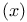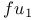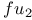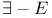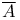Обсудите книгу на
Нашли опечатку?
Выделите ее мышкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter
|
Название: The collected papers of Gerhard Gentzen
Автор: Gentzen G.
Аннотация:
Gerhard Gentzen was born in Greifswald, Pomerania, on November 24th, 1909. He spent his childhood in Bergen on the Isle of Riigen in the Baltic Sea.
Язык: 
Рубрика: Математика/
Статус предметного указателя: Готов указатель с номерами страниц
ed2k:
Год издания: 1969
Количество страниц: 338
Добавлена в каталог: 27.10.2010
Операции: Положить на полку |
Скопировать ссылку для форума | Скопировать ID
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте