јвторизаци€
ѕоиск по указател€м
Weinberg S. Ч The Quantum Theory of Fields. Vol. 1 Foundations
ќбсудите книгу на научном форуме Ќашли опечатку?
Ќазвание: The Quantum Theory of Fields. Vol. 1 Foundationsјвтор: Weinberg S. јннотаци€: In The Quantum Theory of Fields, Nobel Laureate Steven Weinberg combines his exceptional physical insight with his gift for clear exposition to provide a self-contained, comprehensive, and up-to-date introduction to quantum field theory.
язык: –убрика: ‘изика / вантова€ теори€ пол€ /”чебники /—татус предметного указател€: √отов указатель с номерами страниц ed2k: ed2k stats √од издани€: 1996 оличество страниц: 609ƒобавлена в каталог: 09.10.2005ќперации: ѕоложить на полку |
—копировать ссылку дл€ форума | —копировать ID
ѕредметный указатель
127 130Ч1 29 207 159Ч60 207 88 165 202 276 225 227 165 225 227 469 127 Aaron, R. 470 Abelian groups, defined 55 Absorption of photons 18 Accidental symmetries 529Ч31 action 299 307 Aharony, A. 168 Aitken, A. C. 106 Alpha decay 160 Amado, R. D. 470 Anderson, C. D. 12 30 43 45 Annihilation and creation operators 16 19Ч20 23Ч4 26Ч8 169 173 Anomalous Zeeman effect 5 Antiparticles 13Ч14 23Ч8 104 149Ч50 199 567 Antiunitary and antilinear operators, defined 51 Anyons 420 Aramaki, S. 39 Argyres, P. C. 257 Artin, E. 424 Auxiliary fields 302Ч3 314 Axial gauge 346 Bagger, J. 338 532 Bailey, J. 498 Bakamijian, B. 189 Bargmann, V. 106 Baryon number, defined 122 Belinfante tensor 316 Belinfante, F. J. 44 316 338 Berezin integration, defined 403 Berezin, F. A. 403 404 424 Bergmann, P. G. 335 Beta decay 23 29 127 146 228 519 Bethe Ч Salpeter equation 560 Bethe, H. 29 33 36 45 47 560 563 593 596 Beyer, R. T. 39 43 Bhabha (electronЧpositron) scattering 29 Bhabha, H. J. 29 45 Bjorken, J. D. 532 Blackett, P. M. 13 Bloch, F. 33 46 562 Bogoliubov, N. N. 512 532 Bohr, N. 3 11 19 32 42 44 168 198 256 Boltzmann H-theorem 151 Boosts, defined 61 Born approximation 115 156 Born, M. 3 15 16 17 18 19 23 25 40 42 43 46 115 166 292 Bose Ч Einstein statistics 11 Bound states (see УComposite particlesФ) BPHZ prescription 512Ч13 Braid group 420 Breit Ч Wigner formula 162Ч3 Breit, G. 36 48 162 167 168 Bremstrahlung 29 Broken symmetry 443 451 Brown, G. E. 596 Brown, L. 39 40 45 46 167 532 Burgoyne, N. 257 Butler, C. C. 30 45 123 167 Canonical commutation and anticommutation relations 16 19Ч22 293Ч8 529 Canonical transformations 329 Cao, T. Y. 39 Carlson, J. F. 29 30 32 45 Cartan, E. 256 Casimir effect 297 Casimir, H. B. G. 338 Cassen, B. 167 Causality 145 198 463 Center-of-mass frame 139 Central charges 83 Chadwick, J. 45 Charge (see УElectric chargeФ) Charge conjugation (C) for photons 427Ч8 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), accidental symmetry 521 530Ч1 Charge conjugation (C), defined 121 131Ч2 Charge conjugation (C), intrinsic charge conjugation phases 131 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), non-conservation 132 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), transformation of creation operators 177 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), transformation of Dirac fields 226Ч7 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), transformation of fermion bilinears 229 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), transformation of general irreducible fields 241Ч2 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), transformation of scalar fields 206 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Charge conjugation (C), transformation of vector fields 213 (also see УSpecific