јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Weinberg S. Ч The Quantum Theory of Fields. Vol. 1 Foundations
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: The Quantum Theory of Fields. Vol. 1 Foundationsјвтор: Weinberg S. јннотаци€: In The Quantum Theory of Fields, Nobel Laureate Steven Weinberg combines his exceptional physical insight with his gift for clear exposition to provide a self-contained, comprehensive, and up-to-date introduction to quantum field theory.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика / вантова€ теори€ пол€ /”чебники /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1996 оличество страниц: 609ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.10.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
Hepp, K. 512 532 Herzberg, G. 45 Heydenberg, N. 167 Hibbs, A. R. 423 Hilbert space, defined 49 Hocking, J. G. 106 Hoddeson, L. 39 40 46 167 Hole theory 12 29 31 Homotopy groups and classes 89Ч90 96Ч100 419Ч20 Homotopy groups and classes, defined 100 Howard, J. C. 470 Hubbard Ч Stratonovich transformation 461 Hubbard, J. 461 470 Huber, A. 596 Huff, R. W. 596 Hugenholtz, N, M. 178 790 Hypercharge 123 Hyperons 123 Hyperons, discovered 30 Induced emission of photons 18 Induced representations 65 Infield, L. 46 Infinities (see УUltraviolet divergencesФ УInfrared Infrared divergences 32Ч3 491 496 539Ч53 Inoenue Ч Wigner contraction 62 Inoeu, T. 45 Inonue, E. 62 105 Interaction picture 143 287 Interaction picture for derivative coupling 318Ч20 Interaction picture for Dirac field 323Ч5 Interaction picture for electrodynamics 353 Interaction picture for interacting scalar field 304Ч5 Interaction picture for vector field 320Ч3 Internal symmetries 121Ч2 Invariant subgroups and subalgebras 70 88 Irreducible representations, defined 64 Irrelevant couplings 503 Isospin (isotopic spin) 123 Israel, W. 533 Ito, D. 45 Jackiw, R. 40 424 Jackson, J. D. 471 Jacobi identity 83 Jaffe, A. 423 Jammer, M. 39 Jauch, J. M. 257 Jets 550 552 Johnson, W. R. 596 Joliot, F. 45 Joos, H. 257 Jordan, P. 3 10 15 16 17 18 19 23 25 40 41 431 292 Jost, R. 258 Jouvet, B. 470 Julian, R. S. 48 K mesons 123 132Ч3 K mesons, discovered 30 Kabir, P. 530 532 Kaellen, G. 457 470 Kaellen-Lehmann representation 457Ч62 Kahn, B. 48 Kaiser, G. 257 Kamefuchi, S. 424 532 Kanesawa, S. 48 Kemmer, N. 31 46 Kinetic theory 150Ч1 Kinosbita, T. 563 596 Klein Ч Gordon Ч Schrodinger equation 1 13 21 Klein, O. 4 7 13 25 27 29 41 44 200 211 239 277 368 375 Koba, Z. 46 48 Kockel, B. 31 46 533 Kollath, R. 168 Kramers degeneracy 81 Kramers Ч Kronig relation 469 Kramers, H. A. 35 47 81 106 168 469 471 Kroll, N. M. 38 47 593 596 Kubo, R. 190 Kusch, P. 48 Lagrangians 20 297Ч306 Lagrangians for complex scalar field 21 Lagrangians for interacting scalar field 302 Lagrangians integration by parts 305Ч6 Lagrangians irregular 326 Laidlaw, M. G, G. 418 424 Lamb shift 34Ч6 484 578Ч94 Lamb, W. E. 35 36 38 47 48 593 596 Land 41 Landau, L. D. 106 168 418 452 Lang, S. 424 Langer, J. S. 596 Lattes, C. 30 Lederman, L. 106 167 Lee Ч Nauenberg theorem 549Ч53 Lee, T D. 106 127 132 167 178 189 228 424 549 563 Legendre transformations 297 301 Lehmann, H. 438 457 463 470 Leinaas, J. M. 424 Lepton number 122 530 Leptons 472 Leutwyler, H. 533 Lewis, H. W. 46 Lie groups 53Ч5 Liebfried, D. 596 Lifshitz, E. M. 106 168 linear polarization 359 Lippmann Ч Schwinger equation 111 142 Lippmann, B. 111 166 Little groups 64-6 Little groups, 69Ч73 Little groups, 68Ч9 Liu, H. H. T. 498 Local Symmetries 342 (also see УGauge transformationsФ) Local symmetries