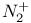јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Zel'dovich Ya.B., Raizer Yu.P. Ч Physics of Shock Waves and High-Temperature Hydrodynamic Phenomena (vol. 1)
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: Physics of Shock Waves and High-Temperature Hydrodynamic Phenomena (vol. 1)јвторы: Zel'dovich Ya.B., Raizer Yu.P. јннотаци€: The physical and chemical processes occurring in gases at high temperatures are the focus of this outstanding text by two distinguished physicists. They discuss essential physical influences on the dynamics and thermodynamics of continuous media, combining material from such disciplines as gas dynamics, shock-wave theory, thermodynamics and statistical physics, molecular physics, spectroscopy, radiation theory, astrophysics, solid-state physics, and other fields. Originally published in two volumes
язык: –убрика: ‘изика /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1966 оличество страниц: 464ƒобавлена в каталог: 11.10.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Delta band system of NO 324 Dense gases 217Ч232 Dense gases, cold 223Ч229 Dense gases, hot 229Ч232 Density ratio across a strong shock 51 52 Detailed balancing principle 120 Detonation mechanism 92 Diatomic gas 184 diatomic molecules 178 Diatomic molecules, dissociation 183Ч188 Diatomic molecules, energy levels 303 ff. Diatomic molecules, notation for electronic state 306Ч308 Diatomic molecules, symmetry properties 308 Dibeler, V.H. 364[21] 435 Diffraction scattering 125 Diffusion approximation for radiation 151 152 154Ч156 163 164 Diffusion approximation for radiation, boundary conditions 148 149 Diffusion approximation for radiation, effect of optical thickness 147 Diffusion coefficient 90 Diffusion coefficient, for photons 146 151 Diffusion coefficient, in recombination model 410Ч412 Diffusion equation for photons 146 147 Diffusion model for recombination 408Ч412 Dilatational viscosity coefficient 73 (see also УSecond viscosity coefficientФ) Dirac, P.A.M. 124 424 Discontinuities, formation of 32 Discontinuities, propagation velocity of 46 (see also УArbitrary discontinuitiesФ УWeak Discontinuity relations see УShock wave relationsФ Dissipative processes see УViscosity and Heat conductionФ Dissociation 183 184 Dissociation energy 186 Dissociation rates 365Ч368 Dissociation relaxation 362Ч368 Dissociation relaxation time 363 Dissociation spectrum 310 Dissociation, nonequilibrium 184 Dissociation, role of vibrational energy in 366 Dissociative equilibrium constant 186 Dissociative recombination 385 386 414Ч416 Ditchburn, R.W. 323[26] 430 Dixon, J.K. 337[35] 431 Doring, W. 346 Doublet splitting, NO 182 Dronov, A.P. 276 431 Duff, R.E. 367[68] 438 Ecker, G. 200[10] 425 Effective absorption coefficient 129 Effective adiabatic exponent 188 207Ч210 Effective front thickness 28 Effective radiation 250 Effective ratio of specific heats see УEffective adiabatic exponentФ Effective temperature see УBrightness temperatureФ Ehler, A.W. 200[10] 425 Einstein coefficient, for absorption 290Ч292 Einstein coefficient, for emission 288Ч292 Einstein coefficients, relation between 120 290 El'yashevich, M.A. 304[41] 431 Electrical conductivity measurement 245 Electrical contact probes 245 Electromagnetic frequency scale see УRadiation spectrumФ Electromagnetic shock tubes 239Ч243 Electron attachment 386 416 Electron avalanche 340Ч343 387 401 Electron beam scattering 244 Electron capture 261Ч264 394 395 Electron capture, cross section for 263 (see also УRecombinationФ) Electron charge 441 Electron concentration from gas luminosity 245 Electron density distribution, compressed atom 226 Electron density distribution, free neutral atom 225 Electron density distribution, slightly compressed atom 226 Electron mass 441 Electron orbits 261 Electron radius 442 Electron scattering from a standing light wave 124 Electron spin 306 Electron temperature 386 417 420 Electronic deexcitation 382 (see also УElectronic excitationФ) Electronic energy 304 