|
|
 |
| Авторизация |
|
|
 |
| Поиск по указателям |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Gentzen G. — The collected papers of Gerhard Gentzen |
|
|
 |
| Предметный указатель |
Definite object 54 111
Definite predicate 54 141
Definite proposition 142
Definition 14 156 160
Definition of the objects of proof theory 194 211
Definition table 158
Definition tables and decision rules 161
Degree of a CJ-inference figure 257
Degree of a cut 256
Degree of a derivation 89
Degree of a formula 15 71 254
Degree of a sentence 43
Degree of an induction proposition 311
Delimitation of the forms of inference in proof theory 138 228
Denton, J. 6
Denumerability 29 200 223 229 241—243 246 247
Denumerability and algebra 223
Denumerability and Skolem's theorem 241
Dependent formula 76
Dependent formulae and propositions 76 150 152
Derivability and logical consequence 2 3 24 33
Derivability of a contradiction 112
Derivable formula 55 112
Derivable formula in arithmetic 55 112
Derivation 55 72 74 151 179 216 257 258 287 309 cf.
Derivation in the ordinary sense 291
Derivation in tree form 73 258
Derivations in tree form 73 258
Derived concept 57 139 144 155—157 160 193
Derived concepts in elementary number theory 155—157
Description operator cf. "The ... such that"
Difficulties involved in consistency proofs 229 seq.
Direct proof 165
Disjunction 70 77 cf.
Disputable forms of inference 158 170 197 261
Distinction of cases 78 153 254 cf.
Dots 54
Dreben, B. 6
Dual(ity) 86 137 138 259
Duality of LK 86 259
e 77
Eigenvariable 77 84 255
Elementary formula 54 71 cf. "Prime
Elementary inference 145
Elementary number theory 3 8 68 132 136—138 154 197 198 223 239 250 287 292 309
Elementary number theory and bound predicate variables 297
Elementary number theory and transfinite induction 292 307
Eliminability of negation 66 67 81
Eliminability of the cut 15 28
Elimination of double negation 81 153 168—170 181 204 259
Elimination of logical connectives 5 80 82 148 150 168 258 259 262 263 269 293
Elimination of the double negation 168—170
Elimination Theorem cf. "Hauptsatz"
Empty antecedent 72
Empty antecendent 72
Empty endsequent 261
Empty endsequent and consistency 261
Empty sequent 16 72 103 255 261
Empty succedent 72 82 112
End formula 73
Endformula 55 73 151
ending 264 300
Endsequent 6 257
Endsequent after the reduction step 181
Endsequent and the subformula property 6
Equality 110 111 216 309
EQUIVALENCE 70
Equivalence between formulae and sequents 115
Equivalence of classical calculi 128 seq.
Equivalence of derivations 116
Equivalence of formulae 73 115
Equivalence of intuitionist calculi 116 seq.
Equivalence of logical calculi 69 115 116 128 131
Equivalence of net elements 49
Equivalence of sequents 115
Equivalence of the classical calculi 128 seq.
Equivalence of the intuitionist calculi 116 seq.
Euclid 5 144 145 148—150 155 170 248
Evaluation of terms 159
Examples, arithmetic axiom formulae 56 57 111 112 114 115
Examples, axioms of elementary number theory 157
Examples, basic logical sequents 180
Examples, basic mathematical sequent 260
Examples, basic sequents 86 257
Examples, circulus vitiosus in analysis 134
Examples, contradiction 262
Examples, degrees of formulae 254
Examples, derivations 258 260
Examples, forms of inference 148
Examples, formulae 54 141 215 253
Examples, inference figure 257
Examples, LJ-derivation 85
Examples, LK-derivation 85
Examples, mix 89
Examples, natural deductions 74 75
Examples, natural sum 296 297
Examples, NJ-derivations 79 80
Examples, ordinal numbers 187
Examples, prime formula 253
Examples, proof 144
Examples, reduction rule 176
Examples, sentence system without an independent axiom system 40
Examples, sequent 255
Examples, subformula property 88
Examples, subformulae 71
Examples, terms 54 141
Examples, theorem in proof theory 137
Examples, true formulae 74
Examples, true numerical propositions 114
Excluded Middle cf. "Law of the excluded middle"
Existence 246 248—250
Existential proposition 201 226
Existential quantifier 4 54 70 77 cf. "
Expression 53 54 70 211
Extended Hauptsatz cf. "Sharpened Hauptsatz"
Extension of a formalism 17 114
Extension of the reduction procedure 17 198
False formula 79 114
False sequent 254 269
Falsity cf. "Truth"
Fan Theorem 8 26
Fermat's last theorem 161
Fermat's last theorem and provability 166
Fermat's last theorem and the decidability of the predicate calculus 239
Fermat's last theorem and the existence of a decision rule 161
Fermat's last theorem and the reduction rule 176
Fermat, P. 161 162 166 176 239
figure 70 72
Finite mathematics 158 seq.
Finite sentence system 39
Finite sets of natural numbers 142 143
Finiteness of the reduction procedure 186 191 193
Finitist 10 18 169 227 250
Finitist forms of inference 135
Finitist interpretation and the statability of a reduction rule 173 201 206
Finitist interpretation of  163—165 169 163—165 169
Finitist interpretation of  167—170 167—170
Finitist interpretation of complete induction 166
Finitist interpretation of Fermat's last theorem 166
Finitist interpretation of number-theoretical axioms 164
Finitist meaning of 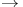 206 206
Finitist nature of transfinite ordinal numbers 277 278 285
Finitist sense of actualist propositions 201
Finitist sense of transfinite propositions 162
Finitist techniques of proof 171 193 194 210 212 238 239
Finsler, P. 315
Fitch, F.B. 12 13 27
follows 212
Formal arithmetic in LK 110 seq.
Formal system 68 233
| Formalization of elementary number theory 138 139 252
Formalization of logical deduction 68
Formalization of logical deductions 68
Formalization of proofs 137 138 228 258
Formalization of propositions 69 70 139 140
Formalization of techniques of proof 139 143
Formalization of the forms of inference 149 seq.
Formalization of the forms of inference in elementary number theory 149 seq.
Formalization of transfinite induction 291
Formalized arithmetic 55
Formally identical S-formulae 72
Forms of inference 30 138 139 144 228
Forms of inference and axiom systems 238
Forms of inference and decision procedures 161 seq.
Forms of inference and restricted transfinite induction 17 308
Forms of inference for sequents 150 151 255 256
Forms of inference in elementary number theory 148 149
Formula 54 70 140 141 214 253 289 314
Formulae and propositions 140 141
Formulae and sequents 72
Four-colour problem 223
Fractions 142
Fraenkel, A. 28 240 314
Free choice sequence 245 246
Free variable 55 141 144 215 288
Frege, G. 4 24 68
Function 69 110 156 158 160 174 194 198 199 211 245 246 260 287 288
Function symbol 140 141 288
Functions in elementary number theory 143 156
Functions in New 253 288
Fundamental conjecture 15
Fundamental principle of constructivism 225 235 247
Fundamental principle of constructivism and classical analysis 247 250
Fundamental principle of intuitionism and the actualist interpretation 235
Fundamental principle of proof theory 162
Fundamental theorem of algebra 236
G 293
Gauss, C.F. 225
General set theory 3 224 240 cf.
Gentzen's fundamental principle 162
Gentzen, G. vi vii viii 1—28 201 314 316 317
Geometry and infinity 224
GLC 13 14
Glivenko, V. x 116 314
Goedel numbers (correlation of natural numbers) 197
Goedel's equivalence theorem 169
Goedel's theorem 4 11 16 17 25 67 138 193 197 238 242 287
Goedel's theorem and consistency proofs 197 229 232 233 236 238—240 284 287
Goedel's theorem and constructivist techniques of proof 239
Goedel's theorem and Incompleteness 233 238 240 308
Goedel's theorem and restricted transfinite induction 16 232 284
Goedel's theorem and Skolem's theorem 242
Goedel's theorem and the consistency of arithmetic 67
Goedel's theorem and the reduction rule 213
Goedel's theorem on completeness 240
Goedel's theorem on decidability 239
Goedel, K. xi 3 4 7 8 11 15—18 24 25 67 138 169 193 197 199 212 213 215 229 232 233 236 238—240 242 287 308 313—317
Goldbach's conjecture 140 161
Goldbach's conjecture and decidability 161 168
Goldbach, C. 140 161
Goodstein, R.L. 26
Hauptsatz 5—7 15 68 69 83 85 87 88 317 cf.
