|
|
 |
| јвторизаци€ |
|
|
 |
| ѕоиск по указател€м |
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
|
| Neter J., Kutner M.H., Wasserman W. Ч Applied Linear Regression Models |
|
|
 |
| ѕредметный указатель |
"Best" subsets algorithms 429
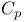 criterion 426Ч428 criterion 426Ч428
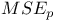 criterion 423Ч425 criterion 423Ч425
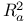 criterion 423Ч425 criterion 423Ч425
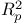 criterion 422Ч423 criterion 422Ч423
Addition theorem 2
Adjusted coefficient of multiple determination 241Ч242
All-possible-regressions selection procedure 421Ч429
Allocated codes 351Ч352
Analysis of variance 84Ч86
Analysis of variance models 343
Analysis of variance table 89Ч90
ANOVA table 89Ч90
Asymptotic normality 70
Autocorrelation 444Ч448
Autocorrelation parameter 448
Autocorrelation, remedial measures 454Ч460
Autocorrelation, test for 450Ч454
Autoregressive error model see "Regression model"
Backward elimination selection procedure 435Ч436
Berkson model 166Ч167
Beta coefficient 262
Biased estimation 394Ч395
Binary variable 330 354 see
Bivariate normal distribution 492Ч496
BMDP 113 251 431
Bonferroni joint estimation procedure for inverse predictions 174
Bonferroni joint estimation procedure for mean responses 158Ч159 245
Bonferroni joint estimation procedure for prediction of new observations 159Ч160 246Ч247
Bonferroni joint estimation procedure for regression coefficients 150Ч154 243
Calibration problem 174
Central limit theorem 6
Chi-square distribution 7Ч8
Chi-square distribution, table of percentiles 520
Cochran's theorem 92
Coefficient of multiple correlation 242 506
Coefficient of multiple correlation, inferences 506Ч507
Coefficient of multiple determination 241 506
Coefficient of multiple determination, adjusted 241Ч242
Coefficient of multiple determination, inferences 506Ч507
Coefficient of partial correlation 288Ч289 507Ч508
Coefficient of partial correlation, first-order 508
Coefficient of partial correlation, inferences 508
Coefficient of partial correlation, second-order 508
Coefficient of partial determination 286Ч288 507Ч508
Coefficient of partial determination, inferences 508
Coefficient of simple correlation 97Ч99 494
Coefficient of simple correlation, inferences 502Ч504
Coefficient of simple determination 96Ч97 501Ч502
Coefficient of simple determination, inferences 502Ч504
Column vector 187
Complementary event 3
Conditional probability 3
Conditional probability function 4
Confidence coefficient, interpretation of 70Ч71 84
Confidence set 152
Consistent estimator 9
Contour diagram 235Ч237 494Ч495
Cook's distance measure 407Ч409
Correction for mean sum of squares 90
Correlation coefficient see "Coefficient of multiple correlation" "Coefficient "Coefficient
Correlation Index 312
Correlation matrix 382
Correlation matrix of the independent variables 381
Correlation model 491Ч492
Correlation model, bivariate normal 492Ч496
Correlation model, multivariate normal 505
Correlation transformation 378Ч379
Covariance models 343
Covariance of two functions of random variables 6
Covariance of two random variables 5
Cox, D.R. 176
Degrees of freedom 7Ч8
Deleted residual 405Ч406
Denominator degrees of freedom 8
Dependent variable 25 28
Determinant of matrix 202
Diagonal matrix 196Ч197
Disturbance term 445
Dummy variable 34 330 see
Durbin Ч Watson test 450Ч454
Durbin Ч Watson test, table of test bounds 530Ч531
Error mean square 47
Error sum of squares 47
Error term 31
Error term variance 31 46Ч48 50
Error term, nonconstancy of error variance 113Ч114 123 133
Error term, nonindependence of 116Ч118 123 133
Error term, nonnormality of 118Ч120 123 133
Expected mean square 90Ч91
Expected value of function of random variables 5Ч6
Expected value of random variable 3
Experimental data 35
Exponential regression function 468
Extra sum of squares 282Ч286
F distribution 8Ч9
F distribution, table of percentiles 521Ч527
Family confidence coefficient 150
Family of estimates 150
First differences 458Ч459
First-order autoregressive error model 448Ч450
First-order autoregressive error model, first differences approach 458Ч460
