"Background" effects in dHvA measure-ments in alloys 508
"d-wave theorem" 474 475
"Magnetic" energy gaps 213
"Self-scattering" artifice 121
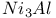 231 266 231 266
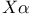 -potential 154 159 202 215 see -potential 154 159 202 215 see
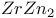 231 266 231 266
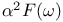 77Ч79 77Ч79
 -orbit in Hg 367 368 -orbit in Hg 367 368
 oscillations, in Fe 259Ч260 oscillations, in Fe 259Ч260
 51 51
 and Fermi liquid theory 83Ч84 87 91 and Fermi liquid theory 83Ч84 87 91
 and Fermi liquid theory, equilibrium properties 84Ч87 92 and Fermi liquid theory, equilibrium properties 84Ч87 92
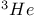 and Fermi liquid theory, Fermi liquid parameters 92Ч94 and Fermi liquid theory, Fermi liquid parameters 92Ч94
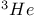 , relaxation time 97 , relaxation time 97
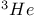 , zero sound 98Ч99 , zero sound 98Ч99
Absorption of electromagnetic waves 197Ч198
Absorption of sound waves see under "Sound waves"
Actinides, early 196
AG see also "Noble metals"
Ag, alloys of, dHvA effect 361
Ag, alloys of, Friedel phase shifts 386
Ag, band energies 179
Ag, domains in 133
Ag, electronic structure of 199Ч204
Ag, g-factor 447Ч449 454
Ag, magnetic interaction in 138Ч139
Al, 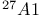 , use for NMR resonance 490 , use for NMR resonance 490
Al, dHvA effect in alloys of 356Ч357 478
Al, g-factor 449
Al, specimen alignment procedure 487
Al, stress dependence of Fermi surface 279 287
Alfven wave 27
Alignment see "Orientation"
Alkali metals 92 see
Alkali metals, g-factors 438 446Ч447 451 452
Alkali metals, orientation determination by rotation diagram 483
Alkaline earth metals, electronic structure of 214Ч215
Alloys 181 see
Alloys, dHvA effect in 321Ч392
Alloys, dHvA effect in, experimental results 356Ч361 379Ч392
Alloys, dHvA effect in, precision required for measurements 479Ч481 492 495 507Ч508
Alloys, electronic structure in a magnetic field 326Ч337
Alloys, electronic structure in a magnetic field, Fermi level shifts 332Ч333
Alloys, electronic structure in a magnetic field, Landau level structure 333Ч337
Alloys, Fermi surfaces 322Ч326
Alloys, models for 337Ч356
Alloys, models for, hybrid phase- shift/plane wave approach 352
Alloys, models for, lattice distortion 352Ч355
Alloys, models for, phase shift analysis 341Ч351
Alloys, models for, pseudopotential models 339Ч341
Alloys, models for, rigid-band model 338Ч339
Amplitude of dHvA oscillations 34 see "Relative
Amplitude of dHvA oscillations and dephasing effects 421Ч435
Amplitude of dHvA oscillations and the electron-phonon interaction 363Ч368
Amplitude of dHvA oscillations, absolute measurements 201 404Ч405 416 437 439 440 443 445Ч446
Amplitude of dHvA oscillations, angular dependence of 262
Amplitude of dHvA oscillations, effect of impurities 362Ч363 459Ч469
Amplitude of dHvA oscillations, temperature dependence of 83 250Ч251 366
Anderson model 457 458 471
Angular shear 280 281 282Ч283
Angular shear, response of Fermi surface to 288 295Ч296 303 307Ч308 317
Angular shear, response of Fermi surface to, for Cu 308 311
Angular shear, response of Fermi surface to, for Pb 304 305
Angular shear, response of Fermi surface to, for W 315Ч316
Anisotropy of attenuation of ultrasonic waves in Cu 317Ч318
Anisotropy of electron-phonon mass enhancement over Fermi surface 201
Anisotropy of Fermi velocity 292 370
Anisotropy of g-factors 454Ч455