Hauptsatz and intuitionist propositional logic 103
Hauptsatz and the cut 5
Hauptsatz and the decision rule 69
Herbrand theorem 6 313
Herbrand — Gentzen theorem 7 313 cf.
Herbrand, J. 6—8 13 25 56 236 313 314
Hertz, P. ix 1 2 29 31 32 40 312
Hessenberg, G. 317
Heyting, A. 3 56 58 61 65 68 69 75 81 106 117 236 249 313 315 316
Hilbert's finitist point of view 4 9 10 22 23 67 222 237
Hilbert's Programme 3 4 8 18 135 214 222 227 236 238
Hilbert's programme and philosophy 237
Hilbert, D. vii x 3 4 6 8 9 13 14 16 18—22 24 26—28 53 54 56 57 61 65 67 68 69 73—75 81 86 103 104 114—117 135 165 214 216 222
Hilbert, D. and Ackermann, W. 14 24 27 53 54 56 57 61 65 68 74 86 103 104 114 117 214 313—315
Hilbert, D. and Bernays, P. 6 9 26 27 315 317
Hjelmslev, J. 18 28 316
i 77
IA 83
Ideal element 18 247 250
Ideal point 247 248 250
Ideal proposition 247
Idealism 19 cf.
Idealization of reality 23 248
Immediate inference 31 cf.
Implication 10 70 77 cf.
Impredicative definition 14
Incompleteness and calculation procedures 245
Incompleteness and consistency proofs 17 198
Incompleteness and Goedel's theorem 233 238 240 308
Incompleteness and restricted transfinite induction 16 17
Incompleteness and the axiomatic method 17
Incompleteness and the reduction procedure 17
Incompleteness of elementary number theory 307 308
Incompleteness of formal systems 7 143 198 233 307
Indefinite number cf. "Term"
Indefinite proposition 140 142
Independent axiom system 2 39
Independent sentence system 39
Indeterminate 314
Indirect existence proof 226 235
Indirect existence proofs 226 235
Indirect existence proofs and the antinomies of set theory 235
Indirect proof 169 250 cf.
Indisputable forms of inference 158 171 193 197 200 228 229
Indisputable forms of inference and consistency proofs 200
Indisputable forms of inference and the constructivist point of view 228 250
Indisputable forms of inference and the proof of finiteness 197
Indisputable forms of inference and the reduction procedure 197
Indisputable forms of inference of elementary number theory 158
Induction cf. also "Complete induction" "Transfinite
Induction axiom 309
Induction proposition 145
Induction step 145
Inference 69
Inference figure 72 73 82 83 249 289
Inference figure schema 77 83 84 117 125 129 255 256 290 291
Inferences in Euclid's proof 145 seq.
Infinite domain of objects 222
Infinite sentence system 29 40
Infinite sets of objects 142 224
infinity 3 223 234 237
Infinity and geometry 224
Infinity and the antinomies of set theory 234
Informal arithmetic 55
Informal completeness of the forms of inference 34
Informal correctness of the forms of inference 33
Informal sense of a formula 141
Initial formula 73 74 76
Initial sentence 35
Initial sequent 83
Insufficiency of the natural numbers as ordinal numbers in proof theory 232
INTEGER 142
Interchange 84 129 151 256
Interchange in the antecedent 84 151
Interchange in the antecendent 84 151
Interchange in the succedent 84 129
Interdependence of the logical connectives 171
Introduction of logical connectives 5 80 82 148 150 168 258 262 263 269 293
Introduction of predicate symbols in logical calculi 111
Intuitionism fundamental principle of - 225 235
Intuitionist 3 10 135 169 227 235 250
Intuitionist analysis 18 244
Intuitionist and finitist uses of infinity 11
Intuitionist arithmetic 4 52 53 54 55
Intuitionist concepts as ideal elements 250
Intuitionist consistency of classical arithmetic 4
Intuitionist delimitation of the forms of inference 135 163
Intuitionist interpretation of infinity 235
|
|
 |
| Реклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
О проекте
|
|
О проекте