First-order autoregressive error model, iterative estimation approach 455Ч458
First-order autoregressive error model, test for autocorrelation 450Ч454
First-order regression model 31 227 229Ч230 see
Fisher, R.A. 503
Fitted value 41
Fitted value in terms of hat matrix 401
Forward selection procedure 435
Full model 95
Functional relation 24
Gauss Ч Markov theorem 39Ч40 64
Gauss Ч Newton method 472Ч479
General linear regression model 230Ч234 237Ч238
General linear test 94Ч96 293Ч296
Hat matrix 220Ч221
Heteroscedasticity 170
Homoscedasticity 170
Hyperplane 230
Idempotent matrix 221
Identity matrix 197
Independence of random variables 5
Independent variable 25 28
Indicator variable 329Ч330 353Ч354
Indicator variable in comparing regression functions 343Ч345
Indicator variable in piecewise linear regression 346Ч350
Indicator variable in time series model 350Ч351
Indicator variable, as dependent variable 354Ч357
Influential observations 407Ч409
Instrumental variable 165Ч166
Interaction effect 232Ч237
Interaction effect coefficient 304
Interaction effect with indicator variables 335Ч339
Intrinsically linear regression model 467
Inverse of matrix 200Ч204
Inverse prediction 172Ч174
Joint confidence region for regression coefficients 147Ч150 217 243
Joint probability function 4
Lack of fit mean square 129
Lack of fit sum of squares 128
Lack of fit test 123Ч132 245Ч246
Least absolute deviations estimation 410Ч411
Least squares criterion 36
Least squares estimation 10
Least squares estimation, control of roundoff errors 377Ч382
Least squares estimation, multiple regression 238Ч239
Least squares estimation, nonlinear regression 470Ч480
Least squares estimation, simple linear regression 36Ч40 44Ч46 210Ч212
Least squares estimation, weighted 167Ч172 219Ч220 263
Leverage 402
| Likelihood function 9
Linear dependence 199Ч200
Linear effect coefficient 301
Linear model 31 466Ч467 see
Linear model, general linear test 94Ч96 293Ч296
Linear regression model see "Regression model"
Linearity, test for 123Ч132
Logistic regression function 361Ч362 468Ч469
Logistic transformation 362
Logit transformation 362
Marginal probability function 4
Marquardt algorithm 479Ч80
Matrix of quadratic form 215
Matrix with all elements 1 198
Matrix, addition 190Ч191
Matrix, definition 185Ч187
Matrix, determinant 202
Matrix, diagonal 196Ч197
Matrix, dimension 186
Matrix, elements 186
Matrix, equality of two 189
Matrix, hat 220Ч221
Matrix, idempotent 221
Matrix, identity 197
Matrix, inverse 200Ч204
Matrix, multiplication by matrix 192Ч196
Matrix, multiplication by scalar 192
Matrix, nonsingular 201
Matrix, random 205Ч208
Matrix, rank 200
Matrix, scalar 197Ч198
Matrix, singular 201
Matrix, square 187
Matrix, subtraction 190Ч191
Matrix, symmetric 196
Matrix, theorems 204Ч205
Matrix, transpose 188Ч189
Matrix, vector 187Ч188
Matrix, zero vector 198Ч199
Maximum Likelihood Estimation 9Ч10
Maximum likelihood estimation of regression parameters 50Ч51
Mean of population, estimation of difference between two 14Ч16
Mean of population, estimation of single 11
Mean of population, test concerning, difference between two 14Ч16
Mean of population, test concerning, single 11Ч12
Mean response 41
Mean response, multiple regression, estimation 244
Mean response, multiple regression, joint estimation 245
Mean response, simple linear regression, interval estimation 75Ч76 217
Mean response, simple linear regression, joint estimation 157Ч159
Mean response, simple linear regression, point estimation 41Ч43
Mean square 46 88
Mean square, expected value of 90Ч91
Mean squared error of regression coefficient 395
Mean squared error, total of n fitted values 426
Measurement errors in observations 164Ч167
Method of steepest descent 479
Minimum absolute deviations method 411
Minimum sum of absolute deviations method 411
Minimum variance estimator 9
Minimum-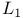 -norm method 411 -norm method 411
Multicollinearity 271Ч278 382Ч390
Multicollinearity, detection of 390Ч393
Multicollinearity, remedial measures 393Ч400
Multiple correlation see "Coefficient of multiple correlation"