Anisotropy of impurity scattering 292 343Ч345 377Ч381
Anisotropy of impurity scattering and mosaic structure 422
Anisotropy of impurity scattering in Au (rare earth alloys 474
Anisotropy of impurity scattering in K alloys 387Ч392
Anisotropy of impurity scattering in noble metal alloys 379Ч386
Anisotropy of impurity scattering, magnetic, of Fermi surface in ferro- magnets 237Ч239
Anti-ferromagnetic exchange in Au alloys 473
Anti-ferromagnetic ordering in Cr 213
Anti-Kondo effect 474 476
APW method 20 150 476
Arbitrary dispersion law 8 10 20Ч22
ASA 160Ч165 166 170 173 174 176 186 188 196 179Ч180
Atomic Sphere Approximation see "ASA" "LD-ASA" "LSD-ASA"
Atomic volume 180 189Ч192 196
Attenuation see "Sound waves"
AU see also "Noble metals"
Au as solute 382
Au, alloys of, (and waveshape analysis) 399 464Ч467 471Ч474
Au, alloys of, dHvA effect 359
Au, alloys of, Friedel phase shifts 386
Au, alloys of, scattering rate over Fermi surface 380Ч381
Au, electronic structure of 199Ч204
Au, g-factors 201 447Ч449 454
Au, magnetoresistance of 150
Au, mosaic structure 427Ч429
Au, quenched 359
Augmented plane-wave (APW) method 20 150 476
Averaged T-matrix approximation 351
Azbel' Ч Kaner resonance 25Ч27
Ba, electronic structure of 214Ч215
Background scattering 422
Backscattering in dilute alloys 344Ч345 347Ч352 354Ч355 374 459
Ball orbits 257Ч258 261Ч264 268 312Ч314
Band structure 149Ч224 see
Band structure and cohesive properties 186Ч193
Band structure and g-factor results 452Ч456
Band structure and hybridization 167 170Ч173 190 199Ч200 210 216Ч217
Band structure and magnetic properties 186Ч189 194Ч197 227Ч231 251Ч255
Band structure, theory 47Ч57 155Ч186 227Ч231
Base line errors 494 496
Bcc structures, alkaline earth metals 214Ч215
Bcc structures, Brillouin zones 150
Bcc structures, transition metals, band structure 152 167Ч173 193 196 210Ч214 252Ч253
Bcc structures, transition metals, strain dependence of Fermi surfaces 309Ч317
Be 127 129
Be, alloys of, dHvA effect in 357
Be, alloys of, magnetoresistance in 43Ч44 143Ч145
Be, alloys of, magnetothermal effects in 140Ч141
Be, alloys of, strain dependence of Fermi surface 279 287 290
Beats in dHvA oscillations 137Ч145 424 426 479 485Ч488
Beats in Pippard oscillations 38
Belly orbits, g-factor 448
Belly orbits, mosaic structure effects 427Ч430
Belly orbits, oscillations for in Cu 480 483 503Ч505
Belly orbits, stress dependence of in Cu 306Ч308 310 311
Belly orbits, turning point in Cu 380
Bessel function spectrometer 400
Bi 31 278 279 439 453
Bi, alloys of, alloys of 357
Bicrystals 423 424Ч426
Binding energy in metals 55
Boltzmann equation 94Ч101 102Ч107 113 114 121
Born approximation 328Ч329 341 352
Bosons 4Ч5
Bragg reflections 454
Brillouin zones 150 342 352Ч353
Brillouin Ч Wigner perturbation theory 70Ч71
bulk modulus 186 191Ч192 196
C alloys 358
Ca, electronic structure of 214Ч215
Calibration of dHvA systems 437 442 492Ч493
Canonical bands 154 155 160Ч161 166Ч174 210
Canonical bands, hybridized 170Ч173
Canonical bands, width of 169Ч170
Canonical number-of-states function 171Ч172
Catastrophic scattering 109 123
Cd alloys 357
chemical potential 58Ч59 70 90 333
Chemical potential, exchange-correlation part of 48 54Ч55 158
Chemical potential, of up- and down-spins 63Ч64 73 227
Cherenkov condition 23
| Chodorow potential 150 306
Closed orbits 8 11 15 41
CO 227 228 237
Co, as solute in dilute alloys 207 471Ч473 476Ч477
Cohen Ч Blount criterion 452Ч453
Coherent potential approximation 328 333 351
Cohesive properties of transition metals 186 189Ч193