particle typesФ) Chew, G. 47 471 Chew-Frautschi plot 469 471 Chinowsky, W. 167 Chiral transformation 520 Christenson, J, H. 106 167 circular polarization 359 ClebschЧGordan coefficients 124 152 154 156 233Ч4 242 569 Clifford aigebra 214 Closed p-forms, defined 369 Cluster decomposition principle 169 177Ч89 197 259 Cohen, R. S. 44 256 Coherent states 189 Collins, R. D. B. 471 532 COLOR 549 Compact and non-compact groups 231 Composite particles 110 461Ч2 Compton (electron-photon) scattering 29 362Ч9 Compton, A. H. 41 362 364 504 Condon, E. U. 167 Connected amplitudes 178Ч82 270 282 286 389 413 Conservation laws for angular momentum 118 (also see УSpecific symmetries and conserved quantitiesФ) Conservation laws for charge 119 199 427 Conservation laws for current 212 307 478 586 Conservation laws for energy and momentum 117Ч18 425Ч7 Conservation laws limitations 253 537Ч8 Constraints 325Ч31 Constraints in electrodynamics 344 346Ч7 Conversi, M. 30 45 Cosmic rays 29 123 Coulomb energy 350 353 355Ч6 560 Coulomb gauge 251 346Ч50 365 Counterterms in quantum electrodynamics 472Ч3 CP-invariance for degenerate multiplets 104 CP-invariance, non-conservation in 132Ч3 CPT-invariance 104 133 244Ч6 459 Creation operators (see УAnnihilation and creation operatorsФ) Crichton, J. R. 189 Cronin, J, W. 106 132 167 Cross sections, defined 137Ч9 Cross sections, high energy limit 158Ч9 Cross sections, partial wave expansions 155Ч6 Crossing symmetry 269 467 554 Cumulants 178 Curie-Joliot, I. 45 Dalitz Plot 141 Dalitz, R, H. 141 168 563 Dancoff, S. M. 33 34 46 Dangerous states 550Ч2 Darwin, C. G. 10 41 42 596 Davisson, C. J. 3 40 de Broglie, L. 3 40 de Kronig, R. 469 471 De Rham cohomology 370 De Witt, C. M. 377 418 424. Deans, W, M. 41 Decay rates, general formula 136Ч7 Dedijer, S. 257 Density matrix 360 Deser, S. 563 Desiderio, A. M. 596 DeWitt, B. S. 39 424 Differential forms (see Уp-formsФ) Diffraction scattering 148Ч9 158 Dimensional regularization 449 477Ч80 497 Dimensionality, of fields and couplings 502 519 525Ч7 Dirac brackets 328Ч31 332Ч7 Dirac brackets in electrodynamics 347Ч9 Dirac equation 1 6Ч14 225 565Ч72 Dirac matrices 8Ч9 214Ч19 Dirac matrices, slash notation, defined 358 Dirac matrices, traces 361 372Ч4 Dirac representation of homogeneous Lorentz group 213Ч19 Dirac, P. A. M. 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 18 19 22 23 24 27 28 29 32 33 34 39 40 41 42 43 44 46 47 49 105 200 213 218 256 292 325 328 329 330 335 345 376 424 457 470 489 565 566 567 596 Dispersion relations 460 462Ч9 Distorted wave Born approximation 146Ч7 Donoghue, J. F. 533 Dotted and undotted indices 230 Drell, S. D. 532 Dresden, M. 61 Drinkwater, J. W. 47 Druehl, K. 424 Duality 232 371 Dyson series 144 259Ч60 Dyson, F. J. 37 48 106 144 168 258 259 287 29/ 376 499 532 Eckart 153 156 162 165 Eclipsing binaries 368 Edmonds, A. R. 106 167 165 257 596 Effective field theories 499 523Ч5 Ehrenfest, P. 15 29 43 45 Einstein, A. 12 13 18 19 43 55 518 Electric charge 341 Electric charge radius, defined 493 Electric charge, conservation 122 537 Electric charge, renormalization 342 442Ч8 473 480Ч3 Electric dipole moments 81 521 Electron, charge radius 493 Electron, classical theory 31 369 496 Electron, magnetic moment 6 10 14 36 457 468 520 Electron, spin 6Ч9 Elliptic polarization 360 Elsasser, W. 3 40 Energy shifts of atomic states 31Ч2 574 Energy shifts of atomic states, ls energy shifts 594 (also see УLamb shiftФ УUehling УMuonic Energy-momentum tensor 310Ч12 entropy 151 Epstein, S. 46 Equivalence principle 537 Erickson, G. W. 