Multiple regression see "Mean response" "Prediction "Regression "Regression "Regression "Selection
Multiplication theorem 3
Multivariate normal distribution 505
Noncentrality parameter 71
Nonexperimental data 35
Nonlinear regression model 468Ч469
Nonlinear regression model, inferences about parameters 480Ч483
Nonlinear regression model, least squares estimation 470Ч480
Nonsingular matrix 201
Normal equations 38
Normal error regression model see "Regression model"
Normal probability distribution 6Ч7
Normal probability distribution, table of areas and percentiles 517
Normal probability plot 118Ч120
Numerator degrees of freedom 8
Observation 25
Observational data 35
Observed value 41
Orthogonal polynomials 319
Outlier 114Ч116 123
Outlier, identification of 400Ч407
Overall F test 281 289
p-value 12Ч13
Paired observations 15Ч16
Partial correlation see "Coefficient of partial correlation"
Partial F test 281 289
Partial regression coefficient 229
Piecewise linear regression 346Ч350
Point estimator 38
Polynomial regression model 300Ч305
Power of tests for regression coefficients 71Ч72
Prediction bias 437
Prediction interval 77Ч78
Prediction of new observation, inverse 172Ч174
Prediction of new observation, multiple regression 246Ч247
Prediction of new observation, simple linear regression 76Ч82 159Ч160 218Ч219
Predictor variable 25 28
Probit transformation 366
Product operator 2
Pure error mean square 127Ч128
Pure error sum of squares 127
Quadratic effect coefficient 301
Quadratic form 215
Quadratic response function 301
Quadratic response function, estimation of maximum or minimum 317Ч319
Quantal response 354
random matrix 205Ч208
Random vector 205Ч208
Rank of matrix 200
Reduced model 95
Regression see "Mean response" "Prediction "Regression "Regression "Regression
Regression coefficients, multiple regression 227Ч229
Regression coefficients, multiple regression, danger in simultaneous tests 278Ч282
Regression coefficients, multiple regression, interval estimation 243
Regression coefficients, multiple regression, joint estimation 243
Regression coefficients, multiple regression, point estimation 238Ч239 263
Regression coefficients, multiple regression, tests concerning 243 285Ч286 289Ч293
Regression coefficients, multiple regression, variance-covariance matrix of 242 263
Regression coefficients, partial 229
Regression coefficients, simple linear regression 33Ч34
Regression coefficients, simple linear regression, interval estimation 65Ч67 69Ч70
Regression coefficients, simple linear regression, joint estimation 147Ч154 217
Regression coefficients, simple linear regression, point estimation 36Ч40 50Ч51 167Ч172 210Ч212 219Ч220
Regression coefficients, simple linear regression, tests concerning 67Ч68 71Ч72 92Ч94
Regression coefficients, simple linear regression, variance-covariance matrix of 216Ч217
Regression coefficients, standardized 261Ч263
Regression curve 27Ч28 see
Regression function 27Ч28
Regression function, comparison of two or more 343Ч45
Regression function, confidence band, simple linear regression 154Ч157
Regression function, confidence region, multiple regression 244
Regression function, estimated regression function 41Ч43
Regression function, test for fit 123Ч132 245Ч246
Regression function, test for regression relation 92Ч93 240Ч241
Regression function, transformations to linearize 134Ч141
Regression mean square 88
Regression model 26Ч29
Regression model, effect of measurement errors 164Ч167
Regression model, first-order autoregressive 448Ч450
Regression model, general linear 230Ч234 237Ч238
Regression model, multiple 226Ч230
Regression model, multiple in matrix terms 237Ч238
Regression model, multiple with interaction effects 232Ч237 335Ч339
Regression model, nonlinear 468Ч469
Regression model, polynomial 300Ч305
|
|
 |
| –еклама |
 |
|
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



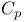 criterion
criterion 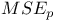 criterion
criterion 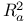 criterion
criterion 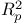 criterion
criterion 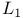 -norm method
-norm method