Electronic excitation 192Ч197 382Ч386 Electronic excitation energy 193 Electronic partition functions 181 182 195 198Ч201 Electronic partition functions, cutoff of 195 196 198Ч201 Electronic partition functions, transformed 194 195 Electronic transitions 111 246 emission 110 113 114 119 Emission coefficient 110 119 120 Emission cross section 252 Emittance 134 Endothermic reactions 190 368 Ener, C. 353[11] 435 Energy distribution in radiation see УSpectral radiant energy densityФ Energy level diagram, nitrogen 307 Energy level diagram, protonЧelectron system 111 Energy levels, hydrogenЧlike atom 262 Energy of radiation see УRadiation energyФ Engineering equation of state 176 Entropy change, shock 53 60Ч62 Entropy change, weak compression shock 64Ч67 Entropy change, weak rarefaction shock 64 Entropy change, with anomalous thermodynamic properties 67Ч69 Entropy change, with viscosity and heat conduction 72 Entropy equation, with radiant heat transfer 143 Entropy of radiation 117 197 Entropy, approximate relation for, with multiple ionization 205 Equation of state 3 176 Equation of state, perfect gas 3 177 Equations for shock front structure 76 77 Equations of gasdynamics, in Eulerian coordinates 1Ч4 Equations of gasdynamics, in Lagrangian coordinates 4Ч7 Equations of gasdynamics, oneЧdimensional with viscosity and heat conduction 69Ч72 Equations of gasdynamics, with radiant heat transfer 143 Equations of gasdynamics, with radiation energy and pressure 168Ч172 Equilibrium radiation 115Ч118 Erkovich, S.P. 323[27] 430 Eschenroeder, A.Q. 416[92] 440 Excitation energies 196 198Ч201 Excitation energies, ionic levels 195 Excitation energies, N, 182 Excitation, by electron impact 390Ч392 396Ч398 Excitation, by heavy particles 398Ч401 Excitation, of excited atoms 396Ч398 Exothermic reactions 189 368 Eyring, H. 370[38] 379[38] 436 F, cross section for photoprocesses 404 F, photoionization 267 268 Faizullov, F.S. 332[48] 432 Fedorenko, N.V. 400[75] 439 Fermi limiting energy 220 221 Fermi Ч Dirac statistics for an electron gas 218Ч222 Fermi, E. 200[9] 425 Ferri, A. (ed.) 234[18] 243[18] 428 Feynman, R.P. 231[33] 426 Filippenko, L.G. 400[75] 439 Fine structure constant 443 Finite amplitude waves 29 44 Finite amplitude waves, "overshooting" of 31 32 Finite amplitude waves, steepening of 31 32 First law of thermodynamics 3 First negative band system of 305 330 334 First positive band system of 305 307 330 334 Fite, W.L. 389[48] 437 Flaks, I.P. 400[75] 439 Fortrat diagrams 310 ForwardЧreverse approximation 149Ч151 Fowler TЧtube 239 240 Fowler, R.G. 239[6] 427 Fowler, R.H. 366[27] 370[27] 436 Frank-Condon factor 319Ч321 Frank-Condon principle 313Ч321 Frank-Kamenetskii, D.A. 374 375[39] 377[39] 378[39] 436 Franklin, J.L. 364[21] 455 Fraser, P.A. 321[22] 430 Free electron states 111 Free energy 176 180 182 Free energy, dissociated diatomic gas 185 Free energy, from Coulomb interactions 216 Free energy, ionized gas 194 Free neutral atom, electron density distribution 225 Free piston, compression by 234 Free-free transitions 112Ч114 248 Free-free transitions, in a highЧtemperature gas 258Ч261 Freezing, of NO 378 Friedrichs, K.O. 20[14] 423 Fyfe, W.I. 415[72] 438 Gabrysh, A.F. 353[11] 435 Gamma band system of NO 305 323 324 328Ч330 334 Gas constant 3 177 Gas constant, universal 3 177 441 Gaunt factor 254 260 Gaydon, A.G. 304[20] 313[20] 319[20b] 362[63] 429 438 Gehman, W. 365[25] 368[25] 436 Geltman, S. 269[9] 429 Generalov, N.A. 332[33] 362[58] 367 431 436 438 Gerrard, J.H. 362[62] 438 Gibbs free energy see УGibbs potentialФ Gibbs potential 176 Gilvarry, J.J. 231[33] 427 Ginzburg, V.L. 282[63] 283[63] 433 Glasstone, S. 370[38] 379[38] 436 Glick, H.S. 368 375[40] 378 436(2) Godnev, I.N. 183[2] 424 Goldstine, H.H. 99[8] 423 Golian, T.C. 416[92] 440 Gombas, P. 223 426 Gorban', N.F. 213 426 Granovskii, V.L. 389[46] 391[46] 401[46] 437 Gray body 141 144 Greene, E.F. 353 353[2 3] 434(2) Griem, H.R. 241[8] 427 Griffith, W.C. 362[64] 438 Ground state, proton-electron system 111 Ground triplet state, O 