498 Euclidean path integrals 384 Euler constant 479 497 Euler Ч Lagrange equations 300 Euler, H. 32 46 523 524 526 533 Exact p-forms 369 Excitation energies, in hydrogen 592Ч3 Exclusion principle 11 Exterior derivatives 369 External fields 266 287Ч90 412Ч13 556Ч62 572Ч8 Fabri, E. 168 Faddeev equations 188 Faddeev, L. D. 190 376 378 424 Feenberg, E. 167 168 Feinberg, G. 167 530 533 Feinberg, J. 335 Fermi Ч Dirac statistics 12 171Ч2 267Ч70 418Ч20 Fermi, E. 11 19 23 39 421 44 292 Ferretti, B. 767 Feynman diagrams 36Ч7 259Ч91 Feynman diagrams for electrodynamics 355Ч8 Feynman gauge 355 417 Feynman parameters 474 486 497 Feynman, R. P. 33 36 37 38 47 45 259 276 280 286 353 354 355 360 375 376 377 400 411 413 417 423 424 426 430 459 472 474 486 495 559 572 Field equations 200 211Ч12 239 Field renormalization 331Ч2 436Ч42 452 461 473 479 484 543Ч4 Field-translation-invariant scalar theory 521Ч3 Fields (see УQuantum fieldsФ) Fierz, M. 20 40 44 46 47 257 Fine structure 4Ч6 570 Fine structure constant 2 5 First class constraints (see УConstraintsФ) Fitch, V. L. 106 133 167 Flanders, H. 106 375 Flavors (of leptons) 529 Floating cutoff 525Ч8 Fock, V. 22 23 41 44 375 Foley, H. M. 45 Forests 512Ч13 form factors 452Ч7 485Ч93 580Ч2 Frautschi, S. C. 471 562 Fredenhagen, K. 424 French, J. B. 35 38 47 593 596 Friedman, J. I. 106 167 Froehlich, H. 48 Froissart bound 159 Froissart, M. 168 Fukuda, H. 47 Functionals, notation 299 Furry's theorem 428Ч9 509 Furry, W. H. 23 27 28 32 44 46 428 470 Gaberdiel, R. 424 Galilean invariance 62 145 217Ч18 Gamow, G. 7 39 42 Garwin, R. 106 167 Gasser, J. 533 Gauge transformations 251Ч2 339Ч43 345 370 448Ч52 УCoulomb УTemporal УAxial УUnitarity УFeynman Gaussian Integrals 420Ч3 Gell-Mann, M. 123 132 167 291 477 556 563 General relativity 255 312 316 369 518Ч19 521 Generators of symmetries 307Ч14 Georgi, H. 257 Germer, L. H. 3 40 Gerstein, I. S. 424 Glimm, J. 423 Global symmetries, defined 307 Gluons 549 Goldberger, M. L. 166 463 471 556 563 Goldstone, J. 178 189 Gordon, W. 4 7 10 13 25 27 41 42 200 211 239 277 596 Goudsmit. S. 5 10 41 Grassmann variables, defined 401 Graviton 73Ч4 253 521 537 548 Green, M. B. 375 Grisaru, M. 563 Grotch, H. 596 Groups, defined 52 (also see УAbelian groupsФ УHomotopy УLie УLittle УRepresentationsФ УSemi-simple Gudehus, T. 257 Guersey, F. 106 Haag, R. 424 Haenscb, T. W. 596 Hafstad, L. D. 767 Hahn, Y. 532 Halter, J. 533 Hamiltonian for complex scalar field 22 Hamiltonian for Dirac equation 8 Hamiltonian for electrodynamics 349Ч50 Hamiltonian for free particles 176 Hamiltonian for interacting Dirac field 323 Hamiltonian for interacting scalar fields 199 302 Hamiltonian for interacting vector field 321 Hamiltonian for one-dimensional scalar field 15Ч17 Harvey, J. 533 Hawking, S. W. 533 Heisenberg picture 109 288 297 425 Heisenberg, W. 3 4 10 15 16 17 20 21 24 25 29 32 33 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 109 766 292 519 532 533 Heitler, W. 29 45 45 Helicity, defined 72 Helicity, limitations for massless particle fields 253Ч4 Helicity, limited to integers and half-integers 90
–еклама
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



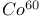 decay
decay 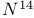 molecular spectrum
molecular spectrum 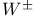 particles
particles 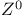 particle
particle  group
group  baryon
baryon  function
function  function
function  meson
meson  meson
meson  -mesons
-mesons  problem
problem  decay
decay