Compressibility 65Ч66 86Ч87 89 92
Compression, response of Fermi surface to 306
Computer-based techniques for analysis of data 462Ч469 497Ч502
constant energy surfaces 206 207 211 218 220
Correlation 54 194 227 229 231
Correlation and screening 58Ч60 see
Correlation, corrugated plane 36
Correlation, definition of 54
Coulomb interaction between electrons 48 52 58 60 87 91 95 157 see
CR 152 153 309
Cr, alloys of 358
Cr, anti-ferromagnetic ordering in 213
Cr, as solute in alloys 471
CS 446Ч447 490 see
Cu 153 490 see
Cu, alloys of 339
Cu, alloys of, (and waveshape analysis) 470Ч471 480
Cu, alloys of, dHvA effects 358Ч359
Cu, alloys of, Friedel phase shifts 354 386
Cu, alloys of, scattering rate over Fermi surface 380Ч383
Cu, alloys of, spectral density of Cu(Ni) 328
Cu, dHvA effects in 34 480
Cu, dHvA effects in, rotation diagram 483
Cu, dHvA effects in, waveshape analysis 492 505
Cu, electronic structure of 199Ч204
Cu, Fermi surface of 150Ч151 268
Cu, Fermi surface of, effect of strain on 304Ч309 310 311 318
Cu, Fermi surface of, scattering rate over 380Ч383 384Ч385
Cu, g-factor 447Ч449 454
Cu, interstitial H in 356 386
Cu, mosaic structure effects 429Ч430
Curie temperature 228 229 230
Curie Ч Weiss behaviour 231
Cyclotron mass 26 127 227 237 322Ч323 334 337 338 356Ч358 363 367Ч368 394 478
Cyclotron resonance 25Ч27 31Ч32 74
d-wave scattering 345 355 356 388 390
Data windows 399 400Ч403 460 466 471 497Ч502
Data windows, Gaussian 499Ч501
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect 7Ч11 see
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect and itinerant ferromagnetism 231Ч251
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect and magnetic interaction 124Ч126
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect in dilute alloys 321Ч392
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect in dilute alloys, experimental results 356Ч361 379Ч392
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect in dilute alloys, precision required for measurements 479Ч481 492Ч495
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect, frequency of oscillations 9 233
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect, high-precision measurements of 479Ч508 see
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect, high-precision measurements of, magnetic field 486Ч492
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect, high-precision measurements of, phase 492Ч502
de Haas Ч van Alphen (dHvA) effect, high-precision measurements of, spurious effects 505Ч507 508
Debye energy 72 78 79
Deformation potential 25
Deformation tensor 283Ч284 317Ч318
Density of energy levels 73Ч77
Density of states 75Ч77 89 194Ч197 253 255
Density of states, for canonical bands 167 170 171Ч173
Dephasing effects see "Waveshapes in the dHvA effect"
dielectric constant 26 28
Dielectric function, and screening 60
Difference frequency 138 139 140 396
Diffuse surface scattering 123
Diffusion 15 18 19
Dilation 280 281 282 283
Dilation, response of Fermi surface to 292 296 299Ч300 307Ч308
Dilation, response of Fermi surface to, for Cu 306Ч307 308 310
Dilation, response of Fermi surface to, for Pb 301 302
Dilation, response of Fermi surface to, for W 311 312
Dilatometer 289
Dilatorquemeter 289
Dingle plots 368 376
Dingle plots and field inhomogeneity 436Ч437
Dingle plots and lattice dislocation scattering 432Ч435
Dingle plots and mosaic structure 425Ч426
Dingle temperature 362Ч370
Dingle temperature and dHvA methods of measuring g-factors 439 440
