-level 513
Instruction, illegal 375
Instruction, jump 385 451 523-524
Instruction, load/store 514
Instruction, no-operation 517
Instruction, prefetch 478 496
Instruction, privileged 408-409 458 539 549
Instruction, source operands 358
Instruction, supervisor-call 491
Instruction, test-and-clear 569 617
Instruction, test-and-set 568-569 571
Instruction, unconditional jump 389
Instruction, vector 615
Instruction, virtual machine 534
Instruction-fetch unit (IFU) 515 522-525 529 614
Instruction-set architecture see architecture instruction-set
Instructions per second 357
Instructions per second, millions of (MIPS) 608 613
Integers 45 287
Integrated circuit (IC) 21-24 105 120 134
Integrated-circuit chip 8 221
Intelligence 622
Interleaving see memory interleaving
Interlock delay 517
Interlocks 526
International Business Machines (IBM) 530
International Business Machines (IBM), Thomas J. Watson Research Center 530
Interpretation 269-279 281 325 335 357 459 514 529 549
Interpretation, cost 273
Interpretation, layers of 269 273 276
Interpretation, levels of 275 281 287 357
Interpretation, of machine instructions 307
Interpretation, of microcode 294
Interpretation, overhead 357 513
Interpretation, vs. compilation 275-277
Interpreter 269 273 276 298 303 356
Interpreter, machine-language 281
Interpretive mechanism 513
Interrupt 254 349 352 411 458 539 567 588
Interrupt Acknowledge 352
Interrupt control, device-specific 591
Interrupt disable 588-592
Interrupt enable 591
interrupt handler 352 592-593
interrupt latency 594 602
Interrupt request 254 352 591-598
Interrupt request, edge-triggered 592
Interrupt vector 352 592-593
Interrupt, alarm-clock 538 567 588
Interrupt, frequency 597-599
Interrupt, implementation 593-594
Interrupt, preemptive 596
Interrupt, service time 594-599
Interrupt-enable flag 588
Interrupt-enable mask 353 408
interval 83 179
Invalidation 495
Inverter ring 76-78
ITab 375
Johnson, M. xx
Join 194-195 198
Karnaugh map 58-62 65 81 145
Karnaugh map, don't care value 60
Kassel, R. xx
Katzenelson, J. xx
Key field 212
Keyword 625
Kirtley, J. xx
Knuth, D. xx
Label 317
Lambda calculus 277 607 623
Lambda expressions 277
Language 275
Language interface 303
Laplace's equation 609
Large-scale integration (LSI) 105
Latch 78-84 100
Latch, D-type 80-83
Latch, D-type, gate input 80
Latch, data input 80
Latch, R-S 78-80 87-88 94 96-97
Latch, R-S, as an asynchronous sequential device 87
Latch, R-S, reset input 78
Latch, R-S, set input 78
Latch, transparent 80-83
latency 201-204 209 224 233 241 247 608 614
Latency, maximum 203-204
Latent time 475
LCM 340
Learning 622
Learning machines 607
Least common multiple 340
Lexical depth 346 401 406 699
Lexical offset 401
lexical scoping see scoping lexical
Lexically containing block 345
Life 607
Lifetime see storage class lifetime
Lisp Machines, Inc. 529
Literal 59
Load delay 516-518 526-528
Load enable 284 290 293 531
Load operation 189 195
Load, electrical 16
Load-enable input 85-86 175 178 188
Loading factor 598
Loading, output 11
Locality 243 610-611
locality of reference 473-475 480 489 496 610
Locality of reference, spatial 475 486
| Locality of reference, temporal 475
Location 295
Location counter 410
Locking 568
Logarithms 204
Logic conventions 54
Logic conventions, active high 54 283
Logic conventions, active low 54 283
logic design 24 65
Logic design, building blocks for 105-134
Logic design, classic approach to 65
Logic design, computer-aided 65
Logic design, digital building blocks 105
Logic design, modular building blocks 212
Logic design, sequential building blocks 82
Logic device 4 605
Logic device, bistable 77 80
Logic device, cascaded 16
Logic device, combinational 4 47 174
Logic device, edge-triggered 247
Logic device, specifications 180 182-183 188
Logic device, timing 187
Logic device, timing specifications 191
Logic diagrams 276
Logic families 8-9 14 24 105
Logic families, complementary MOS (CMOS) 22-24
Logic families, diode-transistor logic (DTL) 15
Logic families, emitter-coupled logic (ECL) 16 21 24
Logic families, N-channel MOS (NMOS) 22 24
Logic families, resistor-transistor logic (RTL) 9 11 14 19-20 22 24 27 295
Logic families, Schottky TTL 21
Logic families, transistor-transistor logic (TTL) 15 19 23-24 106-119
Logic families, TTL, supply-voltage spikes 20
Logic gates 276
Logic gates, circuits 58
Logic gates, inverter 9 51
Logic gates, inverter, ideal finite-delay 78
Logic gates, inverter, RTL 9
Logic gates, MOS 22
Logic gates, NAND gate 106 110 121
Logic gates, noninverting buffer 51
Logic gates, NOR gate 14 96
Logic gates, NOR gate, RTL 14-16
Logic gates, OR gate 238
Logic gates, standard IEEE symbols 51
Logic gates, transfer characteristics 9
Logic gates, XOR (exclusive OR) gate 62
Logic levels 9-12
Logic levels, 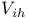 6-7 90 6-7 90
Logic levels, 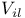 6-7 90 6-7 90