for different momenta 65Ч6 Local symmetries for massless particles 248 Local symmetries, defined 64 London, F. 375 Loops 186Ч7 270 282Ч3 358 413 Lorentz (or Landau) gauge 212 346 418 Lorentz transformations action on creation operators 177 Lorentz transformations action on general states 57 Lorentz transformations action on one-particle states 62Ч73 Lorentz transformations in canonical formalism 314Ч18 Lorentz transformations in off-shell matrix elements 427 Lorentz transformations in perturbation theory 144Ч5 277Ч9 259 Lorentz transformations of cross-sections and decay rates 138 Lorentz transformations of S-matrix 116Ч21 Lorentz transformations, defined 55Ч7 Lorentz transformations, homogeneous Lorentz group, defined 57 Lorentz transformations, homogeneous Lorentz group, general representations 229Ч33 Lorentz transformations, Poincare algebra 58Ч61 Lorentz transformations, Poincare group, defined 57 Lorentz transformations, proper orthochronous Lorentz group 58 Low, F. E. 291 556 563 LSZ theorem (see УReduction formulaФ) Ludwig, G. 40 Lueders, G. 245 257 Lundeen, S. R. 596 Lyubarski, G. Ya. 257 M-matrix, defined 117 Mackey, G. W. 105 Magnetic moments of spin 1/2 particles 456Ч7 485Ч90 520 555Ч6 УMuonФ) Mailer, C. 29 45 46 166 Majorana fermions 226 242 Mandelstam variables 515 Mandelstam, S. 424 Many time formalism 22 Marginal couplings 503 Marshak, R, E. 38 45 Maskawa, T. 329 330 338 Mass renormalization 439Ч42 473 495Ч6 587Ч9 Matrix mechanics 3Ч4 Matthews, P. T. 532 Maxwell equations 1 252 339 342 370 Mayers, D. F. 596 Mehra, J 39 42 Meller (electron-electron) scattering 29 Michelson, A. A. 41 Miller, A. L. 39 44 498 Miyamoto, Y. 47 Momentum operator 61 310Ч11 Muon 38 Muon, discovered 30 Muon, magnetic moment 489Ч90 520 Muonic atoms 483Ч4 Myrheim, J. 424 Nafe, J. E. 48 Nakajima, H. 329 330 338 Nappi, C. R. 257 Nash, C. 106 Nauenberg, M. 549 563 Neddermeyer, S. H. 30 45 Negative energy СstatesТ 10Ч14 23Ч7 567 Nelson, E. B. 48 Neutron 29 Neutron, neutron scattering on complex nuclei 157 160 Neutron-proton scattering 158 Newton, R. G. 166 NeТeman, Y. 123 167 Nishina, Y. 29 44 368 375 NoetherТs theorem 307 Non-compact groups (see УCompact and non-compact groupsФ) Non-linear 337 377 392Ч3 Nordheim, L. 30 45 Nordsieck, A. 33 46 562 Normal ordering 175 200 262 Novikov, V. 533 Nuclear forces 29Ч30 434Ч6 Occhialini, G. P. S. 13 30 45 Ohnuki, Y. 424 Old-fashioned perturbation theory (see УPerturbation theoryФ) Omnes, R. 471 One-particle-irreducible, defined 439 Oppenheimer, J. R. 12 23 27 28 29 30 31 35 37 38 43 44 45 46 Optical theorem 148 Osterwalder Ч Schrader axioms 384 424 Osterwalder, K. 424 Overlapping divergences 511Ч15 p-forms 369Ч72 Pachucki, K. 596 Pair production 29 Pais, A. 39 132 167 Pancini, E. 30 45 Parasiuk, O. 512 532 Parastatistics 420 Parity and space inversion (P) of bound electron states 568Ч9 586 Parity and space inversion (P), accidental symmetry 521 530Ч1 Parity and space inversion (P), defined 58 (see also УSpecific particle typesФ) Parity and space inversion (P), intrinsic parities 125Ч7 (see also УSpecific particle typesФ) Parity and space inversion (P), non-conservation in weak interactions 127 (see also УSpecific particle typesФ) Parity and space inversion (P), transformation of 74Ч6 (see also УSpecific particle TypesФ) Parity and space inversion (P), transformation of creation operators 177 (see also УSpecific particle typesФ) Parity and space inversion (P), transformation of Dirac fields 221 224Ч5 Parity and space inversion (P), transformation of general irreducibie fields 239Ч40 (see also УSpecific particle TypesФ) Parity and space inversion (P), transformation of one-particle states 76Ч9 103 Parity and space inversion (P), transformation of scalar fields 205Ч6 (see also УSpecific particle typesФ) Parity and space inversion (P), transformation of vector fields 213 (see also УSpecific particle typesФ) Partial wave expansions 151Ч9 Paschen, F. 41 Pasternack, S. 47 Path integrals 259 376Ч7 524 Path integrals for derivative coupled scalars 391Ч2 Path integrals for fermions 399Ч13 Path integrals for massive vector fields 393Ч5 Path integrals for non-linear 392Ч3 Path integrals for quantum electrodynamics 413 18 Path integrals for S-matrix 385Ч9 Path integrals Lagrangian version 389Ч95 Path integrals used to derive Feynman rules 395Ч8 Path integrals, derivation 378Ч84 Pauli matrices, defined 217 Pauli term 14 517 520 Pauli Ч Villars regulator 486 494 Pauli, W. 3 11 14 19 20 21 22 23 24 26 28 31 40 42 45. 47 245 257 292 494 495 517 Peierls, R. E. 44 46 47 168 Pendleton, H. 563 Perlmutter, A. 257 Perturbation theory, old-fashioned 142 259 549 564 585Ч6 593 Perturbation theory, time-dependent 142Ч5 (also see УDyson seriesФ УFeynman УPath Petermann, A. 498 Phase shifts 129Ч30 155 Phase space factors 139Ч41 Photon 3 Photon, charge conjugation phase 229 Photon, helicity and polarization 73Ч4 250Ч1 359Ч61 368 Photon, masslessness 343 452 477 Photon, photon-photon scattering 32 509 523Ч5 Photon, propagator 353Ч5 (also see УSoft photonsФ УQuantum Piccioni, O. 30 45 167 Pion-nucleon coupling constant 435 Pions 13 38 435Ч6 521 Pions, 131 Pions, 127 7 Pions, intrinsic charge-conjugation phase of 131 229 Pions, intrinsic parity 127 Pions, prediction and discovery 30 Pions, scattering on nucleons 463 469 Pipkin, F. M. 596 PJaczek, G. 168 Podolsky, B. 22 44 Poincare group and algebra (see УLorentz transformationsФ) PoincareСs theorem 99 370 Poisson brackets, defined 327 Polar decomposition theorem 88 530 Polarization, massive spin one particle 209Ч10 212 Polarization, masslessness 343 Polarization, photon 73Ч4 Polchinski's theorem 526Ч8 Polchinski, J. 424 526 533 Poles in scattering amplitudes 428Ч36 554 564 Pomeranchuk's theorem 468 Pomeranchuk, I. Ja. 468 469 477 Popov, V. N. 377 424 Positivity of energy 75Ч6 302 Positron 12Ч13 567Ч8 585 Positronium 227 Powell, C. F. 30 45 Power counting theorem 505 Present, R. S. 767 Primary constraints (see УConstraintsФ) Principal value function 113 Probabilities in quantum mechanics 7 27Ч8 33 50 Projective representations 53 81Ч91 96Ч100 Propagators 262 274Ч80 397Ч8 506 574Ч8 Proton charge 445 Proton charge radius 38 594 Proton form factors 457 Proton identified as holes 12 Proton in nuclei 29 PT-non-conservation 130Ч1 Quantum chromodynamics 123 531 549 Quantum electrodynamics 29 31Ч8 339Ч62 413Ч18 472Ч97 503 507Ч15 529Ч31 564Ч94 УElectronФ УPhotonФ УGauge УUltraviolet УInfrared Quantum fields, Dirac 23Ч4 219Ч29 Quantum fields, early theory 15Ч31 Quantum fields, free fields 191Ч200 Quantum fields, general quantum fields 233Ч44 Quantum fields, massless particles 246Ч55 Quantum fields, redefinitions 331Ч2 Quantum fields, scalar 21Ч2 24Ч8 201Ч6 Quantum fields, uniqueness of irreducible fields 238 Quantum fields, vector 207Ч12 quantum mechanics 49Ч50
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



 , A.
, A. 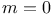
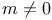
 -model
-model  and
and 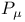
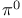 decay
decay 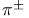 decay
decay