182 Gryzinski, M. 396[84] 439 Guggenheim, E.A. 366[27] 370[27] 436 Gulyaev, R.A. 392[79] 396[79] 439 Gurevich, A.V. 397[85] 407 411[88] 411[85] 412[88] 439(2) H 199 H, cross section for photoprocesses 404 H, degree of ionization 195 H, dissociation energy 212 H, electron energy levels 112 H, excitation of 391 H, excited states 198 H, ionization of 199 200 212 H, ionization potential 111 442 H, photoionization 267 268 Hammerling, P. 332[32] 332[43] 335[32] 368[53] 431(2) 437 Harmonic oscillator, emission from 126 127 Harris, L. 337[36] 431 Harshbarger, F. 234[1] 243[1] 427 Harteck, P. 364[22] 435 Haught, A.F. 338[65] 338[68] 339[65] 343[65] 433(2) He, as shock tube driver gas 237 He, excitation of 391 He, ionization by He 400 He, ionization of 389 Heat conduction 69Ч73 Heat of reaction 190 Heddle, D.W.O. 323[26] 430 Heitler, W. 254[3] 428 Helmholtz free energy see УFree energyФ Herron, J.T. 364[21] 435 Hertzberg band system 323 Hertzberg, A. 416[92] 440 Herzberg, G. 304[20] 310[20a] 312[20a] 313[20] 429 Herzfeld, K.F. 356[13] 360 360[18] 360[18a] 435(3) Hg, excitation of 391 Hg,ionization of 389 Hg,photoionization 276 High-speed photography 243 Hinnov, E. 392[80] 394[80] 407 408[80] 439 Hirschberg, J.G. 392[80] 394[80] 407 408[80] 439 Hornig, D.F. 244 353 353[1] 353[2 3] 368[35] 434(3) 436 Hubbard, J.C. 353[11] 435 Huber, A.W. 361 435 Huebner, W.F., et al. (eds.) 332[64] 433 Hugoniot curves 49Ч52 55Ч59 Hugoniot curves, for absorption wave 345Ч347 Hugoniot curves, physically unattainable states 51 Hugoniot relations 50 Hugoniot relations, with dissociation and ionization 209Ч213 Hugoniot relations, with equilibrium radiation 213Ч215 Hurle, I.R. 362[63] 438 Hydrogen-like atom 198 Hydrogen-like atom, binding energy 199 Hydrogen-like atom, energy levels 198 Hydrogen-like atom, recombination 405 Hydrogen-like atom, transformed electronic partition function 199 Hydrogenic see УHydrogen-likeФ HydrogenЧlike systems 248 Impact parameter 250 Impact-radiative recombination 413 Imshennik, V.S. 106 172[8] 423 424 Induced Compton effect 124 125 Induced emission 118Ч128 Integrated brightness temperature 138Ч140 165 Integrated brightness temperature, plane photosphere 162 Integrated emission coefficient, bremsstrahlung emission 258 Integrated radiant energy density 110 169Ч172 Integrated radiant energy density, equilibrium radiation 117 443 Integrated radiant energy flux 110 Integrated radiant energy flux, perfect black body 118 443 Integrated radiation intensity 110 Interferometry 244 Intermediate complex method see УActivated complex methodФ Internal energy, air, comparison of exact and approximate calculations 206 Internal energy, approximate relation with multiple ionization 205 Internal energy, dissociated diatomic gas 184 Internal energy, from Coulomb interactions 216 Internal energy, ionized gas 193 Internal energy, perfect gas 183 Internal energy, powerЧlaw relation 208 Internal energy, rotational 178 Internal energy, translational 177 178 Internal energy, vibrational 178 183 Ionization 192Ч197 382 Ionization potential, average 203 Ionization potential, effective decrease in 217 218 Ionization potential, first 195 Ionization potential, H 111 442 Ionization potential, lowering due to cutoff 200 201 Ionization potential, mЧion 194 203 204 Ionization potential, N, 192 Ionization potential, second 195 Ionization probes 245 Ionization rate 388 393Ч396 405 Ionization, by electron impact 386Ч390 392Ч396 Ionization, by heavy particles 398Ч401 Ionization, degree of for air 206 Ionization, in air 413Ч416 Ionization, internal energy of air with 206 Ionization, multiple 201Ч207 Ionization, of excited atoms 392Ч396 Ionized gases, with Coulomb interactions 215Ч218 Ionosphere, processes in 416 Ionova, V.P. (ed.) 243[14] 428 Isentropes 50 55Ч61 65Ч67 Isentropes, approximate relation for with multiple ionization 205 Isentropes, with anomalous thermodynamic properties 67Ч69
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



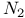 , NO, O,
, NO, O,