Logic levels, 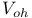 6-7 6-7
Logic levels, 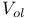 6-7 6-7
Logic levels, continuous to digital mapping 6
Logic levels, negative logic 8 54
Logic levels, positive logic 8 54
Logic levels, restoring 13 15
Logic levels, validity 9
Logic synthesis, from Boolean expressions 52
Logic synthesis, gate-level 65
Logic synthesis, using Karnaugh maps 58-61
Logic synthesis, using multiplexers 110
Logic synthesis, with common subexpressions 57
Logic synthesis, with NAND gates 54-58
Logic synthesis, with NOR gates 57
Logic technology, faster 605
Logic technology, metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) 22
Logic value 5
Long 362 371
Longword 287 362 368 435
Loops 474 629
LRU see replacement strategy least
LSI see large-scale integration
M.I.T. 340 623
M.I.T., Artificial Intelligence Laboratory 340
Machine language 276 281 287 299 303 335-336 353-362 513 529
Machine language, as interface 353-356
Machine language, microcoded implementation 356-358
Mackenzie, K. xx
Macro 317-319 370
Macro, body 318
Macro, call 318
Macro, definition 318 362
Macro, definition file 319
Macros. uasm definition file 319
MAdrFlag 442 445 447
Magnitude comparators 111
Main memory see memory main
malloc 633
Manchester encoding 157 261
Manchester University 497
MAYBE computer 281 341 363 413 593
MAYBE microarchitecture 287-293 340-341 363 386 637-670
MAYBE microarchitecture,  ALU status bit 298 ALU status bit 298
MAYBE microarchitecture,  push button 321 push button 321
MAYBE microarchitecture,  push button 321 push button 321
MAYBE microarchitecture, ADR register 288-289 297 300 304 307 310 320
MAYBE microarchitecture, ADR+ signal 288-289 297 300
MAYBE microarchitecture, ADRHI register 289
MAYBE microarchitecture, ADRLO register 289
MAYBE microarchitecture, ALU operand registers 284
MAYBE microarchitecture, asynchronous interface 291
MAYBE microarchitecture, C (carry) ALU status bit 298
MAYBE microarchitecture, circuit details 640-647
MAYBE microarchitecture, CLK signal 283-298
MAYBE microarchitecture, clock 284
MAYBE microarchitecture, clock cycles 284
MAYBE microarchitecture, communications subsystem 291-292
MAYBE microarchitecture, COND register 294-296 298
MAYBE microarchitecture, control circuitry 293
MAYBE microarchitecture, control ROM 293-295 297 299 303-304 307-308 313 326 637
MAYBE microarchitecture, control ROM coding 295-298
MAYBE microarchitecture, control ROM contents 652-667
MAYBE microarchitecture, control ROM output, default 297
MAYBE microarchitecture, control subsystem 293-299
MAYBE microarchitecture, data bus 283-293 310
MAYBE microarchitecture, data paths 283-310
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRALU signal 283-286
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRAM controller 291
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRAM read 291
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRAM refresh 291
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRAM refresh counter 320
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRAM write 291
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRDRAM signal 290-291
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRI/O signal 292
MAYBE microarchitecture, DRSEL signal 297
MAYBE microarchitecture, dynamic RAM 289-291
MAYBE microarchitecture, E (equal) ALU status bit 298
MAYBE microarchitecture, I/OFLAG signal 292 298 593
MAYBE microarchitecture, LDA signal 283-286 293
MAYBE microarchitecture, LDB signal 283-286
MAYBE microarchitecture, LDDRAM signal 290-291
MAYBE microarchitecture, LDI/O signal 292
MAYBE microarchitecture, LDI/OADR signal 292-293
MAYBE microarchitecture, LDOP signal 295
MAYBE microarchitecture, LDSEL signal 293 297
MAYBE microarchitecture, lights 292-293
MAYBE microarchitecture, MAR register 288 292
MAYBE microarchitecture, MAR register of UART 292-293
MAYBE microarchitecture, microcode ROM ( ROM) 288-289 295 297 303-304 307-308 310 312 320-321 325 357 ROM) 288-289 295 297 303-304 307-308 310 312 320-321 325 357
MAYBE microarchitecture, N (negative) ALU status bit 298
MAYBE microarchitecture, OP register 294-295 297 304 320
MAYBE microarchitecture, PHASE register 294-295 304 320
MAYBE microarchitecture, push buttons 321
MAYBE microarchitecture, refresh counter 311
MAYBE microarchitecture, static RAM 288
MAYBE microarchitecture, switches 292-293
MAYBE microarchitecture, UART 292
MAYBE microcode 513 671-694
MAYBE microinstruction set 647-652
MAYBE microinstruction set, add 304-305 313 323 328-330 649
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте



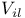
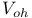
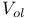
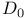 ALU status bit
ALU status bit  push button
push button  push button
push button  ROM)
ROM)