Dingle temperature and Friedel phase shifts 354 384 386
Dingle temperature and MI harmonic content 445
Dingle temperature and mosaic structure 380 425Ч426 429Ч430 445
Dingle temperature, "point" 432Ч433
Dingle temperature, field-dependent 432Ч435 478
Dingle temperature, for alloys 508
Dingle temperature, intercept technique for measuring small changes in 375Ч378
Dingle temperature, orientation dependence of 262 430
Dingle temperature, spin-dependent 408
Dingle temperature, temperature-dependent 478
Dingle temperature, theory of 363
Disc-shaped samples 129
Dislocations, lattice 359 431Ч435
Dispersion law 4Ч5 27Ч28 30
Dispersion law, arbitrary 8 10 20Ч22
Dog's bone orbit, g-factors for, in noble metals 448
Dog's bone orbit, mosaic structure effects 428
Dog's bone orbit, stress dependence of in Cu 307 308 309
domains 16 17 128Ч125 139 140 290
Domains, formation of 133Ч135 290 413
Domains, size of 133
Domains, wall thickness 131Ч133
Dupree Ч Holland criterion 453
Dyson self-energy operator 158
Eddy currents 135 505Ч506
Effective cyclotron mass 26 227 237 334 337 338 363 367Ч368 394 478
Effective free path 110Ч113 117Ч118
Effective g-factor 405Ч407
Effective interelectronic distance 62 64Ч65 452
Effective magnetic breakdown probability 43
effective mass 9 66Ч67 85 89 91Ч92 201 237
Effective mass, due to Coulomb interaction 61Ч62 64Ч65 67
Effective mass, due to electron-phonon interaction 70Ч72 76 77 91 201
Effective potential 48 50 56 58Ч60 84 101
Effective relaxation time 108
Elastic scattering 38Ч39 104 106 107 109 110 329
Elastic stiffness constants 279Ч282 308
Elastic stiffness tensor 287 288 290
Electrical conductivity 15 16 76 101 109 112 see
Electrochemical potential 59
Electromagnetic waves 26Ч27 153 197Ч198
Electron lifetimes in metals 362Ч392
Electron sheet of a Fermi surface 14
Electron theory of metals, geometric concepts in 3Ч45
Electron-electron interaction 48 57Ч67 79 191 229 234 446 451Ч452 see "Coulomb "Exchange "Exchange-correlation" "Screened
Electron-ion interaction 48 295 306
Electron-magnon interaction 227Ч228 234 237 244 247 249 276
Electron-paramagnon interaction 237
Electron-phonon interaction 32Ч34 67Ч83 244 247
Electron-phonon interaction and susceptibility 68 72Ч73
Electron-phonon interaction and the dHvA effect 363Ч368
Electron-phonon interaction and the Fermi surface of paramagnetic metals 234
Electron-phonon interaction, coupling constant 71
Electron-phonon interaction, mass enhancement by 68Ч72 83 91Ч92 201 208 318 338Ч339 451Ч452
Electronic structure of alloys in a magnetic field 326Ч337
Electronic structure of transition metals 149Ч224
Ellipsoidal effective zones 36
Ellipsoidal orbits 257Ч260 309 312Ч315
Energy functional 47Ч55
Energy spectrum 4Ч7 20Ч22 see
entropy 85 140
Eu 214
exchange interaction 5 158 159 451 see
Exchange interaction and magnetic impurities 397Ч399 406Ч407 457Ч477
Exchange interaction and susceptibility enhancement 64Ч65
Exchange interaction in a free-electron gas 52Ч54
Exchange splitting 194Ч195 207 227 231
Exchange splitting and magnetization 228 230 244
Exchange splitting in Fe and Ni 252Ч253 253
|
 |
|
ќ проекте
|
|
ќ проекте



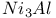
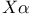 -potential
-potential 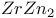
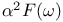
 -orbit in Hg
-orbit in Hg 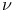 oscillations, in Fe
oscillations, in Fe 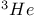
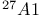 , use for NMR resonance
, use for NMR resonance